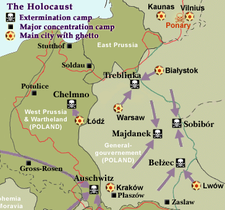
- Sobibor extermination camp
-
Sobibor Extermination camp
Nazi extermination camps in occupied Poland (marked with black and white skulls)Coordinates 51°26′50″N 23°35′37″E / 51.44722°N 23.59361°ECoordinates: 51°26′50″N 23°35′37″E / 51.44722°N 23.59361°E Known for Genocide during The Holocaust Location Near Sobibór, German-occupied Poland Built by Richard Wolfgang Thomalla (death camp)
Erwin Hermann Lambert (gas chambers)Operated by  SS-Totenkopfverbände
SS-TotenkopfverbändeOriginal use Death First built March 1942 – May 1942 Operational 16 May 1942 – 17 October 1943 Number of gas chambers 3 (expanded to 6)[1] Inmates mainly Jews Number of inmates est. 600 – 650 at any given time Killed est. 200,000 Liberated by closed before end of war Notable inmates Thomas Blatt, Leon Feldhendler, Alexander Pechersky Notable books From The Ashes of Sobibor Sobibor was a Nazi German extermination camp located on the outskirts of the town of Sobibór, Lublin Voivodeship of occupied Poland as part of Operation Reinhard; the official German name was SS-Sonderkommando Sobibor. Jews from Poland, France, Germany, Holland, Czechoslovakia, and Soviet prisoners of war (POWs) (many of them Jewish), were transported to Sobibor by rail, and suffocated in gas chambers that were fed with the exhaust of a petrol engine. One source states that up to 200,000 people were killed at Sobibor.[2] Thomas Blatt claims that "In the Hagen court proceedings against former Sobibor Nazis, Professor Wolfgang Scheffler, who served as an expert, estimated the total figure of murdered Jews at a minimum of 250,000."[3]
After a successful revolt on October 14, 1943 about half of the 600 prisoners in Sobibor escaped; the camp was closed, bulldozed, and planted-over with pine trees to conceal its location days afterwards. A memorial and museum are at the site today.
Contents
The camp
Beginning in 1940, the Nazis established 16 forced labor camps in the Lublin district of Poland. The Lublin district was intended to become an agricultural center. Except for Krychów forced labor camp, the camps used existing structures such as abandoned schools, factories, or farms to imprison the laborers. Krychów was the largest of the 16 camps and had been built before World War II as a detention camp for Polish prisoners.
In 1942, Sobibor extermination camp was built near the forced labor camps.[4] Construction began in March 1942, at the same time that Belzec became operational for extermination. Workers employed for building the camp were local people from neighboring villages and towns, but the camp was primarily built by a Sonderkommando under the command of Richard Thomalla. The Sonderkommando was a group of about eighty Jews from ghettos within the vicinity of the camp. A squad of Ukrainians trained at Trawniki concentration camp guarded the Sonderkommando. Upon completion of construction, these Jews were shot.[5] In mid-April 1942, when the camp was nearly completed, experimental gassings took place. About twenty-five Jews from Krychów were brought there for this purpose. Christian Wirth, the commander of Bełżec and Inspector of Operation Reinhard, arrived in Sobibor to witness these gassings.[6]
Reichsführer-SS Heinrich Himmler appointed SS-Obersturmführer Franz Stangl as the first commandant of Sobibor. Stangl was Sobibor's commandant from April 28 to the end of August of 1942.[citation needed] According to Stangl, Odilo Globocnik initially suggested that Sobibor was merely a supply camp for the army, and that the true nature of the camp became known to Stangl only when he discovered a gas chamber hidden in the woods. Globocnik told him that if the Jews "were not working hard enough" he was fully permitted to kill them and that Globocnik would send "new ones".
