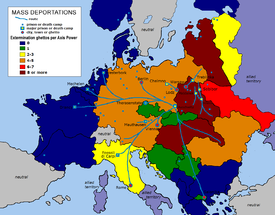
- Extermination camp
-
Extermination camps (or death camps) were camps built by Nazi Germany during the Second World War (1939–45) to systematically kill millions by gassing and extreme work under starvation conditions. While there were victims from many groups, Jews were the main targets. This genocide of the Jewish people was the Third Reich's "Final Solution to the Jewish question".[1] The Nazi attempts at Jewish genocide are collectively known as the Holocaust.[2]
Contents
Background
In 1942, the Reichsführer Heinrich Himmler ordered the Lublin District SS- und Polizeiführer Odilo Globocnik to build the first extermination camps during Aktion Reinhard (1941–43), the operation to annihilate every Jew in the General Government (occupied Poland). Initially, the victims' corpses were buried in mass graves, but later were cremated. After Russian forces began to advance, previously buried victims were also exhumed and burned in Sonderaktion 1005, a Nazi attempt to destroy evidence of the Holocaust.
The first concentration camps were under the direct command of SS–Polizei-führer Globocnik, and operated by SS Police battalions and Trawnikis—volunteers from Eastern Europe; whereas the SS-Totenkopfverbände managed the Nazi Concentration Camps such as Dachau and Ravensbrück. The Nazis did not expect the majority of prisoners taken to the Belzec, Treblinka, and Sobibor extermination camps to survive more than a few hours beyond arrival.[3]
Definitions
The terms extermination camp (Vernichtungslager) and death camp (Todeslager) are interchangeable usages, each referring to camps whose primary function was genocide, not for punishing crime or containing political prisoners, but for the systematic killing of the prisoners delivered there.
Nazi Germany (1933–45) built the most infamous extermination camps in Occupied Poland. These differed from concentration camps, such as Dachau and Belsen, which were initially prison camps for people defined as socially or politically undesirable in Nazi society. In the early years of the Holocaust, the Jews were primarily sent to concentration camps, but from 1942 onwards they were mostly deported to the extermination camps.
Extermination camps are distinguished from the Arbeitslager (forced labor camps) established in German-occupied countries to use the prisoners, including prisoners of war, as slave labor. In most camps (excepting PoW camps for the non-Soviet soldiers and certain labor camps), the high death rates resulted from execution, starvation, disease, exhaustion, and physical brutality.
The Nazis distinguished between extermination camps and concentration camps. As early as September 1942, Dr. Johann Paul Kremer, M.D., an SS physician, witnessed a gassing of prisoners, and in his diary wrote: "They don't call Auschwitz the camp of annihilation [das Lager der Vernichtung] for nothing!"[4] The distinction was evident during the Nuremberg trials, when Dieter Wisliceny (a deputy to Adolf Eichmann) was asked to name the extermination camps, and he identified Auschwitz and Majdanek as such. Then, when asked "How do you classify the camps Mauthausen, Dachau, and Buchenwald?" he replied, "They were normal concentration camps, from the point of view of the department of Eichmann."[5]
The camps
Most Holocaust historians identify six German Nazi extermination camps, all in occupied Poland; two of them, Kulmhof and the Auschwitz II, in the western Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany (October 1939), four in the General Government area. [6]
Besides those six camps, there existed the little-known Maly Trostenets extermination camp, at Minsk, Belarus, in the anti-Communist Lokot Republic (July 1942–August 1943) established in the Nazi-occupied USSR; similar camps existed at Warsaw and Janowska. Moreover, in Yugoslavia there existed the Jasenovac concentration camp (August 1941–April 1945), which was the only central extermination camp outside of Poland, and the only one not operated by Nazis, but by the fascist Ustaše forces of the Independent State of Croatia, the majority of whose victims were Orthodox Christian Serbs, Roma, and Jews.[7][8]
.
