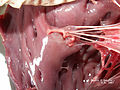
- Papillary muscle
-
Papillary muscle 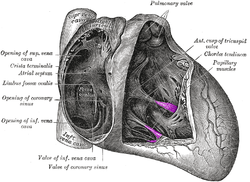
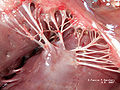
Interior of right side of heart. Papillary muscles labeled in purple. 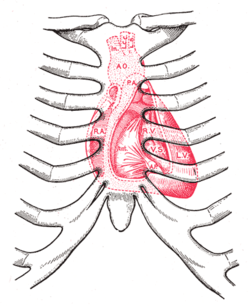
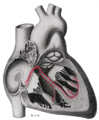
Diagram showing relations of opened heart to front of thoracic wall.
Ant. Anterior segment of tricuspid valve.
A O. Aorta.
A.P. Anterior papillary muscle.
In. Brachiocephalic artery (Innominate).
L.C.C. Left common carotid artery.
L.S. Left subclavian artery.
L.V. Left ventricle.
P.A. Pulmonary artery.
R.A. Right atrium.
R.V. Right ventricle.
V.S. Ventricular septum.Latin musculus papillaris Gray's subject #138 532 In anatomy, the papillary muscles are muscles located in the ventricles of the heart. They attach to the cusps of the atrioventricular valves (a.k.a. the mitral and tricuspid valves) via the chordae tendinae and contract to prevent inversion or prolapse of these valves.[1][2]
Contents
Action
There are five total papillary muscles in the heart, three in the right ventricle and two in the left. The anterior, posterior, and septal papillary muscles of the right ventricle each attach via chordae tendineae to the tricuspid valve. The anterior and posterior papillary muscles of the left ventricle attach via chordae tendineae to the mitral valve.[3]
The papillary muscles of both the right[1] and the left[2] ventricles begin to contract shortly before ventricular systole and maintain tension throughout. This prevents regurgitation--backward flow of ventricular blood into the atrial cavities--by bracing the atrioventricular valves against prolapse--being forced back into the atria by the high pressure in the ventricles.[1]
Rupture
Papillary muscle rupture, as can be caused by a heart infarct, and dysfunction, as can be caused by ischemia, can both lead to the complication of mitral valve prolapse.[4]
Additional images
See also
References
- ^ a b c Moore, K.L., & Agur, A.M. (2007). Essential Clinical Anatomy: Third Edition. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 92. ISBN 978-0-7817-6274-8
- ^ a b Moore, K.L., & Agur, A.M. (2007). Essential Clinical Anatomy: Third Edition. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 94. ISBN 978-0-7817-6274-8
- ^ Netter's Atlas of Human Anatomy, plates 216B and 217A
- ^ Page 40 in:Elizabeth D Agabegi; Agabegi, Steven S. (2008). Step-Up to Medicine (Step-Up Series). Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-7153-6.
External links
- papillary+muscle at eMedicine Dictionary
- SUNY Labs 20:19-0106 - "Heart: The Right Atrioventricular (Tricupsid) Valve" (anterior, posterior, septal papillary muscles)
- SUNY Labs 20:26-0105 - "Heart: The Left Atrioventricular (Mitral) Valve" (anterior, posterior papillary muscles)
- -1368719301 at GPnotebook
- Bioweb at UWLAX Human heart model (left internal anatomy)
- Atlas of anatomy at UMich ht_rt_vent - "Right atrioventricular bundle branch, anterior view"
- Definition of Papillary muscle
- MedicineNet Search Results
- Visit the educational website www.themitralvalve.org
Categories:- Muscle stubs
- Cardiac anatomy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.