- Chemical burn
-
Chemical burn Classification and external resources 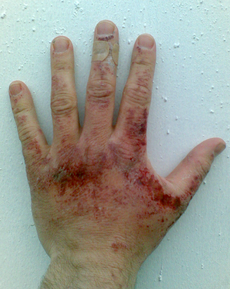
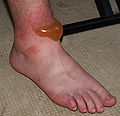
Chemical burn caused by exposure to a sodium hydroxide solution.ICD-10 T26-T28 ICD-9 949 eMedicine derm/777 MeSH D002057 A chemical burn occurs when living tissue is exposed to a corrosive substance such as a strong acid or base. Chemical burns follow standard burn classification and may cause extensive tissue damage. The main types of irritant and/or corrosive products are: acids, bases, oxidizers, solvents, reducing agents and alkylants. Additionally, chemical burns can be caused by some types of chemical weapons e.g. vesicants such as mustard gas and Lewisite, or urticants such as phosgene oxime.
Chemical burns may:
- need no source of heat,
- occur immediately on contact,
- be extremely painful, or
- not be immediately evident or noticeable
- diffuse into tissue and damage structures under skin without immediately apparent damage to skin surface
Presentation
The exact symptoms of a chemical burn depend on the chemical involved. Symptoms include itching, bleaching or darkening of skin, burning sensations, trouble breathing, coughing blood and/or tissue necrosis. Common sources of chemical burns include sulfuric acid (H2SO4), hydrochloric acid (HCl), lye (NaOH), lime (CaO), and silver nitrate (AgNO3). Chemical burns may occur through direct contact on body surfaces including skin and eyes, inhalation, and ingestion. Lipophilic substances that diffuse efficiently in human tissue, e.g. hydrofluoric acid, sulfur mustard and dimethyl sulfate, may not react immediately, but produce the burns and inflammation hours after the contact. Chemical fabrication, mining, medicine, and related professional fields are examples of occupations where chemical burns may occur.
-
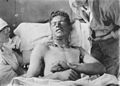
Chemical burns to the arm, caused by a blister agent e.g. mustard gas.
See also
External links
Foreign body In alimentary tract (Bezoar)Other By region Categories:- Cutaneous condition stubs
- Medical emergencies
- Injuries
- Occupational diseases
- Skin conditions resulting from physical factors
- Contact dermatitis
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.