The Nazis used the euphemism Endlösung der Judenfrage (Final Solution of the Jewish Question) to describe their systematic killing of Europe's Jews, which Nazi leaders likely decided during the first half of 1941. The initial, formal killings of the Final Solution were undertaken by the SS Einsatzgruppen (Task Forces) death squads who followed the Wehrmacht during the Operation Barbarossa invasion of the USSR in June 1941. The initial extermination method of shooting people in burial pits proved logistically and psychologically inefficient, so in late 1941, the Nazis established camps specifically for mass extermination via gas chambers. The logistical details were established in the Wannsee Conference (January 1942) and were executed by the administrator Adolf Eichmann. The camps at Treblinka, Bełżec, and Sobibor, were constructed during Operation Reinhard (October 1941–November 1943), for the extermination of Poland's Jews.
Whereas the Auschwitz II (Auschwitz–Birkenau) and Majdanek camps were parts of a labor camp complex, the Operation Reinhard camps and the Chełmno camp were exclusively for the quick extermination of many people (primarily Jews) within hours of their arrival.[9] Some able-bodied prisoners delivered to the death camp were not immediately killed, but were forced into labor units (Sonderkommando) to work at the extermination process, removing corpses from the gas chambers and burning them. Because the extermination camps were physically small (only several hundred metres long and wide) and equipped with minimal housing and support installations, the Nazis deceived the prisoners upon their arrival, telling them that they were at a temporary transit stop, and soon would continue to an Arbeitslager (work camp) farther east.
Numbers of victims
The estimated total number of people killed in these camps is 2,814,500:
Camp Estimated deaths Notes/references Auschwitz–Birkenau 1,100,000 [10] Treblinka 700,000–800,000 The Höfle Telegram indicates some 700,000 killed by 31 December 1942, yet the camp functioned until 1943, hence the true deaths total likely is greater.[11] Bełżec 434,500 [12] Sobibor 167,000–250,000 [13] Chełmno 152,000 [14] Majdanek 78,000 [15] Total 2,631,500–2,814,500 The approximate total numbers of people killed in the lesser-known death camps, vary between 85,000 to 600,000 at the Jasenovac concentration camp in Yugoslavia.[16] At the Maly Trostenets extermination camp in Belarus, USSR, some 65,000 Jews were killed, whilst the number of gentiles (non-Jews, i.e. communists, priests, non-religious, soldiers, et al.) varies between 100,000 to 400,000.[17]
Selection of sites for the camps
See also: "Polish death camp" controversyFor political and logistical reasons, Nazi Germany built most extermination camps in occupied Poland:
- Camps were built where most of the intended victims lived; Poland had the greatest European Jewish populace.[18]
- The camps could be kept secret from the German civil populace. [19]
Operation of the camps
The formal mass-killing method at an extermination camp was poison gas (made to order by the IG Farben chemicals company); besides gas chambers, the camp guards continued killing prisoners via mass shooting, starvation, torture, et cetera.[20] After the war, the diary of the Auschwitz Commandant, Rudolf Höss, revealed that psychologically "unable to endure wading through blood any longer", many Einsatzkommandos—the killers — either went mad or killed themselves. [21]
Operationally, there were three types of death camp:
(1) Aktion Reinhardt extermination camps: Treblinka, Sobibor, Belzec, where prisoners were promptly killed upon arrival. Initially, the camps used carbon monoxide gas chambers; at first, the corpses were buried, but then incinerated atop pyres. Later, gas chambers and crematoria were built in Treblinka and Belzec; Zyklon-B was used in Belzec. [22]
(2) Concentration–extermination camps where some prisoners were selected for slave labor, instead of immediate death; they were kept alive as camp inmates, available to work wherever the Nazis required. These camps — including Auschwitz, Majdanek, and Jasenovac — later were retrofitted with Zyklon-B gas chambers and crematoria, remaining operational until war's end in 1945.[23]
(3) Minor extermination camps such as Sajmiste in Serbia, Maly Trostenets in the USSR, Janowska, in Poland, and Gornija Rijeka, initially operated as prisons and transit camps, then as extermination camps late in the war, using portable gas-chambers and gas vans. Gas vans were initially developed at the Chelmno extermination camp, before being used elsewhere.[24]