Stangl first studied the camp operations and management of Bełżec, which had already commenced extermination activity. He then accelerated the completion of Sobibor.[7]
Erich Fuchs, who spent time at the three Reinhard death camps of Sobibor, Treblinka and Bełżec, explained how the gassing operation at Sobibor began:
“ Upon arriving in Sobibor I discovered a piece of open ground close to the station on which there was a concrete building and several other permanent buildings. The Sonderkommando at Sobibor was led by Thomalla. Amongst the SS personnel there were Floss, Bauer, Stangl, Schwarz, Barbl and others. We unloaded the motor. It was a heavy, Russian petrol engine (presumably a tank or tractor engine) of at least 200 HP (carburettor engine, eight-cylinder, water-cooled). We put the engine on a concrete plinth and attached a pipe to the exhaust outlet. Then we tried out the engine. At first it did not work. I repaired the ignition and the valve and suddenly the engine started. The chemist whom I already knew from Belzec went into the gas chamber with a measuring device in order to measure the gas concentration. After this a test gassing was carried out. I seem to remember that thirty to forty women were gassed in a gas chamber. The Jewesses had to undress in a clearing in the wood which had been roofed over, near the gas chamber. They were herded into the gas chamber by the above-mentioned SS members and Ukrainian volunteers. When the women had been shut up in the gas chamber I attended to the engine together with Bauer. The engine immediately started ticking over. We both stood next to the engine and switched it up to "release exhaust to chamber" so that the gases were channelled into the chamber. On the instigation of the chemist I revved up the engine, which meant that no extra gas had to be added later. After about ten minutes the thirty to forty women were dead. The chemist and the SS gave the signal to turn off the engine.
I packed up my tools and saw the bodies being taken away. A small wagon on rails was used to take them away from near the gas chamber to a stretch of ground some distance away. Sobibor was the only place where a wagon was used.[8] — Erich Fuchs
” On either 16 or 18 of May 1942, Sobibor became fully operational and began mass gassing operations. Trains entered the railway station, and the Jews onboard were told they were in a transit camp, and were forced to undress and hand over their valuables. They were then led along the 100 meter long "Road to Heaven" (Himmelstrasse) which led to the gas chambers, where they were killed using carbon monoxide released from the exhaust pipes of tank engines. SS-Oberscharführer Kurt Bolender described the way the gassing operations ran during his trial:
“ Before the Jews undressed, Oberscharführer Hermann Michel made a speech to them. On these occasions, he used to wear a white coat to give the impression he was a physician. Michel announced to the Jews that they would be sent to work. But before this they would have to take baths and undergo disinfection, so as to prevent the spread of diseases. After undressing, the Jews were taken through the "Tube", by an SS man leading the way, with five or six Ukrainians at the back hastening the Jews along. After the Jews entered the gas chambers, the Ukrainians closed the doors. The motor was switched on by the former Soviet soldier Emil Kostenko and by the German driver Erich Bauer from Berlin. After the gassing, the doors were opened and the corpses were removed by a group of Jewish workers.[9] ”  The Gold Medal winning Dutch Olympic gymnastics team of 1928: 4th from left Helena Nordheim; 6th from left Ans Polak; 5th from right Estella Agsteribbe (murdered in K-Z Auschwitz 1943); 2nd from right Elka de Levie (died 1979); extreme right Jud Simons. Coach Gerrit Kleerekoper was murdered 2 July 1943 at Sobibor
The Gold Medal winning Dutch Olympic gymnastics team of 1928: 4th from left Helena Nordheim; 6th from left Ans Polak; 5th from right Estella Agsteribbe (murdered in K-Z Auschwitz 1943); 2nd from right Elka de Levie (died 1979); extreme right Jud Simons. Coach Gerrit Kleerekoper was murdered 2 July 1943 at Sobibor
Victims included 18-year-old Helga Deen, whose diary was discovered in 2004, writer Else Feldmann, gymnasts Helena Nordheim, Ans Polak and Jud Simons, Gym Coach Gerrit Kleerekoper and magician Michel Velleman.[citation needed]
Female prisoners were sometimes sexually abused and later murdered. For instance, two women from Austria who were film or theater actresses were used by the SS men for orgies before being shot. Erich Bauer testified about this:
