- Sea kayak
-
A sea kayak or touring kayak is a kayak developed for the sport of paddling on open waters of lakes, bays, and the ocean. Sea kayaks are seaworthy small boats with a covered deck and the ability to incorporate a spraydeck. They trade off the maneuverability of whitewater kayaks for higher cruising speed, cargo capacity, ease of straight-line paddling, and comfort for long journeys.
Sea kayaks are used around the world for marine (sea) journeys from a few hours to many weeks, as they can accommodate one to three paddlers together with room for camping gear, food, water, and other supplies. A sea kayak usually ranges anywhere from 10–18 feet (3–5½ meters) for solo craft, and up to 26 feet (8 meters) for tandem craft. Width may be as little as 21" (50 cm), and may be up to 36" (90 cm).
Contents
Origins
Contemporary sea kayaks trace their origin to the native boats of Alaska, northern Canada, and Southwest Greenland. Eskimo hunters developed a fast sea going craft to hunt seals and walrus.[1] The ancient Aleut name for a sea kayak is Iqyak,[2] and earliest models were constructed from a light wooden frame (tied together with sinew or baleen) and covered with sea mammal (sea lion or seal) hides. Archaeologists have found evidence indicating that kayaks are at least 4000 years old.[3] Wooden kayaks and fabric kayaks on wooden frames (such as the Klepper) were dominating the market up until 1950s, when fiberglass boats were first introduced. Rotomolded plastic kayaks first appeared in 1984.
Design
Modern sea kayaks come in a wide array of materials, designs, and sizes to suit a variety of intended uses. In sea kayaking, where the designs continue along primarily traditional lines, the primary distinction is between rigid kayaks and folding kayaks. Folding kayaks are in some ways more traditional boats, being similar in design to skin-on-frame kayaks used by native people. Modern folding kayaks use contemporary materials such as aluminum for the frame, and replace the sealskin covering with synthetic waterproof fabrics. Unlike native kayaks, folding kayaks can be easily disassembled and packed for transport. Many folding kayaks include inflatable sponsons that improve the secondary stability of the vessel, helping to prevent capsize. More recently, a class of inflatable folding kayaks has emerged, combining a more limited rigid frame with a tightly inflated skin to produce greater rigidity than an inflatable boat alone.
Most rigid sea kayaks also derive from the external designs of native vessels, especially those from Greenland, but the strength of modern materials such as fiberglass, rotomolded plastic and carbon fiber eliminate the need for an internal frame, though significantly increasing weight. Modern skin-on-frame sea kayaks constructed with nylon skins represent an ultralight niche within the rigid sea kayak spectrum. Some recent design innovations include:
- Recreational kayaks—shorter sea kayaks with wide beams and large cockpits intended for sheltered waters
- Sit-on-top kayaks—rotomolded boats without an enclosed cockpit, but with the basic hull shape of a kayak.
A different class of vessel has also emerged, the Surf ski, a long, narrow boat with low inherent stability that is intended for use in surf and following waves.
Size
Most production sea kayaks are between 12 feet (3.7 m) and 24 feet (7.3 m) in length, the larger kayaks often built for two (or in rare cases, three) paddlers. The width (beam) of typical kayaks varies from 18 inches (460 mm) to 32 inches (810 mm), though specialized boats such as surf skis may be narrower. The length of a kayak affects not only its cargo capacity (for both gear and paddlers) but may also affect its "tracking" ability—the ease with which the boat travels in a straight line. While other design features also impact tracking, very long kayaks are easier to paddle straight (and harder to turn). The width of a kayak affects the cargo capacity, the maximum size of the cockpit (and thus the size of the paddler in that cockpit), and (to a degree that depends on the design of the hull) the stability.
Material
Most rigid production kayaks are now made out of fiberglass, rotomolded polyethylene, or carbon-kevlar. More exotic materials include carbon fiber and foam core. Some kayaks are hand-built from plywood or wood strips covered with fiberglass. Skin-on-frame kayaks are built on wood or aluminum frames covered in canvas, dacron, or other fabrics, and may include inflatable tubes called sponsons.
Okoume is the highest quality marine plywood available today and provides a high strength to weight ratio for kayak construction.[citation needed]
Bow, stern, and deck
There are many design approaches for the bow, stern, and deck of kayaks. Some kayaks have upturned bows, which are meant to provide better performance when paddling into waves, as well as better wave-shedding ability. Other kayaks achieve this through increased buoyancy in the bow. Kayaks with unobstructed stern decks may ease certain types of self-rescue. Waterproof bulkheads in modern kayaks provide flotation in the event of capsize.
Sea kayak decks typically include one or more hatches for easy access to the interior storage space inside. Kayak decks often include attachment points for deck lines of various kinds, which are aids in self-rescue and attachment points for above-deck equipment.
