- Chow Chow
-
Chow chow 
A red Chow Chow puppy Other names Chow, Chowdren Country of origin China Traits Weight Male 55 to 70 pounds(25 to 32 kilograms) Female 45 to 60 pounds (20 to 27 kilograms) Height Male 19–22 in (48–56 cm) Female 18–20 in (46–51 cm) Coat Thick and coarse Color Red (light gold to deep red-brown)
Cinnamon (light tan to brown)
Blue (dark blue to gray)
Black
CreamLitter size 5 - 7 Life span 9–15 years Classification and standards AKC Non-sporting standard ANKC Group 7
Non-sportingstandard CKC Group 6
Non-sportingstandard KC (UK) Utility standard NZKC Non-sporting standard UKC Northern Breeds standard Dog (Canis lupus familiaris) Chow chow is a breed of dog that was developed in China,[1] where it is referred to as Songshi Quan (Pinyin: sōngshī quǎn 鬆獅犬), which literally means "puffy-lion dog".
Contents
Appearance
The chow is a sturdily built dog, square in profile, with a broad skull and small, triangular, erect ears, which are rounded at the tips. The breed has a very dense double coat that can be either smooth or rough. The fur is particularly thick around the neck, giving the distinctive ruff or mane appearance. The coat may be one of five colors including red, black, blue, cinnamon/fawn, and cream.
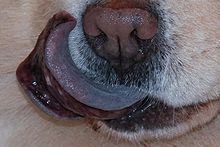
The eyes should be deep set and almond in shape. Chows are distinguished by their unusual blue-black/purple tongue and very straight hind legs, resulting in a rather stilted gait. The bluish color extends to the chow's lips; the chow is the only dog breed with this distinctive bluish color in its lips and oral cavity (other dogs have black or a piebald pattern skin in their mouths). One other distinctive feature is the curly tail. It has thick hair and lies curled on its back. The nose should be black (except the blue which can have a solid blue or slate colored nose). Any other tone is disqualification for showing in the United States under AKC breed standard.[2] However, FCI countries do allow for a self-colored nose in the cream.[3]
The blue-black/purple tongue gene appears to be dominant, as almost all mixed breed dogs that come from a chow retain the tongue color.[citation needed] This is not to say, however, that every mixed breed dog with spots of purple on the tongue is descended from chows, as purple spots on the tongue can be found on a multitude of pure breed dogs.[4]
Temperament
The Chow Chow is most commonly kept as a pet. Chows can be fiercely protective of their people and property and may not be an appropriate dog for a first-time dog owner. However AKC standards consider aggressive or timid Chows to be unacceptable.[5] The Chow Chow is considered to be suspicious of strangers and protective of family.[6] However, others characterize the Chow Chow as having a personality similar to that of a cat.[7][8]
Owning a Chow Chow can raise the cost of homeowners insurance as some companies regard them as "high risk dogs." [9] In a study done by Vet Med Today, from 1979 to 1998, out of a total of 238 fatalities related to dog bites, Chow Chows were responsible for 8.[10]
Chows are not a particularly active breed, meaning they can be kept in an apartment, if they are given enough opportunity for regularly scheduled physical activity each day.
Health
The Chow Chow can suffer from entropion,[11][12] glaucoma,[13][14] juvenile cataracts,[15] lymphoma,[16] hip dysplasia,[17] diabetes mellitus,[18] canine pemphigus,[19] and gastric cancer.[20] Chows are a high risk breed for Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)[21] and are at a predisposition for skin melanoma.[22]
Due to the Chow Chow's thick coat fleas can become a problem.[23]
History
Recent DNA analysis confirms that the Chow Chow is one of the oldest breeds of dog.[24] Research indicates it is one of the first primitive breeds to evolve from the wolf, and is thought to have originated in the arid steppes of northern China/Mongolia. A Chinese bas-relief from 150 BC shows a hunting dog and a dog very friendly toward children similar in appearance to the Chow. Later, Chow Chows were bred as general-purpose working dogs for hunting, herding, pulling and protection of the home. The black tongued chow was also bred for human consumption.[25] Some scholars claim the Chow was the original ancestor of the Samoyed, Norwegian Elkhound, Pomeranian and Keeshond.[26]
In the United States, the Chow Chow was a highly popular pet among the rich and famous during the Roaring Twenties. President Calvin Coolidge and his wife owned a black chow named Timmy.[27][28] Chow Chows were also popular in the 1930s and 1980s.
Famous Chow Chow Owners
President Calvin Coolidge and his wife owned a black chow named Timmy.[27][28] Sigmund Freud had a Chow Chow named Jo-Fi who attended all of his therapy sessions because he felt that dogs had a special sense that allows them to judge a person's character accurately, and admitted he depended on Jo-Fi for an assessment of a patient's mental state.[29] Martha Stewart had a chow named Genghis Khan that died in a kennel fire.[30][31] Peri Gilpin had a chow chow named Charlie. Janet Jackson had a chow chow named Buckwheat.[32][33] Drew Berrymore, Selena Gomez and Matthew McConaughey had chow-lab mixes. Manchester United winger Nani is also an owner of a Chow Chow named Panda.[34] Actor Madhavan owns a chow chow named "Simba".[35]
See also
References
- ^ Case, Linda P. (2005). The Dog: Its Behavior, Nutrition, and Health (2nd ed.), p. 23. Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 0-8138-1254-2.