“ I was blamed for being responsible for the death of the Jewish girls Ruth and Gisela, who lived in the so-called forester house. As it is known, these two girls lived in the forester house, and they were visited frequently by the SS men. Orgies were conducted there. They were attended by Bolender, Gomerski, Karl Ludwig, Franz Stangl, Gustav Wagner, and Steubel. I lived in the room above them and due to these celebrations could not fall asleep after coming back from a journey....[10] ” The camp was split into four sections:[citation needed]
Garrison Area: This included the main entrance gates and the railway platform where the victims were taken off the trains. The Commander's lodge was opposite the platform and was on the right side to the Guardhouse and on the left by the armoury.[citation needed]
Lager (Camp) I: This was built directly west and behind the Garrison Area. It was made escape proof by extra barbed wire fences and a deep trench filled with water. The only opening was a gate leading into the area. This camp was the living barracks for Jewish prisoners and included a prisoner's kitchen. Each prisoner was given about 12 square feet (1.1 square meters) of sleeping space.[citation needed]
Lager (Camp) II: This was a larger section and included an assortment of vital services for both the killing process and the everyday operation of the camp. 400 prisoners, including women, worked here. Lager II contained the warehouses used for storing the objects taken from the dead victims, including hair, clothes, food, gold and all other valuables. This Lager also housed the main administration office. It was at Lager II that the Jews were prepared for their death. Here they undressed, women's hair was shaved, clothing searched and sorted, and documents destroyed in the nearby furnace. The victims' final steps were taken on a path framed by barbed wire. It was called the "Road to Heaven" and led directly to the gas chambers.[citation needed]
Lager (Camp) III: This was where the victims met their end. Located in the north-western part of the camp, there were only two ways to enter the camp from Lager II. The camp staff and personnel entered through a small plain gate. The entrance for the victims descended immediately into the gas chambers and was decorated with flowers and a Star of David.[citation needed]
Camp guards
While the camp officers were German and Austrian SS members, the camp guards under their command were Ukrainian (Volksdeutsche) as well as Soviet POWs primarily from Ukraine.[11]
Before they were sent as guards to the concentration camps, most of the Soviet POWs underwent special training in Trawniki, which originally was a holding center for those refugees and Soviet POWs, whom the Sipo security police and the SD had designated either as potential collaborators or as dangerous persons.[12] The Stroop Report listed a Trawniki Guard Battalion assisting in the suppression of the 1943 Warsaw Ghetto Uprising.
John Demjanjuk, a former Soviet POW, worked as a watchguard at Sobibor. On May 12, 2011, Demjanjuk, then 91 years old, was convicted by a German court of complicity in the murder of over 28,000 Jews whilst serving at Sobibor, and was sentenced to 5 years in jail.[13]
The uprising
Sobibor was the site of one of two successful uprisings by Jewish prisoners in a Nazi extermination camp — there was a similar revolt at Treblinka on August 2, 1943. A revolt at Auschwitz-Birkenau on October 7, 1944 led to one of the crematoria being blown up, however nearly all the escapees were killed. Among the few who survived the Auschwitz revolt was Henryk Mandelbaum, who served as a tourist guide at the camp after the war.[citation needed]
On October 14, 1943, members of the Sobibor underground, led by Polish-Jewish prisoner Leon Feldhendler and Soviet-Jewish POW Alexander Pechersky, succeeded in covertly killing eleven German SS officers and a number of camp guards. Although their plan was to kill all the SS and walk out of the main gate of the camp, the killings were discovered and the inmates ran for their lives under fire. About 300 out of the 600 prisoners in the camp escaped into the forests.[citation needed]
Only 50 to 70[14] escapees survived the war, however. Some died on the mine fields surrounding the site, and some were recaptured in a dragnet and executed by the Germans in the next few days. Most of those who did survive were hidden from the Germans by other Poles, at the risk of their own and their families' lives.[citation needed]
The revolt was dramatized in the 1987 British TV film Escape from Sobibor, directed by Jack Gold. An award-winning documentary about the escape was made by Claude Lanzmann, entitled Sobibor, 14 Octobre 1943, 16 Heures (Sobibor, Oct. 14, 1943, 4 p.m.).
