- Dry Tortugas
-
Dry Tortugas 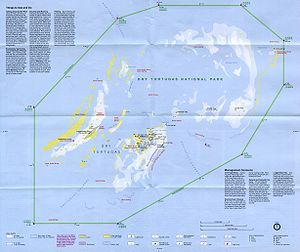
National Park Service map of the Dry TortugasGeography Location Gulf of Mexico Coordinates 24°38′00″N 82°55′12″W / 24.6333333°N 82.92°WCoordinates: 24°38′00″N 82°55′12″W / 24.6333333°N 82.92°W Archipelago Florida Keys Total islands 7 Major islands Garden Key Area 0.224 sq mi (0.58 km2) Country United StatesState Florida County Monroe County, Florida Census County Division Lower Keys Demographics Population 0 Additional information Eastern Standard Time[1] The Dry Tortugas are a small group of islands, located at the end of the Florida Keys, USA, about 70 miles (113 km) west of Key West, and 37 miles (60 km) west of the Marquesas Keys, the closest islands. Still further west is the Tortugas Bank, which is completely submerged. The first Europeans to discover the islands were the Spanish in 1513 by explorer Juan Ponce de León. They are an unincorporated area of Monroe County, Florida and belong to the Lower Keys Census County Division. With their surrounding waters, they constitute the Dry Tortugas National Park.
Contents
Geography
The keys are low and irregular. Some keys have thin growths of mangroves and various other vegetation, while others have only small patches of grass or are devoid of plant life. In general, they rise abruptly from relatively deep water. They are continually changing in size and shape. The Tortugas Atoll has had up to 11 islets during the past two centuries. Some of the smaller islands have disappeared and reappeared multiple times as a result of hurricane impact.
Islands (keys)
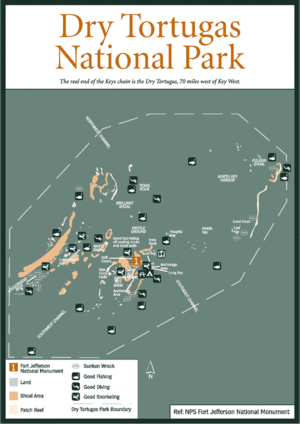
The total area of the islets, some of which are little more than sand bars just above the water mark, is about 580,000 square meters (143 acres). Their area changes over time as wind and waves reshape them. There are seven islets, which are from West to East:
- Loggerhead Key, with Dry Tortugas lighthouse (46 meters high), 250 by 1200 meters in size, with an area of 260,000 m2 the largest, 1 meter high. This island has the highest elevation in the Dry Tortugas, at 10 feet (3.0 m).[2]
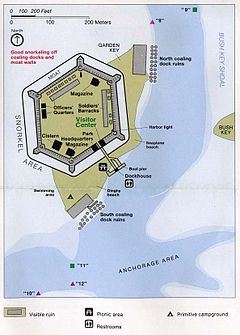
- Garden Key, with Fort Jefferson and the inactive Garden Key lighthouse (20 meters high), 4 km east of Loggerhead Key. Garden Key is the second largest island in the chain, at 400 by 500 meters in size, with an area of 170,000 m2. The original size, before construction of Fort Jefferson, has been estimated at 30,350 m2 to 35,610 m2.
- Bush Key, formerly named Hog Island because of the hogs that were raised there to provide fresh meat for the prisoners at Fort Jefferson, just a few meters east of Garden Key. At times, Bush Key is connected to Garden Key by a sand bar. The island is the third largest, 150 by 900 meters in size, area 120,000 m2, less than 1 meter high. Bush Key is the site of a large tern rookery. It is closed to visitors from April to September to protect nesting Sooty Terns and Brown Noddys.
- Long Key, 50 meters south of the eastern end of Bush key, 50 by 200 meters in size, area 8,000 m2
- Hospital Key, so called because a hospital for the inmates of Fort Jefferson had been built there in the 1870s. The island was formerly called Middle Key or Sand Key. It lies 2.5 km northeast of Garden Key and Bush Key, 70 meters in diameter, area 4,000 m2, and is 1 meter high at its highest point.
- Middle Key, 2.5 km east of Hospital key, 90 meters in diameter, area 6,000 m2, due to various seasonal changes, storm patterns and tidal cycles it is not always above sea level, disappearing for weeks or months only to reappear again.
- East Key, 2 km east of Middle Key, 100 by 200 meters in size, area 16,000 m2, over 2 meters high
The three westernmost keys, which are also the three largest keys (Loggerhead Key, Garden Key, and Bush Key), make up about 93 percent of the total land area of the group.
Former islands
Formerly existing keys were, from West to East:
- Southwest Key, disappeared by 1875, today a shoal south off Loggerhead Reef
- Bird Key (formerly Booby Key), was about 1.5 km southwest of Garden Key, disappeared in 1935, current names in the area are Bird Key Bank and Bird Key Harbor
- North Key, probably identical with former Booby Island, current name in the area is North Key Harbor, an anchorage WSW of Pulaski Shoal, disappeared by 1875
- Northeast Key (earlier called Sand Key), was between East Key and North Key, slightly to the North, disappeared by 1875
Shoals with lights
- Pulaski Shoal (Pulaski Reef), marking the northeast edge of the group at 24°41′36″N 82°46′24″W / 24.69333°N 82.77333°W, is not an island, but the former location of the Pulaski Shoal Light.
