- Oblique cord
-
Oblique cord 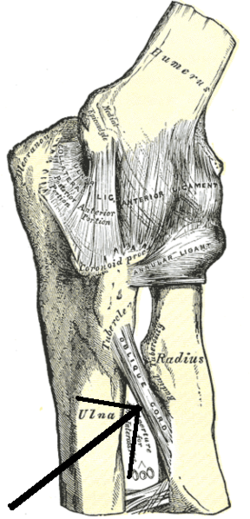
Left elbow-joint, showing anterior and ulnar collateral ligaments. (Oblique cord visible as diagonal white line near center bottom.) 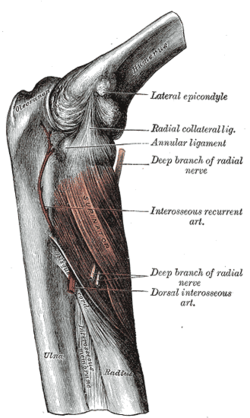
The Supinator. (Oblique cord visible at center.) Latin chorda obliqua membranae interosseae antebrachii Gray's subject #85 325 The oblique cord is a ligament between the two ulnar and radius bones in the lower arm near its elbow. It takes the form of a small, flattened band, extending downward and lateralward, from the lateral side of the ulnar tuberosity at the base of the coronoid process to the radius a little below the radial tuberosity.[1] Its fibers run in the opposite direction to those of the Interosseous membrane of the forearm.[1]
It is called by other names including oblique ligament, chorda obliqua, radio-ulnar ligament, chorda oblique antebrachii anterior, proximal interosseous band, dorsal oblique accessory cord, proximal band of the interosseous membrane, superior oblique ligament, oblique ligament proper, round ligament, and ligament of Weitbrecht.[2]
It has no known function and can be cut without apparent consequence.[2]
Contents
Dimensions
A study upon the arms of 38 people found that its mean length is 3.4 cm (range 2.4 to 4.2 cm) and in most people it tapers from the ulna to the radius end, being at the ulna 9 mm, in its middle, 7mm and its radius end 4 mm.[2]
Function
It has been suggested to strengthen the interosseus membrane proximally,[1] provide restraint for the rotatory movements of the forearm,[3] or that the ligament may stop bone bending and preventing buckling failure.[3] However, due the orientation of its fibers, the oblique cord is unlikely to transfer force due to limb loading from the radius to the ulna.[4]
One recent comparative study upon primates concluded:
The oblique cord does not limit supination, nor does it seem to have a role in preventing radial buckling failure or reducing bending strain. What, then, is the oblique cord for? The oblique cord may simply be an additional tie between the radius and ulna aiding other soft tissue structures such as the annular ligament and interosseous membrane. Additionally, the oblique cord may prevent anterior shearing of the proximal radius under extreme compressive loads.[4]
A study on humans concluded that it "appears insignificant in stability of the proximal forearm."[2] It has been suggested that its presence in modern humans may be a vestigial body part for a biped that was important due to the load-bearing function of the upper limb in evolutionarily earlier quadruped human ancestors.[4]
Variability
The shape and form of the ligament have been found in humans cadavers to vary from a rounded cord to a flat membrane.[3] Further, it is not found in all humans being variably found to be absent in half of arms,[2] and a third[3] or 15% of people.[5] It is found in most primates though not in the family of New World monkeys that includes spider and woolly monkeys called atelines.[4]
Notes
- ^ a b c Platzer, Werner (2004). Color Atlas of Human Anatomy, Vol. 1: Locomotor System. p 122 (5th ed.). Thieme. ISBN 3-13-533305-1.
- ^ a b c d e Tubbs RS, O'Neil JT Jr, Key CD, Zarzour JG, Fulghum SB, Kim EJ, Lyerly MJ, Shoja MM, George Salter E, Jerry Oakes W. (2007). The oblique cord of the forearm in man. Clin Anat. 20(4):411–5. PMID 16683244
- ^ a b c d Martin BF.(1958). The oblique cord of the forearm. J Anat. 92(4):609–15. PMID 13587394
- ^ a b c d Patel BA. (2005). Form and function of the oblique cord (chorda obliqua) in anthropoid primates.Primates. 46(1):47–57. PMID 15241636
- ^ Skahen JR 3rd, Palmer AK, Werner FW, Fortino MD. (1997). The interosseous membrane of the forearm: anatomy and function. J Hand Surg Am. 22(6):981–5.PMID 9471064
External links
Joints and ligaments of upper limbs (TA A03.5, GA 3.313) Shoulder Elbow Radial collateralUlnar collateralAnular · Oblique cordForearm Joints of hand Dorsal radiocarpal/Palmar radiocarpal · Dorsal ulnocarpal/Palmar ulnocarpal · Ulnar collateral/Radial collateralRadiate carpal · Dorsal intercarpal · Palmar intercarpal · Interosseous intercarpal · Scapholunate · Pisiform joint (Pisohamate, Pisometacarpal)OtherM: JNT
anat(h/c, u, t, l)/phys
noco(arth/defr/back/soft)/cong, sysi/epon, injr
proc, drug(M01C, M4)
Categories:- Ligaments of the upper limb
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