Timeline of Sobibor
Timeline of Sobibor March 1942 – May 1942 Under the supervision of Richard Thomalla, SS and police authorities construct Sobibor extermination camp in the spring of 1942 in an isolated area not far from the local Chelm-Wlodawa rail line.[15] early April 1942 The first test subjects for the gas chambers at Sobibor: The SS deports 2,400 Jews from Rejowiec, Lublin Voivodeship in early April 1942, the first deportation to Sobibor, and murders almost all of them upon arrival.[15] April 28, 1942 Franz Stangl arrives in Sobibor to take up the position of camp commandant. Stangl had been the deputy supervisor of the "euthanasia" institution at Hartheim, near Linz, Austria. As the purpose of the "euthanasia" operation was to murder institutionalized persons with physical and mental disabilities in gas chambers at facilities like Hartheim, Stangl was familiar with using carbon monoxide gas for killing large numbers of people.[15] May 3, 1942

Regular transports to Sobibor begin. The first transport consists of 200 Jews from Zamość. The camp staff conducts gassing operations in three gas chambers located in one brick building. Some 400 prisoners are selected to survive, temporarily, to supply manual labor necessary to support the mass murder function of the killing center. During this first phase of deportations, from early May until the end of July 1942, the Sobibor killing center authorities kill at least 61,400 Jews. Many of them were deported from cities and towns in the north and east of Lublin District; the majority were Jews deported from the German Reich, the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, and Slovakia either directly or via the transit camp-ghetto in Izbica.[15] end of July 1942 The SS halts deportations to Sobibor in order to modernize the railway spur into the camp.[15] October 8, 1942

Camp authorities resume mass murder operations in the gas chambers of Sobibor with the arrival of more than 24,000 Slovak Jews between October 8 and October 20 from the transit camp-ghetto Izbica in the Lublin District of the General Government. The camp authorities kill virtually all of the deportees upon arrival in reconstructed and newly added gas chambers, completed during the two month lull in transports to Sobibor. The improvements in capacity enable the camp authorities to kill up to 1,300 people at a time. Newly constructed as well was a narrow railway trolley from the reception platform to the burial pits in order to facilitate the transfer of the sick, the dead, and those unable to walk directly to the open ovens. Those still alive after this journey are shot by the SS staff or the Trawniki-trained guards.[15] February 12, 1943 Heinrich Himmler visits Sobibor to inspect operations. Several SS officers at the camp are promoted as a result. March 5, 1943

Deportations from the Netherlands. German SS and Police authorities begin deportations of Dutch Jews from the police transit camp at Westerbork in the Netherlands to Sobibor. In 19 transports from this date until July 1943, SS authorities in Westerbork deport over 34,000 Jews to Sobibor. Camp staff and guards kill almost all of them in the gas chambers or by shooting on arrival in the camp.[15] April 1943

Deportations from France. Two transports containing a total of 2,000 Jews from France arrive at Sobibor from the police transit camp Drancy, outside Paris. Deportations from France to camps in the east, primarily Auschwitz, began in March 1942 and continue until August 1944.[15] July – October 1943

Deportations from the Soviet Union. Following Himmler's order of July 1943 to liquidate the ghettos in Reichskommissariat Ostland, SS and police units liquidate ghettos in Minsk, Lida, and Wilno (Vilnius, Vilne) and deported those who survived to Sobibor. The first transports from Minsk and Lida leave for Sobibor on September 18. Included in the first deportation from Minsk (arrived September 22) is Alexander "Sasha" Pechersky, a Soviet-Jewish prisoner of war, who, because of his military training, came to play a central role in the resistance movement in Sobibor. In September 1943 alone, SS and police authorities transported at least 13,700 Jews from ghettos in the occupied Soviet Union to Sobibor. The camp authorities gas or shoot most of them upon arrival.[15] October 14, 1943