The corpses were incinerated in crematoria and the ashes either buried or scattered; yet, at Sobibor, Treblinka, Belzec, and Chelmno, the corpses were incinerated on pyres. The efficiency of industrialised killing at Auschwitz-Birkenau produced too many corpses to adequately burn or bury, so the crematoria (manufactured to specification by Topf und Söhne) were put into use to handle the disposals around the clock, day and night.[25]
Systematic killing
Each extermination camp operated differently, yet each was identically designed for quick and efficient industrialized killing. To wit, SS Obersturmführer Kurt Gerstein, of the Institute for Hygiene of the Waffen-SS, during the war told a Swedish diplomat of life in a death camp, of how, on 19 August 1942, he arrived at Belzec extermination camp (which was equipped with carbon monoxide gas chambers) and was shown the unloading of 45 train cars filled with 6,700 Jews, many already dead, but the rest were marched naked to the gas chambers, where:
Unterscharführer Hackenholt was making great efforts to get the engine running. But it doesn't go. Captain Wirth comes up. I can see he is afraid, because I am present at a disaster. Yes, I see it all and I wait. My stopwatch showed it all, 50 minutes, 70 minutes, and the diesel [engine] did not start. The people wait inside the gas chambers. In vain. They can be heard weeping, "like in the synagogue", says Professor Pfannenstiel, his eyes glued to a window in the wooden door. Furious, Captain Wirth lashes the Ukrainian [prisoner] assisting Hackenholt twelve, thirteen times, in the face. After 2 hours and 49 minutes — the stopwatch recorded it all — the diesel started. Up to that moment, the people shut up in those four crowded chambers were still alive, four times 750 persons, in four times 45 cubic meters. Another 25 minutes elapsed. Many were already dead, that could be seen through the small window, because an electric lamp inside lit up the chamber for a few moments. After 28 minutes, only a few were still alive. Finally, after 32 minutes, all were dead . . . Dentists [then] hammered out gold teeth, bridges, and crowns. In the midst of them stood Captain Wirth. He was in his element, and, showing me a large can full of teeth, he said: "See, for yourself, the weight of that gold! It's only from yesterday, and the day before. You can't imagine what we find every day — dollars, diamonds, gold. You'll see for yourself!" [26]
Auschwitz Camp Commandant Rudolf Höss reported that the first time Zyklon B gas was used on the Jews, many suspected they were to be killed — despite having been deceived into believing they were to be deloused and then interned to the camp. As a result, the Nazis identified and isolated "difficult individuals" who might alert the prisoners, and removed them from the mass —lest they incite revolt among the deceived majority of prisoners en route to the gas chambers. The "difficult" prisoners were led to a site out of view to be killed off discreetly.
A prisoner Sonderkommando (Special Detachment) effected the most of the processes of extermination; they accompanied the Jews into the gas chamber, and remained with them until the chamber door closed. To psychologically maintain the "calming effect" of the delousing deception, an SS guard stood at the door, as if awaiting the prisoners. The Sonderkommando hurried them to undress and enter the "shower room" (gas chamber) as quickly as possible; to that effect, they also assisted the aged and the very young in undressing.[27]
To further persuade the prisoners that nothing harmful was happening, the Sonderkommando deceived them with small talk about camp life. Fearing that the delousing "disinfectant" might harm their children, many mothers hid their infants beneath their piled clothes. Camp Commandant Höss reported that the "men of the Special Detachment were particularly on the look-out for this", and encouraged the women to take their children into the "shower room". Likewise, the Sonderkommando comforted older children who might cry "because of the strangeness of being undressed in this fashion".[28]
Yet, not every prisoner was deceived by such psychological warfare tactics; Commandant Höss reported of Jews "who either guessed, or knew, what awaited them, nevertheless . . . [they] found the courage to joke with the children, to encourage them, despite the mortal terror visible in their own eyes". Some women would suddenly "give the most terrible shrieks while undressing, or tear their hair, or scream like maniacs"; the Sonderkommando immediately took them away for immediate execution by shooting.[29] In such circumstances, others, meaning to save themselves at the gas chamber's threshold, betrayed the identities and "revealed the addresses of those members of their race still in hiding".[30]
