- Cimmerian Plate
-
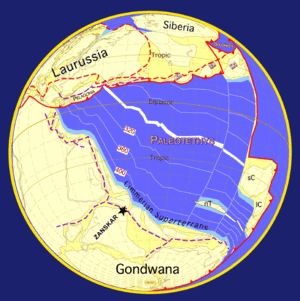
The Cimmerian Plate is an ancient tectonic plate that comprises parts of present-day Anatolia, Iran, Afghanistan, Tibet, Indochina and Malaya regions. The Cimmerian Plate was formerly part of the ancient supercontinent of Pangaea. Pangaea was shaped like a vast "C", facing east, and inside of the "C" was the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. Two microcontinents, which are part of present-day China, lay in the eastern expanse of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. About 300 Mya (million years ago), a rift started opening from the east which split a long, thin arc off of the inside of the southern arm of the continent, which comprised present day Australia, Antarctica, India, and Africa-Arabia. This micro-continent has been named Cimmeria. Behind this new micro-continent the rift formed a new ocean, the Tethys Ocean. As the Tethys Ocean widened, it pushed Cimmeria and the floor of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean northward towards Laurasia, the northeastern arm of Pangaea.
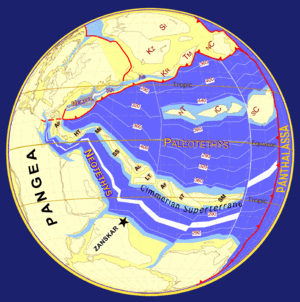
As it moved north, the floor of the Paleo-Tethys subducted under Laurasia and Cimmeria eventually collided with Laurasia, first at its western end c. 220 Ma, and Paleo-Tethys began to disappear altogether, closing from west to east. The collision of the continents raised mountains along the suture, called the Cimmerian orogeny. On its eastern end, Cimmeria collided with the Chinese micro-continents c. 200 Ma, and the Cimmerian orogeny was extended along the entire northern boundary of the plate. Most of Paleo-Tethys disappeared by c.150 Ma. More mountains were raised as the northern edge of the China plates collided with eastern Laurasia. After it collided with Laurasia around 200 Ma (Early Jurassic), the Tethyan Trench formed on southern Cimmeria, subducting the Tethys Ocean which created island arcs and new mountain ranges in the area.The Tethys rift eventually extended westward to split Pangaea in two, and the growing Atlantic Ocean separated the northern supercontinent of Laurasia from the southern supercontinent Gondwana. Around 150 Ma Gondwana also began to rift apart c. 150 Ma, and the continents of India and Africa-Arabia began to drift north towards Laurasia, of which Cimmeria now formed the southern coast. Africa-Arabia and India eventually collided with Asia c. 30 Ma, reuniting Cimmeria with its former Gondwanian neighbors and buckling and folding the former Cimmerian continent to form the Alps, Caucasus, Zagros Mountains, Hindu Kush, the Pamir Mountains, the Sulaiman Mountains, the Iranian plateau, the Himalayas, the Tibetan Plateau, and the Burmese highlands. This is called the Alpine orogeny).
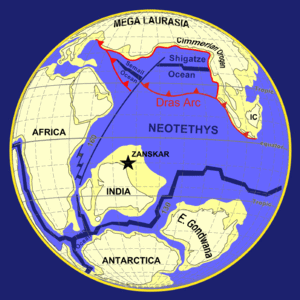 The Cimmerian Plate has collided with Laurasia about 200 - 190 million years ago. Its collision formed mountains, and the Tethyan Trench.
The Cimmerian Plate has collided with Laurasia about 200 - 190 million years ago. Its collision formed mountains, and the Tethyan Trench.
~100 mya (Middle Cretaceous)See also
External links
- Website of the PALEOMAP Project
- Late Permian paleoglobe showing the expanding Tethys Ocean, the closure of Paleo-Tethys, and the movement of the Cimmerian Plate
- Early Jurassic paleoglobe showing the a narrow seaway of Paleo-Tethys Ocean, and beginnings of the Cimmerian Orogeny
Categories:- Tectonic plates
- Historical tectonic plates
- Historical geology
- Permian
- Mesozoic
- Natural history of Asia
- Website of the PALEOMAP Project
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.