Sobibor revolt. Prisoners carry out a revolt in Sobibor, killing nearly a dozen German staff and Trawniki-trained guards. Of 600 prisoners left in Sobibor on this day, 300 escape during the uprising. Among the survivors is Alexander Pechersky, the Soviet prisoner of war who played a key role in planning the revolt. Of those prisoners who escape, SS and police personnel from Lublin district recapture and shoot some 100. Some of the prisoners selected for temporary survival in Sobibor organized an underground resistance organization in early summer of 1943 as it became apparent that gassing operations at Sobibor were slowing. Once the gassing operations were finished, the SS planned to dismantle the killing center and reconfigure the facility first as a holding pen for women and children deported from villages in Belarus, which had been destroyed in the course of so-called anti-partisan operations, and, later, as an ammunition depot. Though no further prisoners arrived after the killing center was remodeled, the facility was guarded by a small Trawniki-trained detachment until at least the end of March 1944. During the year and a half in which the Sobibor killing center operated, camp authorities and the Trawniki-trained guards murdered at least 167,000 people. Virtually all of the victims were Jews.[15] October 17, 1943 Heinrich Himmler orders that Sobibor be closed and all evidence of the camp's existence be removed.[citation needed] Aftermath
Within days after the uprising, the SS chief Heinrich Himmler ordered the camp closed, dismantled and planted with trees.[citation needed]
Karl Frenzel, commandant of Sobibor's Lager I, was convicted of war crimes in 1966 and sentenced to life, but ultimately released on health grounds in 1982.[3][16] In a 1983 interview, Frenzel — who was at the camp from its inception to its closure — admitted the following about Sobibor:
“ Poles were not killed there. Gypsies were not killed there. Russians were not killed there...only Jews, Russian Jews, Polish Jews, Dutch Jews, French Jews.[17] ” Frenzel's testimony contrasts greatly with a memorial plaque at the site today, which reads "HERE THE NAZIS KILLED 250,000 RUSSIAN PRISONERS OF WAR, JEWS, POLES AND GYPSIES."[17]
Franz Stangl, chief commandant of Sobibor and later of Treblinka fled to Syria. Following problems with his employer taking too much interest in his adolescent daughter, Stangl went to Brazil in the 1950s. He worked in a car factory and was registered with the Austrian consulate under his own name. He was eventually caught, arrested and sentenced to life imprisonment. In 1971 he died in prison in Düsseldorf, a few hours after concluding a series of interviews with British historian Gitta Sereny.[3][18]
Gustav Wagner, the deputy Sobibor commander, was on leave on the day of uprising (survivors such as Thomas Blatt say that the revolt would not have succeeded had he been present). Wagner was arrested in 1978 in Brazil. He was identified by Sobibor escapee Stanisław Szmajzner, who greeted him with the words "Hallo Gustl"; Wagner replied that he remembered Szmajzner and that he had saved him and his three brothers. The court of first instance agreed to his extradition to Germany but on appeal this extradition was overturned. In 1980, Wagner committed suicide.[19][20]
John Demjanjuk, one of the guards was sentenced to 5 years in prison on May 12, 2011. He was convicted as an accessory to the murder of 27,900 Jews.[21][22]
Erich Bauer, commander of Camp III and gas chamber executioner, explained the perpetrators' sense of teamwork in order to reach an atrocious result:
“ We were a band of "fellow conspirators" ("verschworener Haufen") in a foreign land, surrounded by Ukrainian volunteers whom we could not trust....The bond between us was so strong that Frenzel, Stangl and Wagner had had a ring with SS runes made from five-mark pieces for every member of the permanent staff. These rings were distributed to the camp staff as a sign so that the "conspirators" could be identified. In addition the tasks in the camp were shared. Each of us had at some point carried out every camp duty in Sobibor (station squad, undressing, and gassing).[23] ” Memorial
Following the celebration of the 60th anniversary of the revolt in 2003, the grounds of the former death camp received a grant largely funded by the Dutch government to improve the site. New walkways were introduced with signs indicating points of interest, but close to the burial pits, bone fragments still litter the area.[citation needed]In the forest outside the camp is a statue honoring the fighters of Sobibor.[citation needed]
Survivors
Main article: List of survivors of SobiborChain of command
Organizers of the camp
- Odilo Lotario Globocnik, SS-Hauptsturmführer (at the time) (Captain) and SS-Polizeiführer (SS Police Chief), Head of Operation Reinhard[1][3]
- Hermann Julius Höfle, SS-Hauptsturmführer (Captain), Coordinator of Operation Reinhard[3]
- Richard Wolfgang Thomalla, SS-Obersturmführer (at the time) (First Lieutenant), Head of death camp construction during Operation Reinhard[1][3]