Equipment
Sea Kayaks have a wide range of hull designs, which greatly expands their range of performance. Designs can accommodate a wide range of physical fitness, or usage. Boats come in many lengths, whereby shorter boats are generally more maneuverable, and longer boats generally travel straighter and faster. Width of beam can affect a boat's stability, speed, and ability to bring to an edge. The amount of rocker (the curve from bow to stern) can greatly affect the ability of a boat to turn.
Many have steering gear or tracking aids in the form of rudders or skegs. In most cases rudders are attached at the stern and operated by wires from foot pedals in the cockpit. Rudders are typically retractable for beach landings. Skegs are straight blades that drop from a well in the stern of the boat. Both devices assist in paddling when a strong wind is coming from a direction other than directly in front.[4]
Paddles
Sea-kayak paddles, and the associated paddling styles, fall into three basic classifications:
- European
- two roughly spoon-shaped blades at either end of a cylindrical shaft. This paddle style was developed for fast acceleration and sudden maneuvering in Whitewater kayaking, and then back-ported to sea-kayaking. Euro paddles can be made of aluminum, plastic or even wood, but the best are usually formed of more expensive materials like carbon-fiber for lightness. Often the two blades are feathered, or set at an angle relative to each other (both for ergonomic efficiency, and so that as one blade moves backwards through the water, the opposite blade moving forward through the air presents its edge, rather than its face).
- Greenland
- Relatively narrow blades which are rounded and full near the loom and blade roots, and becoming oval near the blade tips. Some paddles feature a "shoulder", or abrupt transition between the loom and blade roots. Greenland paddle blades are most often not feathered. Short Greenland paddles (generally one arm-span in length), called storm paddles, are used with a sliding stroke, where the hands are shifted along the blades for each stroke. Storm paddles are often used as spares and in very windy locations, as there is very little outboard blade to catch the wind.
- Wing
- The blade of the paddle is shaped with a profile like a wing. When used with a special stroke, the blade actually produces lift as it moves through the water, enabling the kayaker to produce more forward motion than with any other kind of paddle. The paddling technique is different from both European style paddles and Greenland style. It is most often used in racing, but also sees some limited use in recreational paddling such as touring.
Dimensions
True Sea kayaks, not to be mistaken for wider, more stable recreational kayaks, come in many designs. The length of a solo sea kayak can range anywhere from 14 to 20 feet (3.7m-5.8m) long, and tandem kayaks can range from 18 to 24 feet (4.6m-6.1m) long. Sea kayaks can range in width from 20 inches (510 mm) to 24 inches (57 cm-76 cm). Wider touring kayaks of 23 inches (580 mm) to 24 inches (66–76 cm) are better for bigger paddlers, or small/average sized paddlers looking for more initial stability and maneuverability. Narrower beams of 20 inches (510 mm) to 23 inches (56 cm-63.5 cm) are good for small-medium sized paddlers who want more speed and less maneuverability. And lastly, kayak depth (or the height from the hull to the highest area of the deck) can range from 11 inches (280 mm) to 13 inches (33 cm-40 cm) high.


This design is typical of modern sea kayaks and has a low rear deck for easy rolling, a white water cockpit, compartments that allow the kayaker to reach into them while at sea, and a sloping rear bulkhead that enables the kayak to be emptied by lifting the bow.
Safety
A sea kayak's primary safety device is its paddler. Although some kayakers consider a well-practised self-righting move such as an Eskimo roll to be essential to safe open-water kayaking, it is the technique of bracing that every well-trained, experienced kayaker practises to maintain an upright position in their kayak. Practice in bracing is often neglected by inexperienced kayakers once they have learned the Eskimo roll. However, the reality is that having to roll really means having to recover from a failed brace. Being in the capsized position in some environments due to missing a brace can put the paddler in danger of colliding with obstacles under the water. Staying upright in surf zones, rock gardens, and rivers is most important and is only accomplished through well practised and successful bracing.
While there are a number of techniques for unassisted righting and re-entry of a kayak after a capsize, most paddlers consider it safest to paddle with one or more others, as assistance is useful if attempting to roll up solo fails. Even if the assistance fails to get you righted, it's a lot easier to climb back into a boat in the open sea if you've got another boat and paddler to help and your boat's been emptied of water first. Nonetheless, experienced paddlers do attempt open water crossings unaccompanied, and several major long-distance kayak expeditions have been carried out solo.
The use of a Paddle float self rescue device, generally consisting of foam, or inflatable bag, attached to the end of a paddle, allows a paddler to use the paddle as an outrigger, while climbing back into the cockpit. Be sure if you use an inflatable paddle float that you use a dual chambered model, but only train with one chamber inflated. A double chambered device will give you redundancy in case of a failure in one chamber. Training with one chamber inflated won't leave you handicapped if one chamber does fail. In many areas (Canada for instance) this is a coast guard required item. This fairly reliable rescue technique, if well practised, allows one to paddle with confidence when not equipped with a 'bombproof' roll.