Once the door of the filled gas chamber was sealed, pellets of Zyklon B were dropped through special holes in the roof. Nazi regulations required that the Camp Commandant supervise the preparations, the gassing (through a peephole), and the aftermath looting of the corpses. Commandant Höss reported that the gassed victims "showed no signs of convulsion"; the Auschwitz camp physicians attributed that to the "paralyzing effect on the lungs" of the Zyklon-B gas, which killed before the victim began suffering convulsions.[31]
The remnants of "Crematorium II" used in Auschwitz-Birkenau during its operation between March of 1943 to its complete destruction by the Schutzstaffel on January 20th, 1945After the gassings, the Sonderkommando removed the corpses from the gas chamber, then extracted any gold teeth, and — to minimize the distinct smell of burning human hair — they shaved the corpses, before delivering them to the crematoria or to the fire pits, thus maintaining secret the existence of the extermination camp. The Sonderkommando were responsible for burning the corpses, and stoking the fires, draining body fat, and turning over the "mountain of burning corpses" for even combustion and a peak fire-temperature. Commandant Höss was impressed by the diligence of the Sonderkommando prisoners, despite their being "well aware that . . . they, too, would meet exactly the same fate", yet always doing their jobs "in such a matter-of-course manner that they might, themselves, have been the exterminators". Höss further reported that the men ate and smoked "even when engaged in the grisly job of burning corpses", in the course of which they occasionally encountered the corpse of a relative, but, although they "were obviously affected by this . . . it never led to any incident" of revolt, as in the case of a Sonderkommando who so encountered the corpse of his wife, yet behaved "as though nothing had happened".[32]
As a matter of political training, some high-rank Nazi Party leaders and SS officers were sent to Auschwitz–Birkenau to witness the gassings; Höss reported that "all were deeply impressed by what they saw . . . [yet some] . . . who had previously spoken most loudly, about the necessity for this extermination, fell silent once they had actually seen the 'final solution of the Jewish problem'." As the Auschwitz Camp Commandant Rudolf Höss justified the extermination by explaining the need for "the iron determination with which we must carry out Hitler's orders"; yet saw that even "[Adolf] Eichmann, who certainly [was] tough enough, had no wish to change places with me."[33]
The post-war period
In 1944, as the Red Army advanced into eastern Poland, the Nazis either partly or completely dismantled the eastern-most extermination camps to conceal the mass killings done there, and the buried remains (excepting Auschwitz–Birkenau, which was partially demolished in 1947). Because most of the death camps in the far east of the country (Belzec and Sobibor) had been constructed with local lumber, the physical installations were quickly deteriorated, eroded, and destroyed, by the natural elements.
In the post-war period, the Communist government of the People's Republic of Poland (1944–90) created monuments at the extermination camp sites, that mentioned no ethnic, religious, or national particulars of the Nazi victims. In 1989, upon the collapse of Polish communism, the extermination camps sites became accessible to Western visitors to Poland; the camps are tourist attractions, especially the most-infamous Nazi death camp, Auschwitz concentration camp, near the town of Oświęcim (Auschwitz). In the early 1990s, Jewish Holocaust organisations disputed with Polish Catholic groups about: "What religious symbols of martyrdom are appropriate as memorials in a Nazi death camp such as Auschwitz?" The Jews opposed to the erection of Christian memorials at a quarry adjacent to the Auschwitz camp, wherein featured the Auschwitz cross — a Roman cross erected near death camp Auschwitz I, where mostly Poles were killed, rather than at Auschwitz II (Auschwitz-Birkenau), where mostly Jews were killed.
Holocaust denial
Holocaust deniers are people and organisations who assert that the Holocaust did not occur, or that it did not occur in the historically recognized manner and extent.
In 1979, the French academic Robert Faurisson in his publications said that "Hitler's 'gas chambers' never existed" — that the existence of gas chambers in the extermination camps was "essentially of Zionist origin"; that The Diary of Anne Frank is inauthentic; that Elie Wiesel lied about what he lived in under the Nazis; and that no more than 6 million people were killed in the camps.
In 2005, in Austria, where Holocaust denial is a crime, the Austrians, acting upon a 1989 arrest warrant, detained British author David Irving for the crime of "trivialising the Holocaust"; his trial earned him thirteen months imprisonment in 2006, and subsequent perpetual banishment from Austria.