- Erwin Hermann Lambert, SS-Unterscharführer (Corporal), Head of gas chamber construction during Operation Reinhard[3]
- Karl Steubl, SS-Sturmbannführer (Major), Commander of transportation units during Operation Reinhard[3][19]
- Christian Wirth, SS-Hauptsturmführer (at the time) (Captain), Inspector of Operation Reinhard[3]
Commandant
- Franz Paul Stangl, SS-Obersturmführer (First Lieutenant), April 28, 1942— August 30, 1942 (transferred to Commandant of Treblinka extermination camp)[1][3][19]
- Franz Karl Reichleitner, SS-Obersturmführer (First Lieutenant), September 1, 1942— October 17, 1943[1]; promoted to Hauptsturmführer (Captain) after Himmler's visit on February 12, 1943[19]
Deputy commanders
- Gustav Franz Wagner, SS-Oberscharführer (Staff Sergeant), Deputy commandant (Quartermaster-sergeant of the camp)[1][3][19]
- Johann Niemann, SS-Untersturmführer (Second Lieutenant), Deputy commandant[3][19][24] — killed in revolt
- Karl August Wilhelm Frenzel, SS-Oberscharführer (Staff Sergeant), Commandant of Camp I (forced labor camp)[1][3][19]
- Hermann Michel, SS-Oberscharführer (Staff Sergeant), Deputy commandant, gave speeches to trick prisoners into entering gas chambers[3][19][25]
Executioners
- Hermann Erich Bauer, SS-Oberscharführer (Staff Sergeant), operated gas chambers[1][3][19]
- Heinz Kurt Bolender, SS-Oberscharführer (Staff Sergeant), operated gas chambers[1][3][19]
Other officers
- Ernst Bauch[19]
- Rudolf Beckmann, SS-Oberscharführer (Staff Sergeant)[24][19] — killed in revolt
- Gerhardt Börner, SS-Untersturmführer (Second Lieutenant)[23]
- Paul Bredow, SS-Unterscharführer (Corporal)[1][19]
- Max Bree[19] — killed in revolt
- Arthur Dachsel[3][19]
- Werner Karl Dubois, SS-Oberscharführer (Staff Sergeant)[1][3][19]
- Herbert Floss, SS-Scharführer (Sergeant)[1][19]
- Erich Fritz Erhard Fuchs, SS-Scharführer (Sergeant)[1][19][23]
- Friedrich Gaulstich, SS-Scharführer (Sergeant)[24][19] — killed in revolt
- Anton Getzinger[19]
- Hubert Gomerski, SS-Unterscharführer (Corporal)[3][19]
- Siegfried Graetschus, SS-Oberscharführer (Staff Sergeant), Head of Ukrainian Guard (2/2)[1][3][19] — killed in revolt
- Ferdinand "Ferdl" Grömer[19]
- Paul Johannes Groth[3]
- Lorenz Hackenholt, SS-Hauptscharführer (First Sergeant)
- Josef "Sepp" Hirtreiter, SS-Scharführer (Sergeant)[1]
- Franz Hödl[3][19]
- Jakob Alfred Ittner, SS-Oberscharführer (Staff Sergeant)[3][19]
- Robert Emil Franz Xaver Jührs, SS-Unterscharführer (Corporal)[3]
- Aleks Kaizer[3]
- Rudolf "Rudi" Kamm[19]
- Johann Klier, SS-Untersturmführer (Second Lieutenant)[3][19][24]
- Fritz Konrad, SS-Scharführer (Sergeant)[19][24] — killed in revolt
- Erich Gustav Willie Lachmann, SS-Scharführer (Sergeant), Head of Ukrainian Guard (1/2)[3][19]
- Karl Emil Ludwig[3][19]
- Willi Mentz, SS-Unterscharführer (Corporal)[3]
- Adolf Müller[19]
- Walter Anton Nowak, SS-Scharführer (Sergeant)[1][3][19] — killed in revolt
- Wenzel Fritz Rehwald[3][19]
- Karl Richter[19]
- Paul Rost, SS-Untersturmführer (Second Lieutenant)[1]
- Walter "Ryba" (real name: Hochberg), SS-Unterscharführer (Corporal)[19][24] — killed in revolt
- Klaus Schreiber[24]
- Hans-Heinz Friedrich Karl Schütt, SS-Scharführer (Sergeant)[1][3][19]
- Thomas Steffl, SS-Scharführer (Sergeant)[19][24] — killed in revolt
- Ernst Stengelin[19] — killed in revolt
- Heinrich Unverhau, SS-Unterscharführer (Corporal)[3][19]
- Josef Vallaster, SS-Scharführer (Sergeant)[19][24] — killed in revolt
- Otto Weiss[19]
- Wilhelm "Willie" Wendland[3][19]
- Franz Wolf, SS-Oberscharführer (Staff Sergeant)[1][3][19]
- Josef Wolf, SS-Scharführer (Sergeant)[19][24] — killed in revolt
- Ernst Zierke, SS-Unterscharführer (Corporal)[3]
Guards
Germans
- Heinrich Barbl, SS-Rottenführer (Private First Class)[19][26]
Ukrainians
- B. Bielakow[3][24]
- Ivan Demjanjuk[27]
- Ivan Klatt[24][28]
- M. Matwiejenko[3][24]
- Ivan Nikiforow[3][24]
- W. Podienko[3][24]
- Mikhail Affanaseivitch Razgonayev[29]
- Emanuel Schultz[24]
- Fiodor Tichonowski[3][24]
- Libodenko Wartownick[3]
- J. Zajcew[3][24]
- other Volksdeutsche and prisoners of war (up to 200)[3]
See also
- List of Nazi concentration camps
- Kaiser Wilhelm Institute of Anthropology, Human Heredity, and Eugenics
- Research Materials: Max Planck Society Archive
- Shark Island, German South West Africa
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s The Holocaust: Lest we forget: Extermination camp Sobibor
- ^ Raul Hilberg. The Destruction of the European Jews. Yale University Press, 1985, p. 1219. ISBN 978-0300095579
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar Sobibor - The Forgotten Revolt
- ^ Aktion Reinhard Camps. Sobibor Labour Camps. 15 June 2006. ARC Website.