- ^ "AKC Chow Chow Profile". http://www.akc.org/breeds/chow_chow/.
- ^ "FCI Breed Standard for the Chow Chow". http://www.chowchow.at/en/breed/the-FCI-chow-chow-breed-standard.shtml.
- ^ Chow Chow Welfare: The Truth About Those Black Tongues
- ^ "AKC Chow Chow Breed Profile". http://www.akc.org/breeds/chow_chow/.
- ^ "Chow Chow Profile Petfinder". http://www.petfinder.com/dog-breeds/Chow-Chow.
- ^ "Chow Chow Tips For Animal Shelters". http://www.chowwelfare.com/cciw/sheltereval.htm.
- ^ "Chow Chow Dog Breed Profile Information". http://dogtime.com/dog-breeds/chow-chow#personality.
- ^ "Will your canine affect your homeowners insurance?". http://www.insuranceagents.com/2009-06-canine.html.
- ^ "Vet Med Today: Special Report". Vet Med Today. http://www.cdc.gov/HomeandRecreationalSafety/images/dogbreeds-a.pdf.
- ^ "Chow Welfare - Entropion". http://www.chowwelfare.com/cciw/entropion.htm.
- ^ "Vet Info - Entropion". http://www.vetinfo.com/entropion-dogs-eyelids-folding-inward.html.
- ^ "Animal Eye Care". http://www.animaleyecare.net/diseases/glaucoma.htm.
- ^ "VetInfo - Breed Specific Problems". http://www.vetinfo.com/breed-specific-problems.html.
- ^ "VetInfo - Juvenile Cataracts in Dogs". http://www.vetinfo.com/juvenile-cataracts-in-dogs.html.
- ^ "Vet Info - Dog Lymphoma Symptoms". http://www.vetinfo.com/dog-lymphoma-symptoms.html.
- ^ "Canine Hip Dysplasia". http://www.recoverysa.com/hip_dysplasia_pro.htm#03.
- ^ "Diabetes Mellitus". http://www.akcchf.org/canine-health/your-dogs-health/disease-information/diabetes-mellitus.html.
- ^ "Vet Info - Pemphigus". http://www.vetinfo.com/canine-pemphigus-treatment-with-prednisone.html.
- ^ "Positional Cloning of the Gene(s) for Gastric Cancer in the Chow Chow". http://www.akcchf.org/research/funded-research/1093.html.
- ^ "Establishment of a Genetic Database for Disease Association Studies in the Major Histocompatibility complex for Purebred Dogs". http://www.akcchf.org/research/funded-research/0079.html.
- ^ "Canine Skin Melanoma". http://www.vetinfo.com/canine-skin-melanoma.html.
- ^ Atkinson, James (1988). Chow Chows. Haupaugge, NY: Barron's Educational Series, Inc.. pp. 76. ISBN 0-8120-3952-1. http://books.google.com/books?id=RH1AdVc42LsC&pg=PA54&lpg=PA54&dq=chow+chow+fleas#v=onepage&q=chow%20chow%20fleas&f=false.
- ^ Collie or Pug? Study Finds the Genetic Code. New York Times Online. May 21, 2004. Accessed December 25, 2006.
- ^ Schwabe, Calwin W.: Unmentionable Cuisine, page 168. University of Virginia Press, 1979
- ^ Chow Chow | American Kennel Club
- ^ a b Atkinson, James (1988). Chow chows, p. 5. Barron's Educational Series. ISBN 0-8120-3952-1.
- ^ a b Coolidge Pets
- ^ Coren, Stanley (1997). What Do Dogs Know?. Free Press. pp. 128.
- ^ "Beginners Guide to the Chow Chow". http://www.ticket-and-travel.com/blog/a-beginners-guide-to-the-chow-chow/.
- ^ "Martha Blog - A Terrible Event". http://www.themarthablog.com/2009/03/a-terrible-event.html.
- ^ "Beginners guide to the Chow Chow". http://www.ticket-and-travel.com/blog/a-beginners-guide-to-the-chow-chow/.
- ^ "Canine Aristocracy". http://www.dogname.org/10-canine-aristocracy.htm.
- ^ "Celebrity Owned Dogs". http://www.mybuddydog.com/celebdogs.htm.
- ^ "Madhavan on his best friend and his next big film". Behindwoods.com. http://www.behindwoods.com/tamil-movie-news-1/oct-11-03/maddy-18-10-11.html. Retrieved 27 October 2011.
External links
- The Chow Chow Club, Inc.
- The Netherlands Chow Chow Club
- The Royal Belgian Chow Chow Club
- Quality Dogs - Chow Chow Information
Categories:- Dog breeds originating in China
- Spitz breeds
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.