 Documentary evidence: A Reichsbahn consignment note for delivering prisoners (Häftlinge) to Sobibor in November 1943
Documentary evidence: A Reichsbahn consignment note for delivering prisoners (Häftlinge) to Sobibor in November 1943
Holocaust denial is contradicted by the testimonies of camp survivors and Final Solution perpetrators, material evidence (the remaining camps, etc.), Nazi photographs and films of the killings, and camp administration records. Educational efforts, such as those of the Nizkor Project and the Simon Wiesenthal Center, and the books of Deborah Lipstadt and Simon Wiesenthal, and those at Holocaust resources, all track and explain Holocaust denial. The books of (Holocaust) historians, such as Raul Hilberg (The Destruction of the European Jews, 1961, 1985), Lucy Davidowicz (The War Against the Jews, 1975), Ian Kershaw, and others identify Holocaust denial as a fringe historical belief.
Contemporary Holocaust debate about the Nazi concentration camps concerns the complicity of the local populations who claimed ignorance of the camps and their activities. The responses in fact ranged from attempts to save their Jewish neighbors, through indifference, to active collaboration, for example betraying Jews to the authorities. Other debates include the extent to which the Nazis had a plan to destroy the Jews even before they came to power, as opposed to the Final Solution arising in a haphazard manner. This is known as the functionalism versus intentionalism question. Many other aspects of the Holocaust continue to attract vigorous research efforts.
See also
- Extermination through labor
- German camps in occupied Poland during World War II
- Holocaust in Nazi-occupied Poland
- World War II crimes in Poland
- Soap made from human corpses
References
Bibliography
- Bartov, Omer (ed.). The Holocaust, 2000.
- Gilbert, Martin. Holocaust Journey: Travelling in Search of the Past, Phoenix, 1997. An account of the sites of the extermination camps as they are today, plus historical information about them and about the fate of the Jews of Poland.
- Klee, Ernst. "'Turning the tap on was no big deal' — The gassing doctors during the Nazi period and afterwards," in Dauchau Review, vol. 2, 1990.
- Levi, Primo. The Drowned and the Saved, 1986.
Notes
- ^ "Die Endlösung der Judenfrage" - Adolf Hitler (In English, "The final solution of the Jewish question"). Furet, François. Unanswered Questions: Nazi Germany and the Genocide of the Jews. Schocken Books (1989), p. 182; ISBN 978-0-8052-4051-1
- ^ Doris Bergen,Germany and the Camp System, part of Auschwitz: Inside the Nazi State, Community Television of Southern California, 2004-2005
- ^ Minerbi, Alessandra (2005). A New Illustrated History of the Nazis: Rare Photographs of the Third Reich. David & Charles. p. 168. http://books.google.com/books?id=TFbfiRCVLTUC&pg=PA168&lpg=PA168&dq=%22extermination+camps%22+%2Bhours&source=web&ots=LDIfGuiKoP&sig=HW2xVgYy0mfZv-7dqaHdhUBel7I&hl=en&sa=X&oi=book_result&resnum=2&ct=result.
- ^ Diary of Johann Paul Kremer
- ^ Overy, Richard. Interrogations, p. 356–7. Penguin 2002. ISBN 978-0-14-028454-6
- ^ Holocaust Timeline: The Camps Archived 26 January 2010 at WebCite
- ^ "Encyclopedia of the holocaust"
- ^ M. Shelach (ed.), "History of the holocaust: Yugoslavia".
- ^ Aktion Reinhard: Belzec, Sobibor & Treblinka, Nizkor Project
- ^ "It is estimated that the SS and police deported at a minimum 1.3 million people to Auschwitz complex between 1940 and 1945. Of these, the camp authorities murdered 1.1 million." (Number includes victims killed in other Auschwitz camps.) Archived 17 January 2010 at WebCite
- ^ Reinhard: Treblinka Deportations
- ^ Between March and December 1942, the Germans deported some 434,500 Jews, and an indeterminate number of Poles and Roma (Gypsies)to Belzec, to be killed. http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/article.php?lang=en&ModuleId=10005191
- ^ In all, the Germans and their auxiliaries killed at least 167,000 people at Sobibor. http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/article.php?lang=en&ModuleId=10005192
- ^ In total, the SS and the police killed some 152,000 people in Chelmno. http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/media_cm.php?lang=en&ModuleId=10005194&MediaId=130[dead link]
- ^ A recent study reduced the estimated number of deaths at Majdanek, in "Majdanek Victims Enumerated", by Pawel P. Reszka, Lublin, in the Gazeta Wyborcza 12 December 2005, reproduced on the site of the Auschwitz–Birkenau Museum, Lublin scholar Tomasz Kranz established that figure, which the Majdanek museum staff consider authoritative. Earlier calculations were greater: ca. 360,000, in a much-cited 1948 publication by Judge Zdzislaw Lukaszkiewicz, of the Main Commission for the Investigation of Nazi Crimes in Poland; and ca. 235,000, in a 1992 article by Dr. Czesaw Rajca, formerly of the Majdanek museum.