- ^ Yitzhak Arad (1987). Belzec, Sobibor, Treblinka: The Operation Reinhard Death Camps, Bloomington: Indiana University Press, pg. 30.
- ^ Arad, Yitzhak: Belzec, Sobibor, Treblinka: the Operation Reinhard death camps. Bloomington: Indiana University Press 1987, p. 184.
- ^ Christian Zentner, Friedemann Bedürftig. The Encyclopedia of the Third Reich, p. 878. Macmillan, New York, 1991. ISBN 0028975022
- ^ Klee, Ernst, Dressen, Willi, Riess, Volker. The Good Old Days: The Holocaust as Seen by Its Perpetrators and Bystanders, p. 231. ISBN 1-56852-133-2.
- ^ Yitzhak Arad. Belzec, Sobibor, Treblinka: The Operation Reinhard Death Camps, p. 76. Indiana University Press, 1987.
- ^ Yitzhak Arad (1987). Belzec, Sobibor, Treblinka: The Operation Reinhard Death Camps, Bloomington: Indiana University Press, pp. 116-117.
- ^ Sobibor The Forgotten Revolt by Thomas (Toivi) Blatt HEP Issaquah 1998.
- ^ Trawniki
- ^ "John Demjanjuk guilty of Nazi death camp murders". BBC News. 12 May 2011. http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-12321549. Retrieved 12 May 2011.
- ^ Schelvis, Jules. Sobibor: A History of a Nazi Death Camp. Berg, Oxford & New Cork, 2007, p. 168, ISBN 978-1-84520-419-8.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Sobibor: Chronology
- ^ Sobibor Trial
- ^ a b Frenzel interview
- ^ "SOME SIGNIFICANT CASE - Franz Stangl". Simon Wiesenthal Archiv. Simon Wiesenthal Center. http://www.simon-wiesenthal-archiv.at/02_dokuzentrum/02_faelle/e02_stangl.html. Retrieved 2009-11-30.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as Sobibor Interviews: Biographies of SS-men
- ^ Arad, Yitzhak: Belzec, Sobibor, Treblinka: the Operation Reinhard death camps, p. 192. Bloomington: Indiana University Press 1987.
- ^ Matussek, Karin (12 May 2011). "Demjanjuk Convicted of Helping Nazis to Murder Jews During the Holocaust". Bloomberg. http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2011-05-12/demjanjuk-convicted-of-helping-nazis-to-murder-jews-during-the-holocaust.html. Retrieved 12 May 2011.
- ^ "John Demjanjuk zu fünf Jahren Haft verurteilt". Die Welt. 12 May 2011. http://www.welt.de/politik/deutschland/article13367603/John-Demjanjuk-zu-fuenf-Jahren-Haft-verurteilt.html. Retrieved 12 May 2011.
- ^ a b c Klee, Ernst, Dressen, Willi, Riess, Volker The Good Old Days: The Holocaust as Seen by Its Perpetrators and Bystanders. ISBN 1-56852-133-2.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r H.E.A.R.T. - Holocaust Education & Archive Research Team
- ^ Nizkor Web Site Retrieved on 2009-04-09
- ^ Belzec: Stepping Stone to Genocide - Chapter 6
- ^ BBC News (12 May 2011). "John Demjanjuk guilty of Nazi death camp murders". http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-12321549. Retrieved 12 May 2011.
