- Ocimene
-
Ocimene 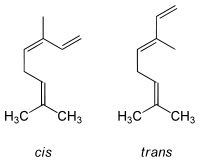 α: 3,7-dimethyl-1,3,7-octatriene
α: 3,7-dimethyl-1,3,7-octatriene
β: 3,7-dimethyl-1,3,6-octatrieneIdentifiers CAS number 502-99-8, (α)
cis-β: [3338-55-4]
trans-β: [3779-61-1]PubChem 5320249 ChemSpider 4478389 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C=C\C(=C\CCC(=C)C)C
Properties Molecular formula C10H16[1] Molar mass 136.24 g/mol Density 0.800 g/cm3 Melting point 50 °C
Boiling point mix of isomers: 100 °C at 70 mmHg
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Ocimene refers to several isomeric hydrocarbons. The ocimenes are monoterpenes found within a variety of plants and fruits. α-Ocimene and the two β-ocimenes differ in the position of the isolated double bond: it is terminal in the alpha isomer. α-Ocimene is 3,7-dimethyl-1,3,7-octatriene. β-Ocimene is 3,7-dimethyl-1,3,6-octatriene. β-Ocimene exist in two stereoisomeric forms, cis and trans, with respect to the central double bond. The ocimenes are often found naturally as mixtures of the various forms. The mixture (as well as the pure compounds) is an oil with a pleasant odor. It is used in perfumery. Like the related acyclic terpene myrcene, ocimenes are unstable in air.[2] Like other terpenes, the ocimens are nearly insoluble in water, but soluble in common organic solvents.
References
- ^ "CID 5281553 -- PubChem Compound Summary". http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=5281553. Retrieved 2008-02-17.
- ^ Karl-Georg Fahlbusch, Franz-Josef Hammerschmidt, Johannes Panten, Wilhelm Pickenhagen, Dietmar Schatkowski, Kurt Bauer, Dorothea Garbe, Horst Surburg “Flavors and Fragrances” in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. {{DOI: 10.1002/14356007.a11_141}}

This article about a hydrocarbon is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