- ^ [1] Yad Vashem
- ^ See Maly Trostinec at the camps Yad Vashem website
- ^ "The evacuation of Jews to Poland", Jewish Virtual Library.'.' Retrieved 2009-07-28.
- ^ Ellen Land-Weber, "Conditions for Polish Jews During WWII" in To Save a Life: Stories of Holocaust Rescue.'.' Retrieved 2009-07-28.
- ^ Borkin, Joseph (1978). The Crime and Punishment of IG Farben. New York: Free Press. ISBN 978-0-02-904630-2.
- ^ Hoss [sic], Rudolf (2005). "I, the Commandant of Auschwitz," in Lewis, Jon E. (ed.), True War Stories, p. 321. Carroll & Graf Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7867-1533-6.
- ^ See: M. Lifshitz, "Zionism" (משה ליפשיץ, "ציונות" )p. 304. Compare with H. Abraham, "History of Israel and the nations in the era of Holocaust and uprising (חדד אברהם, "תולדות ישראל והעמים בתקופת השואה והתקומה")"
- ^ Ibidem
- ^ Ibidem, pp. 101-102
- ^ Berenbaum, Michael; Yisrael Gutman (1998). Anatomy of the Auschwitz Death Camp. Indiana University Press. p. 199. ISBN 978-0-253-20884-2. http://books.google.com/books?id=ZrU2oS8fP3cC&pg=PA199&lpg=PA199&dq=auschwitz+furnaces+day+night&source=web&ots=KnAFUCsuv6&sig=bVDl5vVGLFVpVdK2Ax0xQj8dW7s&hl=en&sa=X&oi=book_result&resnum=3&ct=result.
- ^ The Nazi Sourcebook: An Anthology of Texts. Routledge. 2002. p. 354. ISBN 978-0-415-22213-6.
- ^ Höss, pp. 321–322.
- ^ Höss, pp. 322–323.
- ^ Höss, p. 323.
- ^ Höss, p. 324.
- ^ Höss, pp. 320, 328.
- ^ Höss, pp. 325–326.
- ^ Höss, p. 328.
Bibliography
- Bartov, Omer (ed.). The Holocaust: origins, implementation, aftermath. London: Routledge, 2000 ISBN 0415150353
- Gilbert, Martin. Holocaust Journey: travelling in search of the past, Phoenix, 1997. An account of the sites of the extermination camps as they are today, plus historical information about them and about the fate of the Jews of Poland.
- Klee, Ernst. "'Turning the tap on was no big deal': the gassing doctors during the Nazi period and afterwards," in Dachau Review, vol. 2, 1990.
- Levi, Primo. The Drowned and the Saved. London: Michael Joseph, 1986 ISBN 0718130634
External links
- The Holocaust History Project
- Holocaust and concentration camps information
- The Holocaust Education & Archive Research Team
- Official U.S. National Archive Footage of Nazi camps
The Holocaust - Related articles by country: Belarus
- Estonia
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Poland
- Norway
- Russia
- Ukraine
Early elements Camps Transit and collectionExterminationMethods- Inmate identification
- Gas van
- Gas chamber
- Extermination through labor
- Human medical experimentation
- Inmate disposal of victims
Divisions: SS-Totenkopfverbände - Concentration Camps Inspectorate
- Politische Abteilung
- Sanitätswesen
History of the Jews
during World War II- Wannsee Conference
- Operation Reinhard
- Holocaust trains
- Extermination camps
Resistance- Death marches
- Wola
- Bricha
- Displaced persons
Other victims Responsibility OrganizationsIndividualsAftermath Lists - Holocaust survivors
- Victims and survivors of Auschwitz
- Survivors of Sobibor
- Timeline of Treblinka
- Victims of Nazism
- Rescuers of Jews
Resources Remembrance - Days of remembrance
- Memorials and museums
Categories:- Inventions of the Third Reich
- Nazi extermination camps
- Internments
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.