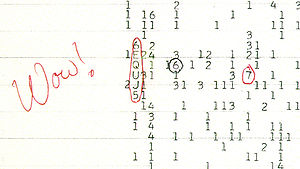
- Wow! signal
-
The Wow! signal was a strong narrowband radio signal detected by Dr. Jerry R. Ehman on August 15, 1977, while working on a SETI project at the Big Ear radio telescope of The Ohio State University then located at Ohio Wesleyan University's Perkins Observatory, Delaware, Ohio.[1] The signal bore expected hallmarks of potential non-terrestrial and non-solar system origin. It lasted for the full 72-second duration that Big Ear observed it, but has not been detected again. The signal has been the subject of significant media attention.
Amazed at how closely the signal matched the expected signature of an interstellar signal in the antenna used, Ehman circled the signal on the computer printout and wrote the comment "Wow!" on its side. This comment became the name of the signal.[1]
Contents
Interpretation of the paper chart
The circled alphanumeric code 6EQUJ5 describes the intensity variation of the signal. A space denotes an intensity between 0 and 1, the numbers 1 to 9 denote the correspondingly numbered intensities (from 1.000 to 10.000), and intensities of 10.0 and above are denoted by a letter ('A' corresponds to intensities between 10.0 and 11.0, 'B' to 11.0 to 12.0, etc.). The value 'U' (an intensity between 30.0 and 31.0) was the highest detected by the telescope, on a linear scale it was over 30 times louder than normal deep space.[1] The intensity in this case is the unitless signal-to-noise ratio, where noise was averaged for that band over the previous few minutes.[2]
Two different values for its frequency have been given: 1420.356 MHz (J. D. Kraus) and 1420.4556 MHz (J. R. Ehman). The frequency 1420 is significant for SETI searchers because, it is reasoned, hydrogen is the most common element in the universe, and hydrogen resonates at about 1420 MHz, thus extraterrestrials might use that frequency on which to transmit a strong signal.[1] The frequency of the Wow! signal matches very closely with the hydrogen line, which is at 1420.40575177 MHz. It is worth noting that the two different values given for the frequency of the Wow! signal (1420.356 MHz and 1420.4556 MHz) are the same distance apart to the hydrogen line - the first being about 0.0498 MHz less than the hydrogen line, and the second being about 0.0498 MHz more than the hydrogen line. The bandwidth of the signal is less than 10 kHz (each column on the printout corresponds to a 10 kHz-wide channel; the signal is only present in one column).
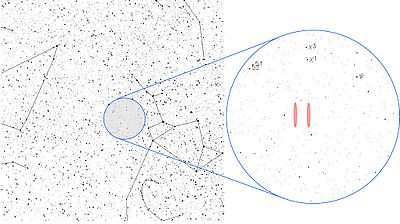 The location of the signal in the constellation Sagittarius, near the Chi Sagittarii star group. Because of the design of the experiment, the location may lie in either one of the two red bands, and there is also significant uncertainty in the declination (vertical axis). For clarity, the widths of the red bands are not drawn to scale; they should actually be narrower.
The location of the signal in the constellation Sagittarius, near the Chi Sagittarii star group. Because of the design of the experiment, the location may lie in either one of the two red bands, and there is also significant uncertainty in the declination (vertical axis). For clarity, the widths of the red bands are not drawn to scale; they should actually be narrower.
The original print out of the Wow! signal, complete with Jerry Ehman's famous exclamation, is preserved by the Ohio Historical Society.[3]
Location of the signal
Determining a precise location in the sky was complicated by the fact that the Big Ear telescope used two feed horns to search for signals, each pointing to a slightly different direction in the sky following Earth's rotation; the Wow! signal was detected in one of the horns but not in the other, although the data was processed in such a way that it is impossible to determine in which of the two horns the signal entered. There are, therefore, two possible right ascension values:
- 19h22m24.64s ± 5s (positive horn)
- 19h25m17.01s ± 5s (negative horn)
The declination was unambiguously determined to be −27°03′ ± 20′. The preceding values are all expressed in terms of the B1950.0 equinox.[4]
Converted into the J2000.0 equinox, the coordinates become RA= 19h25m31s ± 10s or 19h28m22s ± 10s and declination= −26°57′ ± 20′
This region of the sky lies in the constellation Sagittarius, roughly 2.5 degrees south of the fifth-magnitude star group Chi Sagittarii. Tau Sagittarii is the closest easily visible star.