There is a strong culture of self-sufficiency amongst sea kayakers and extensive safety equipment such as compass, towing lines, manual pumps, repair kits including wet application repair tape, flares, paddle leash, spare paddles, and survival gear are routinely carried; along with supplies of food and a flask of non-caffeinated beverage for non-emergency use. GPS, charts, lights, radios and cell phones, and radar reflectors are also sometimes carried.
Forms of sea kayaking
Kayak Sailing
Developed by kayak enthusiasts, kayak sails enhance the paddling experience. Kayak sails either augment the effort of paddling or effectively eliminate the need for paddling. They are great for touring, and have established a strong following with sensible, recreational sea kayakers, expedition paddlers and adventure racers.
Expedition Trips
Weekend trips with overnight camping are popular amongst recreational kayakers, and many people combine kayaking with watching wildlife. Modern sea kayaks are designed to carry large amounts of equipment, and unsupported expeditions of two weeks or more are conducted in environments from the tropics to the Arctic. Expedition kayaks are designed to handle best when loaded, so it may be necessary to ballast them on shorter trips.
Surf Kayaking
For more details on this topic, see Surf Kayaking.For more details on this topic, see Surf skis.Closely related to surf boards and requiring a mix of surfing and kayaking skills, a wide range of sea kayaks are specifically designed for the sport of wave surfing.
Sea Fishing
The sea kayak has long been a means of transportation and a means of accessing fishing grounds and kayak fishing has gained popularity due to the availability of purpose built stable designs. This technological development also solves some ergonomic problems that are associated with sitting for long hours without being able to change positions and special kayaks for fishing are accessorized for this sport, including specially-designed hatches, built-in rod holders, catch bags and equipment mounts.
Many of the techniques used in kayak fishing are the same as those used on other fishing boats. The difference is in the set-up, how each piece of equipment is fitted to the kayak, and how each activity is carried out on such a small craft. Contemporary kayaks can be equipped with fishing aids such as rod holders, electronic fish-finders and live-bait containers. Kayak anglers target highly-prized bottom feeders like halibut and cod and also pelagics like amberjacks, tuna, sailfish, wahoo, and even marlin.
Pioneering sea kayak expeditions
- Pre-1900
- There is controversial evidence to suggest early trans-atlantic kayak journeys from Labrador or Greenland to Scotland by Inuit paddlers. Indeed at the end of the 17th century there were at least three separate kayaks preserved in Scotland. One kayak, with associated equipment, is preserved in Aberdeen's Marischal Museum. It was found, with dying occupant, on a nearby shore. Some suggest the occupants were escaped Inuit from European ships, Inuit storm-driven from Greenland, or from a European source. Many suggest Inuit and their kayaks to be the origin of the Celtic Finnman, or Selkie, legends.[5]
- 1920s
- Franz Romer crossed the Atlantic Ocean solo in a kayak in 1928. His crossing from the Canary Islands and Puerto Rico took 58 days at sea but he was lost in a hurricane trying to get to New York[6][7]
- 1930s
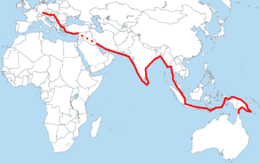
- Oskar Speck paddled from Germany to Australia in 1932-1939.
- 1950s
- Hannes Lindemann paddled, with the help of a sail, from the Canary Islands to the Caribbean in 1956. Documented in the book "Alone at sea".[8]
- 1970s
- Derek Hutchinson was the first to cross the North sea in 1976. After several near-death failures he finally managed it in 31 hours.[9]
- Nigel Foster and Geoff Hunter were the first to circumnavigate Iceland in 1977.
- Frank Goodman was the first to circumnavigate Cape Horn in 1977.
- Paul Caffyn was the first person to circumnavigate the South Island of New Zealand in 1977. He describes it in his book Obscured by Waves.
- 1980s
- Paul Caffyn and Nigel Dennis were the first sea kayakers to circumnavigate Britain in 1980, a distance of 2,200 miles (3,500 km) in 85 days
- Nigel Foster solo crossing of Hudson Strait from Baffin Island to Northern Labrador 1981
- Paul Caffyn was the first person to circumnavigate Australia in 1981/2 covering a distance of 9,420 miles (17,400 km)
- David Taylor and James Moore were the first to circumnavigate The Faroe Islands (mid way between Shetland and Iceland) in 1985.
- Ed Gillet paddled from California to Hawaii in 1987.