- Iowa Rock, halfway between Garden Key and Hospital Key, is another site of a navigational light (and weather station) built in shallow water. It was destroyed by Hurricane Hugo, with three bare stumps left[citation needed].
Environment
The islands get their name from their distinctive characteristics: Dry, because none of the islands has fresh water and Tortugas, because Ponce de León, a Spanish explorer, saw an abundance of sea turtles on the island. Later seafarers would keep the turtles on their backs in the holds of sailing ships and butcher them when they wanted fresh meat. They are not related to the Caribbean island of Tortuga, near Hispaniola.
The islands are home to Dry Tortugas National Park, and are only accessible by boat or seaplane. The large seabird colony, including Sooty Terns, Brown Noddy, Masked Booby and Magnificent Frigatebird, and the regular occurrence of Caribbean vagrant birds makes them a popular birding destination.
History
The first European to discover the islands was Spanish explorer Ponce de León. He gave them the name on his first visit in 1513. The name is the second oldest surviving European place-name in the U.S.[3] They were given the name Las Tortugas (The Turtles) due to 170 sea turtles taken on the islands and shoals by de León's men. Soon afterward, the word "Dry" was added to the name, to indicate to mariners the islands' lack of fresh water.
In 1742 HMS Tyger wrecked in the Dry Tortugas. The stranded crew lived on Garden Key for 56 days, and fought a battle with a Spanish sloop, before sailing to Jamaica in several boats.[4]
The United States government never completed Fort Jefferson after 30 years on Garden Key, and this bastion remained in Union hands throughout the Civil War. It later was used as a prison until abandoned in 1874. Dr. Samuel Mudd, famous for being the doctor who treated John Wilkes Booth in the wake of the Lincoln assassination, was imprisoned here until early 1869. During the 1880s, the Navy established a base at Tortuga; and it subsequently set up a coaling (refueling) and a wireless (radio) station there as well. During World War I, a seaplane base was established on the islet, but it was abandoned soon thereafter.
From 1903 until 1939 the Carnegie Institute of Washington operated the Marine Biology Laboratory on Loggerhead Key which "…quickly became the best-equipped marine biological station in the tropical world.” Through the years, over 150 researchers used the facilities to perform a wide range of research.[5]
An account of a visit to the fort at the Dry Tortugas by President Franklin D. Roosevelt and Justice-to-be Robert H. Jackson can be found in the book, That Man: An Insider's Portrait of Franklin D. Roosevelt, by Robert H. Jackson, edited and introduced by John Q. Barrett (Oxford University Press, New York, 2003).
In August 2004, the Dry Tortugas were directly struck by Hurricane Charley. The following day, a Cessna airplane crashed into the water near the islands, killing cinematographer Neal Fredericks while he was filming scenery for the feature film CrossBones.
Visiting the Dry Tortugas
Because it is located 70 miles (110 km) west of Key West, the Dry Tortugas Park is one of the least accessible National Parks in the U.S. Visiting the park by private boat is difficult because of its distance, so most visitors come by ferry, catamaran, or seaplane from Key West, Florida. Official ferry and transportation services to the Dry Tortugas includes the Yankee Freedom II, Sailboat Charter and the Key West Seaplane Adventures.
Graphics
See also
- Caribbean
- Dry Tortugas National Park
- Dry Tortugas Ferry to Fort Jefferson
- Florida Keys
- Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary
- Nature reserve
- Ponce de León
References
- ^ Fodor's South Florida - Google Books. http://books.google.com/books?id=tWJSHm_153oC&pg=PA334&lpg=PA334&dq=dry+tortugas+in+central+time+zone%3F#v=onepage&q=dry%20tortugas%20in%20central%20time%20zone%3F&f=false. Retrieved 2010-06-23.
- ^ "Loggerhead Key High Point". Peakbagger.com. http://www.peakbagger.com/peak.aspx?pid=7938.
- ^ Florida was named earlier, April 2, 1513, by Ponce de León -- From Spanish historian Antonio de Herrera y Tordesillas's account, published in 1601 -- Stewart, George (1945). Names on the Land: A Historical Account of Place-Naming in the United States. New York: Random House. p. 13. ISBN 1590172736.
- ^ The Dry Tortugas and Marquesas Keys - The British Castaways of HMS Tyger - Retrieved July 6, 2007
- ^ Carnegie Institution of Washington Administration Records, 1890-2001
- Dry Tortugas National Park Official National Park Service Site
External links
- Topographic and Floristic Change of the Dry Tortugas Keys, with description and areas of keys
- Dry Tortugas National Park by Park Vision A Photographic Guide to the Park.
- Dry Tortugas Satellite View Google Maps
- History and Ecology of Mangroves in the Dry Tortugas
- Fort Jefferson - Florida Ghost Town
Categories:- Parks in Monroe County, Florida
- Uninhabited islands of Monroe County, Florida
- Beaches of Florida
- Dry Tortugas National Park
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.