Time variation
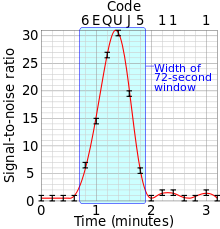
The Big Ear telescope was fixed and used the rotation of the Earth to scan the sky. At the speed of the Earth's rotation, and given the width of the Big Ear's observation "window", the Big Ear could observe any given point for just 72 seconds. A continuous extraterrestrial signal, therefore, would be expected to register for exactly 72 seconds, and the recorded intensity of that signal would show a gradual peaking for the first 36 seconds—until the signal reached the center of Big Ear's observation "window"— and then a gradual decrease.
Therefore, both the length of the Wow! signal, 72 seconds, and the shape of the intensity graph may correspond to a possible extraterrestrial origin.[5]
Searches for recurrence of the signal
The signal was expected to appear three minutes apart in each of the horns, but this did not happen.[5] Ehman unsuccessfully looked for recurrences of the signal using Big Ear in the months after the detection.[6]
In 1987 and 1989, Robert Gray searched for the event using the META array at Oak Ridge Observatory, but did not re-detect it.[6]
In a July 1995 test of signal detection software to be used in its upcoming Project Argus search, SETI League executive director H. Paul Shuch made several drift-scan observations of the 'Wow' signal's coordinates with a 12 meter radio telescope at the National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Green Bank WV, also achieving a null result.
In 1995 and 1996, Gray also searched for the signal using the Very Large Array, which is significantly more sensitive than Big Ear.[6]
Gray and Dr. Simon Ellingsen later searched for recurrences of the event in 1999 using the 26m radio telescope at the University of Tasmania's Mount Pleasant Radio Observatory.[7] Six 14-hour observations were made at positions in the vicinity, but did not detect anything similar to the Wow! signal.[5]
Speculations on the signal's origin
Interstellar scintillation of a weaker continuous signal—similar, in effect, to atmospheric twinkling—could be a possible explanation, although this still would not exclude the possibility of the signal being artificial in its nature. However, even by using the significantly more sensitive Very Large Array, such a signal could not be detected, and the probability that a signal below the Very Large Array level could be detected by the Big Ear radio telescope due to interstellar scintillation is low.[6] Other speculations include a rotating lighthouse-like source, a signal sweeping in frequency, or a one-time burst. Some have also suggested it could have come from a moving space vehicle of extraterrestrial origin.
Ehman has stated his doubts that the signal is of intelligent extraterrestrial origin: "We should have seen it again when we looked for it 50 times. Something suggests it was an Earth-sourced signal that simply got reflected off a piece of space debris."[8]
He later recanted his skepticism somewhat, after further research showed an Earth-borne signal to be very unlikely, due to the requirements of a space-borne reflector being bound to certain unrealistic requirements to sufficiently explain the nature of the signal.[9] Also, the 1420 MHz signal is problematic in itself in that it is "protected spectrum": it is bandwidth in which terrestrial transmitters are forbidden to transmit.[10][11] In his most recent writings, Ehman resists "drawing vast conclusions from half-vast data" -- acknowledging the possibility that the source may have been military in nature or otherwise may have been a production of Earth-bound humans.
See also
- Arecibo message
- Quasar CTA-102, which was believed by Dr. Nikolai S. Kardashev to have an extraterrestrial signal encoded in it before further examination proved it to be a quasar, the first widely reported work of SETI activity.
- Pulsar LGM-1 ("Little Green Men 1"), the first pulsar signal to be recognised.