- Howard Rice first solo around Cape Horn in 1989.
- 1990s
- Adventurer Chris Duff has circumnavigated both Ireland in 1996 and New Zealand's South Island in 2000.
- The crossing of Europe by various rivers in 1998.[10]
- Trys Morris and Bob Timms have attempted to paddle from UK to Australia 1999 & 2000, abandoning the expedition in Athens, Greece due to lack of funds and visas for Arabian countries.
- 2000s
- Jon Turk and his team was the first to cross the Bering strait as they paddled from Japan to Alaska in 2000.[11]
- In his book Cold Oceans (1999), Jon Turk describes his attempt to solo circumnavigate Cape Horn.[12]
- Peter Bray crossed from Canada to Ireland in 2001.
- Trys Morris, Gemma Rawlings and Justine Curgenven successfully circumnavigated Tasmania in 2004. This journey is featured in This Is The Sea 2
- Harry Whelan, Barry Shaw and Phil Clegg are considered to have been the fastest around Britain in 2005, completing the circumnavigation in 80 days
- In November 2005 the first kayak circumnavigation of South Georgia in the Southern Atlantic was completed by The Adventure Philosophy team of Graham Charles, Marcus Waters and Mark Jones in 18 days, a distance of 600 km.[13]
- Eric Stiller and Tony Brown attempted circumnavigation of Australia. Described in the book Keep Australia on your left (2002).
- Solo Kayak Circumnavigation of Iceland - Rotem Ron in the year (2006) Circumnavigation of Iceland.[14]
- Andrew McAuley, an Australian solo kayaker, was lost at sea in February 2007 only 30 nautical miles (56 km) short of his destination of Milford Sound, New Zealand, during his attempt to cross from Australia to New Zealand.[1]
- Justin Jones and James Castrission made the first crossing from Australia to New Zealand, arriving on 13 January 2008, a journey that took 61 days. This is the longest two man kayak expedition ever undertaken.[15]
- In 2009 there are 2 separate expeditions attempting to circumnavigate the Falkland Islands. One British team[16] and Marcus Demuth, a solo American.[17]
- Freya Hoffmeister made the "Race Around Australia" and successfully circumnavigate Australia at 2009.
- 2010s
- Fastest solo circumnavigation of Great Britain in 80 days Marcus Demuth (2010)
- On the turn 2010/2011, polish kayaker Aleksander Doba crossed from Dakar (Africa - Senegal) to Fortaleza (South America - Brasil)[18]
- On August 30, 2011 Freya Hoffmeister began a circumnavigation of South America.
See also
- Kayak
- Recreational kayak
- Whitewater kayaking
- Surf Kayaking
- Folding kayak
References
- ^ Hutchinson, Derek. C. (1994). The Complete Book of Sea Kayaking. A&C Black. pp. 177–181. ISBN 0-7136-6675-7.
- ^ Traditional Arctic Kayak Symposium (TAKS) San Simeon California
- ^ Made in Anglesey, paddled in the Arctic: the Inuits' plastic kayak rules the waves TimesOnline December 2006
- ^ Hutchinson, Derek. C. (1994). The Complete Book of Sea Kayaking. A&C Black. pp. 3–4. ISBN 0-7136-6675-7.
- ^ MacRitchie, Scot, The Aberdeen Kayak and its Congeners, Royal Scottish Geographical Society Magazine, Feb 12, 1912, http://ads.ahds.ac.uk/catalogue/adsdata/PSAS_2002/pdf/vol_046/46_213_241.pdf
- ^ Mahaffey, Dexter (April 2003). "The 10 All-time Greatest Sea Kayaking Expeditions". Paddler Magazine. http://www.paddlermagazine.com/issues/2003_4/article_221.shtml
- ^ "Long Way Across The Atlantic", October 1931, Popular Mechanics
- ^ Lindermann, Hannes (1998). Alone at Sea A Doctor's Survival Experiments During Two Atlantic Crossings in a Dugout Canoe and a Folding Kayak. Germany: Pollner Verlag. ISBN 3-925660-27-5.
- ^ Paddler Magazine Online : The 10 All-time Greatest Sea Kayaking Expeditions
- ^ :: Dragoman Doğa Sporları Merkezi ::
- ^ In the wake of the Jomon
- ^ Cold Oceans
- ^ November 2, 2005: South Georgia Expedition Update | Outside Online
- ^ http://seakayak.co.il/eblog/?cat=1
- ^ Home :: Crossing the Ditch - Trans-Tasman Kayak Expedition :: James Castrission & Justin Jones
- ^ http://www.justgiving.com/kayakfalklands2009
- ^ http://seakayakinguk.com/newsblog/?tag=falklands
- ^ http://www.aleksanderdoba.pl
Categories:- Kayaks
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.