- Thyroglossal duct
-
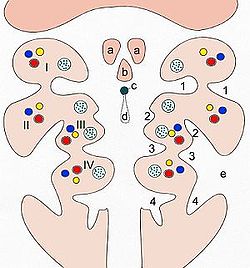
Thyroglossal duct Duct not labeled, but arises nearest to region identified as 'pyramidal lobe') Pattern of the branchial arches. I-IV branchial arches, 1-4 branchial pouches (inside) and/or pharyngeal grooves (outside)
a Tuberculum laterale
b Tuberculum impar
c Foramen cecum
d Ductus thyreoglossus
e Sinus cervicalisLatin ductus thyroglossalis Carnegie stage 14 Code TE E5.4.2.0.0.1.22 The thyroglossal duct is an embryological anatomical structure forming an open connection between the initial area of development of the thyroid gland and its final position.
The thyroid gland starts developing in the oropharynx in the fetus and descends to its final position taking a path through the tongue, hyoid bone and neck muscles. The connection between its original position and its final position is the thyroglossal duct. This duct normally atrophies and closes off before birth but can remain open in some people.
Clinical significance
A thyroglossal duct that fails to atrophy is called a persistent thyroglossal duct, a condition that may lead to the formation of a thyroglossal duct cyst.
External links
- thyroglossal+duct at eMedicine Dictionary
Pituitary Stomodeal ectodermThyroid Prenatal development/Mammalian development of digestive system, coelom and septa, and mesenchymal mesenteric masses (GA 11.1101, TE E5.4, 5.8-9) Gut Foregut: upper GI (Buccopharyngeal membrane, Rathke's pouch, Tracheoesophageal septum) · accessory (Pancreatic bud, Hepatic diverticulum)Abdominopelvic OtherCategories:- Head and neck
- Embryology
- Developmental biology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.