- Cannabis sativa
-
Not to be confused with Cannabis indica.
Cannabis sativa Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae (unranked): Angiosperms (unranked): Eudicots (unranked): Rosids Order: Rosales Family: Cannabaceae Genus: Cannabis Species: C. sativa Binomial name Cannabis sativa
LinnaeusSubspecies C. sativa subsp. sativa
C. sativa subsp. indicaCannabis sativa is an annual herbaceous plant in the Cannabaceae family. Humans have cultivated this herb throughout recorded history as a source of industrial fibre, seed oil, food, recreation, spiritual enlightenment and medicine. Each part of the plant is harvested differently, depending on the purpose of its use.
Contents
Common uses
Its seed, chiefly used as caged-bird feed, is a valuable source of protein. The flowers (and to a lesser extent the leaves, stems, and seeds) contain psychoactive and physiologically active chemical compounds known as cannabinoids that are consumed for recreational, medicinal, and spiritual purposes. When so used, preparations of flowers (marijuana) and leaves and preparations derived from resinous extract (hashish) are consumed by smoking, vaporizing and oral ingestion. Historically, tinctures, teas, and ointments have also been common preparations.
Plant physiology
The flowers of the female plant are arranged in racemes and can produce hundreds of seeds. Male plants shed their pollen and die several weeks prior to seed ripening on the female plants. Although genetic factors dispose a plant to become male or female, environmental factors including the diurnal light cycle can alter sexual expression.[citation needed] Naturally occurring monoecious plants, with both male and female parts, are either sterile or fertile but artificially induced "hermaphrodites" (a commonly used misnomer) can have fully functional reproductive organs. "Feminized" seed sold by many commercial seed suppliers are derived from artificially "hermaphrodytic" females that lack the male gene, or by treating the seeds with hormones or silver thiosulfate.
A Cannabis plant in the vegetative growth phase of its life requires more than 12–13 hours of light per day to stay vegetative. Flowering usually occurs when darkness equals at least 12 hours per day. The flowering cycle can last anywhere between nine to fifteen weeks, depending on the strain and environmental conditions.
In soil, the optimum pH for the plant is 6.3 to 6.8. In hydroponic growing, the nutrient solution is best at 5.2 to 5.8, making Cannabis well-suited to hydroponics because this pH range is hostile to most bacteria and fungi.
- Cultivars primarily cultivated for their fiber, characterized by long stems and little branching.
- Cultivars grown for seed from which hemp oil is extracted.
- Cultivars grown for medicinal or recreational purposes. A nominal if not legal distinction is often made between industrial hemp, with concentrations of psychoactive compounds far too low to be useful for that purpose, and it is also known as marijuana.
Pharmacology
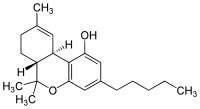
Although the main psychoactive chemical compound in Cannabis is Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the plant is known to contain about sixty cannabinoids; however, most of these "minor" cannabinoids are only produced in trace amounts. Besides THC, another cannabinoid produced in high concentrations by some plants is cannabidiol (CBD), which is not psychoactive but has recently been shown to block the effect of THC in the nervous system.[1] Differences in the chemical composition of Cannabis varieties may produce different effects in humans. Synthetic THC, called dronabinol, does not contain CBD, CBN, or other cannabinoids, which is one reason why its pharmacological effects may differ significantly from those of natural Cannabis preparations.
Chemical constituents
Cannabis chemical constituents including about 100 compounds responsible for its characteristic aroma. These are mainly volatile terpenes and sesquiterpenes.
- Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol
- α-Pinene[2]
- Myrcene[2]
- Trans-β-ocimene[2]
- α-Terpinolene[2]
- Trans-caryophyllene[2]
- α-Humulene,[2] contributes to the characteristic aroma of Cannabis sativa
- Caryophyllene-oxide,[2] with which some hashish detection dogs are trained[3]
See also
- Cannabis (drug)
- Cannabis indica
- Cannabis ruderalis
- Cannabis flower essential oil
- Hemp
- Medical cannabis
- Religious and spiritual use of cannabis
References
- ^ West, D. P, Ph.D. 1998. Hemp and Marijuana: Myths & Realities. North American Industrial Hemp Council. Retrieved on 23 April 2007
- ^ a b c d e f g Novak J, Zitterl-Eglseer K, Deans SG, Franz CM (2001). "Essential oils of different cultivars of Cannabis sativa L. and their antimicrobial activity". Flavour and Fragrance Journal 16 (4): 259–262. doi:10.1002/ffj.993.
- ^ Essential Oils
Cannabis General Preparations Usage Effects Short-term · Long-term (dependence · withdrawal · respiratory disease) · Cannabidiol · Cannabinoids · Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) · Endocannabinoid systemNotable strains Acapulco Gold · BC Bud · Holland's Hope · G-13 · Kush · Netherlands Weed · Northern Lights · Panama Red · Quebec Gold · Skunk · White WidowOrganizations Culture Cannabis portal Ancient anaesthesia Plants/animals Aconite • Castoreum • Cannabis • Coca • Deadly nightshade • Henbane • Lactucarium • Mandrake • Metel nut • Opium • Poison hemlock • Saussurea • Toloatzin • WillowPeople Abulcasis • Avenzoar • Avicenna • Celsus • Dioscorides • Galen • Hippocrates • Rhazes • Sabuncuoğlu • Sushrutha • Theophrastus • ZhangCompounds Aconitine • Δ9-THC • Atropine • Cocaine • Coniine • Hyoscyamine • Morphine • Salicylate • ScopolamineMedicinal herbs and fungi Herbs Regional practices Related subjects
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.