- Radio source SHGb02+14a
References
- ^ a b c d "Aliens Found In Ohio? The 'Wow!' Signal", by Robert Krulwich, NPR, May 29, 2010
- ^ Ehman, Jerry. "Explanation of the Code "6EQUJ5" On the Wow! Computer Printout". http://www.bigear.org/6equj5.htm. Retrieved 2010-01-01.
- ^ http://ohiohistory.wordpress.com/2010/07/03/wow/
- ^ Gray, Robert; Kevin Marvel (2001). "A VLA Search for the Ohio State 'Wow'". The Astrophysical Journal 546 (2): 1171–1177. Bibcode 2001ApJ...546.1171G. doi:10.1086/318272. http://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/full/10.1086/318272.
- ^ a b c Shostak, Seth (2002-12-05). "Interstellar Signal From the 70s Continues to Puzzle Researchers". Space.com. http://www.space.com/searchforlife/seti_shostak_wow_021205.html.
- ^ a b c d Alexander, Amir (2001-01-17). "The 'Wow!' Signal Still Eludes Detection". The Planetary Society. http://www.planetary.org/news/2001/0117_The_Wow_Signal_Still_Eludes.html.
- ^ Gray, Robert; S. Ellingsen (2002). "A Search for Periodic Emissions at the Wow Locale". The Astrophysical Journal 578 (2): 967–971. Bibcode 2002ApJ...578..967G. doi:10.1086/342646. http://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/full/10.1086/342646.
- ^ Kawa, Barry (1994-09-18). "The Wow! signal". Cleveland Plain Dealer. http://www.bigear.org/wow.htm. Retrieved 2006-06-12.
- ^ Jerry R. Ehman (February 3, 1998). "The Big Ear Wow! Signal. What We Know and Don't Know About It After 20 Years". http://www.bigear.org/wow20th.htm. Retrieved February 27, 2010
- ^ "Frequencies Allocated to Radio Astronomy Used by the DSN". NASA. http://dsnra.jpl.nasa.gov/freq_man/ra_freqs.html. Retrieved November 2007.
- ^ Committee on Radio Astronomy Frequencies Handbook for Radio Astronomy, European Science Foundation, 3rd edition, 2005, p. 101.
External links
- Ehman, J. R. (2007). The Big Ear Wow! Signal (30th Anniversary Report)
- Location on Google Sky
- Location on YourSky
- APOD NASA GOV NASA Signal 2002
- APOD NASA GOV NASA Signal 2004
- APOD NASA GOV NASA Signal 2011
Extraterrestrial life Events and objects ALH84001 · Close encounter · Murchison meteorite · Radio source SHGb02+14a · Shergotty meteorite · Wow! signalExtraterrestrial bodies Solar System: Europa · Mars · Titan · Enceladus · Extrasolar · Goldilocks planet · Gliese 581 g (unconfirmed) · Gliese 581 d · HD 85512 bCommunication Active SETI · Allen Telescope Array · Arecibo message · Arecibo Observatory · Bracewell probe · Communication with Extraterrestrial Intelligence · Interstellar communication · Lincos (language) · Pioneer plaque · Project Cyclops · Project Ozma · Project Phoenix · SERENDIP · SETI · SETI@home · setiQuest · Xenolinguistics · WaterholeRelated topics Astrobiology · Astroecology · Biosignature · Brookings Report · Catalog of Nearby Habitable Systems · Exopolitics · Exotheology · Extraterrestrials in fiction · Extraterrestrial liquid water · Habitable zone · Habitability of red dwarf systems · Hypothetical types of biochemistry · Life on Mars · Noogenesis · Planetary habitability · Planetary protection · San Marino Scale · Shermer's Last Law · XenoarchaeologyHypotheses Ancient astronauts · Aurelia and Blue Moon · Back-contamination · Cosmic pluralism · Drake equation · Fermi paradox · Great Filter · Kardashev scale · Mediocrity principle · Neocatastrophism · Panspermia · Planetarium hypothesis · Rare Earth hypothesis · Sentience quotient · Zoo hypothesisMissions Exhibitions Planetary habitability Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.