- Ballistic trauma
-
Ballistic trauma Classification and external resources 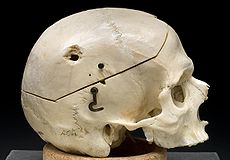
Male skull showing bullet exit wound on parietal bone, 1950s.ICD-10 T14.1, W34, X95 ICD-9 E922.9 DiseasesDB 5480 MeSH D014948 The term ballistic trauma refers to a form of physical trauma sustained from the discharge of arms or munitions.[1] The most common forms of ballistic trauma stem from firearms used in armed conflicts, civilian sporting and recreational pursuits, and criminal activity.[2]
Contents
Destructive effects
The degree of tissue disruption caused by a projectile is related to the size of the temporary versus permanent cavity it creates as it passes through tissue.[3] The extent of cavitation, in turn, is related to the following characteristics of the projectile:
- Kinetic energy: KE = mv2/2 (where m is mass and v is velocity). This helps to explain why wounds produced by missiles of higher mass and/or higher velocity produce greater tissue disruption than missiles of lower mass and velocity.
- Yaw
- Deformation
- Fragmentation
The immediate damaging effects of the bullet are typically bleeding, and with it the potential for hypovolemic shock, an inadequate amount of blood in the circulatory system. More immediate effects can result when a bullet strikes a critical organ such as the heart or damages a component of the central nervous system such as the spine or brain. Common causes of death following gunshot injury include exsanguination, hypoxia caused by pneumothorax, heart failure and brain damage. Non-fatal gunshot wounds can result in serious disability.
Gunshot injuries can vary widely from case to case since the location of the injury can be in any part of the body, with wide variations in entry point. Also, the path and possible fragmentation of the bullet within the body is unpredictable. The study of the dynamics of bullets in gunshot injuries is called terminal ballistics.
Non-fatal gunshot wounds frequently have severe and long-lasting effects, even after the victim has made a successful recovery.[4] Typically, the consequences involve some form of major disfigurement and/or permanent disability. As a rule, all gunshot wounds are considered medical emergencies that require immediate hospital treatment.
See also
- Battlefield medicine
- Emergency medicine
- Hydrostatic shock
- Multiple gunshot suicide
- Penetrating trauma
- Stopping power
- Vincent Di Maio
References
- ^ Mahoney, P. F., et al. (2004). Section 1 : Introduction, Background and Science p4
- ^ Mahoney, P. F., et al. (2004). The International Small Arms Situation p6
- ^ Wound Ballistic Research of the Past Twenty Years: A Giant Step Backwards
- ^ Negligent discharge page
Bibliography
- Mahoney, P. F. , Ryan, J., Brooks, A. J., Schwab, C. W. (2004) Ballistic Trauma – A practical guide 2nd ed. Springer:Leonard Cheshire
- Krug E. E., ed. World Report on Violence and Health. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2002.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Small arms and global health. Paper prepared for SALW talks. Geneva: July 2001.
External links
General wounds and injuries (T08-T35, 870-949) General Wound/
traumaBlister (Blood blister • Coma blister • Delayed blister • Edema blister • Fracture blister • Friction blister • Sucking blister)
Bruise/Hematoma/Ecchymosis (Battle's sign, Raccoon eyes, Black eye, Subungual hematoma, Cullen's sign, Grey Turner's sign, Retroperitoneal hemorrhage)
Animal bite: Insect bite · Spider biteAnimal bite: Snakebite · Lizard bite
Ballistic traumaForeign body In alimentary tract (Bezoar)Other By region Drug reactions (Y40-Y59, E930-E949) Adverse drug reaction/
drug eruptionantibiotics: Penicillin drug reaction · Sulfonamide hypersensitivity syndrome · Urticarial erythema multiforme · Adverse effects of fluoroquinolones
hormones: Steroid acne · Steroid folliculitis
chemotherapy: Chemotherapy-induced acral erythema · Chemotherapy-induced hyperpigmentation · Scleroderma-like reaction to taxanes · Hydroxyurea dermopathy · Exudative hyponychial dermatitis
blood: Anticoagulant-induced skin necrosis · Warfarin necrosis · Vitamin K reaction · Texier's disease
anticonvulsant: Anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome
water-balance/acid-base: Allopurinol hypersensitivity syndrome
pulmonary: Leukotriene receptor antagonist-associated Churg–Strauss syndrome
other specified agents: Adverse reaction to biologic agents · Adverse reaction to cytokines · Bromoderma · Halogenoderma · Iododerma · Red man syndrome · Methotrexate-induced papular eruption
unspecified agent: Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis · Bullous drug reaction · Drug-induced acne · Drug-induced angioedema · Drug-related gingival hyperplasia · Drug-induced lichenoid reaction · Drug-induced lupus erythematosus · Drug-induced nail changes · Drug-induced pigmentation · Drug-induced pseudolymphoma · Drug-induced urticaria · Fixed drug reaction · Stevens–Johnson syndrome · Injection site reaction · Linear IgA bullous dermatosis · Toxic epidermal necrolysis · HIV disease-related drug reaction · Photosensitive drug reaction · Serum sickness-like reactionCategories:- Medical emergencies
- Causes of death
- Injuries
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