- ^ Survivors of the revolt - Sobibor Interviews
- ^ Sobibor Watchman
- From the Ashes of Sobibor by Thomas Blatt
- Belzec, Sobibor, Treblinka. The Operation Reinhard Death Camps by Yitzhak Arad
Further reading
- Freiberg, Dov 2007, "To Survive Sobibor", Gefen Publishing House. ISBN 978-9652293886
- Lev, Michael 2007, "Sobibor", Gefen Publishing House. ISBN 978-9652294081
- Schelvis, Jules (2007). Sobibor: A History of a Nazi Death Camp. Berg. ISBN 978-1845204181.
- Sereny, Gitta (1974). Into That Darkness: from Mercy Killing to Mass Murder. ISBN 0070562903.
- Bialowitz, Philip with Joseph Bialowitz (2010) "A Promise at Sobibor: A Jewish Boy's Story of Revolt and Survival in Nazi Occupied Poland", The University of Wisconsin Press, ISBN 978-0-299-24800-0
External links
- Sobibor - The Forgotten Revolt website of Thomas Blatt, one of the few survivors
- SOBIBOR United States Holocaust Memorial Museum
- The Sobibor Death Camp
- Sobibor Archaeological Project
- My Trip to Sobibor
Camp organizers Odilo Lotario Globocnik • Hermann Julius Höfle • Richard Wolfgang Thomalla • Erwin Hermann Lambert • Karl Steubl • Christian WirthCommandant Deputy commanders Gas chamber executioners Hermann Erich Bauer • Heinz Kurt BolenderOther officers Ernst Bauch • Rudolf Beckmann • Gerhardt Börner • Paul Bredow • Max Bree • Arthur Dachsel • Werner Karl Dubois • Herbert Floss • Erich Fritz Erhard Fuchs • Friedrich Gaulstich • Anton Getzinger • Hubert Gomerski • Siegfried Graetschus • Ferdinand "Ferdl" Grömer • Paul Johannes Groth • Lorenz Hackenholt • Josef "Sepp" Hirtreiter • Franz Hödl • Jakob Alfred Ittner • Robert Emil Franz Xaver Jührs • Aleks Kaizer • Rudolf "Rudi" Kamm • Johann Klier • Fritz Konrad • Erich Gustav Willie Lachmann • Karl Emil Ludwig • Willi Mentz • Adolf Müller • Walter Anton Nowak • Wenzel Fritz Rehwald • Karl Richter • Paul Rost • Walter "Ryba" (Hochberg) • Klaus Schreiber • Hans-Heinz Friedrich Karl Schütt • Thomas Steffl • Ernst Stengelin • Heinrich Unverhau • Josef Vallaster • Otto Weiss • Wilhelm "Willie" Wendland • Franz Wolf • Josef Wolf • Ernst ZierkeGuards Germans/Austrians: Heinrich Barbl
Ukrainians: B. Bielakow • Ivan Demjanjuk • Ivan Klatt • M. Matwiejenko • Ivan Nikiforow • W. Podienko • Mikhail Razgonayev • Emanuel Schultz • Fiodor Tichonowski • Libodenko Wartownick • J. Zajcew • other Volksdeutsche and prisoners of war (up to 200)Prominent victims Helga Deen • Anna Dresden-Polak • Else Feldmann • Isidore Goudeket • Jakob van Hoddis • Han Hollander • Gerrit Kleerekoper • Helena Nordheim • Abraham de Oliveira • Emanuel Querido • Jud Simons • Leo Smit • Michel VellemanResistance and survivors List of survivors of Sobibor (Thomas Blatt • Selma Engel-Wijnberg • Leon Feldhendler • Elka de Levie • Alexander Pechersky • Jules Schelvis)Nazi occupation and organizations Planning, methods,
documents and evidenceWar crimes investigations and trials Memorials Related articles Categories:- 1943 establishments
- 1942 in Poland
- 1943 disestablishments
- 1943 in Poland
- Jewish resistance during the Holocaust
- Prison uprisings
- 1943 riots
- Sobibor extermination camp
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.