- Regions of Chile
-
Chile 
This article is part of the series:
Politics and government of
Chile- Law
- President
- National Congress
- Ministries
- Political parties
- Elections
- Administrative divisions
- Foreign relations
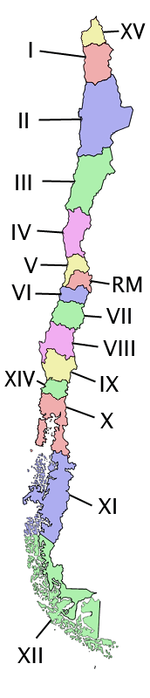
Chile is divided into 15 regions (in Spanish, regiones; singular región), which are the country's first-level administrative division. Each region is headed by an intendant (intendente), appointed by the President, and an indirectly-elected body known as regional board (consejo regional).
Regions are divided into provinces (second-level administrative division), each headed by a governor (gobernador), appointed by the President. There are 54 provinces, in total. Provinces are further divided into communes (third and lowest level administrative division), which are governed by municipalities.
Contents
Naming
Each region is given a Roman numeral, followed by a name (e.g. IV Región de Coquimbo, read as "fourth region of Coquimbo" in Spanish). When the regional structure was created, Roman numerals were assigned in ascending order from north to south, with the northernmost region designated as I (first) and the southernmost region as XII (twelfth). The Santiago Metropolitan Region, located in the center of the country and home to the country's capital Santiago, was excluded from this naming scheme and given instead the initials RM, standing for Región Metropolitana ("Metropolitan Region" in Spanish). With the creation of regions XIV in the south and XV in the north (XIII is not used) in 2007, the north-south Roman numeral order was broken.
History of the regional structure
The current administrative divisions of Chile were created in 1974 and limited to 13 regions (this limitation was eliminated in 2005 via a constitutional reform). Previously, Chile was divided into 25 provinces, which were further divided into departments, and then into communes. The new territorial organization was implemented in phases with some initial "pilot regions" beginning to operate in 1974, extending the process on January 1, 1976 to the rest of the country. The Santiago Metropolitan Region began to operate in April 1980.
In December 2006 two new regions were created: the northern Arica and Parinacota Region, by taking out the two northernmost provinces from the Tarapacá Region; and Los Ríos Region in the south, encompassing the province of Valdivia, formerly part of the Los Lagos Region.[1] Both regions became operative in October 2007.
List of regions
Main article: Ranked list of Chilean regionsKey Name (English/Spanish) Capital Area (km2) Population XV Arica and Parinacota
Región de Arica y ParinacotaArica 16,898.6 189,644 I Tarapacá
Región de TarapacáIquique 41,799.5 238,950 II Antofagasta
Región de AntofagastaAntofagasta 126,049.1 493,984 III Atacama
Región de AtacamaCopiapó 75,176.2 254,336 IV Coquimbo
Región de CoquimboLa Serena 40,579.9 603,210 V Valparaíso
Región de ValparaísoValparaíso 16,396.1 1,539,852 VI O'Higgins
Región del Libertador General Bernardo O'HigginsRancagua 16,387 780,627 VII Maule
Región del MauleTalca 30,296.1 908,097 VIII Biobío
Región del BiobíoConcepción 37,062.6 1,861,562 IX Araucanía
Región de la AraucaníaTemuco 31,842.3 869,535 XIV Los Ríos
Región de Los RíosValdivia 18,429.5 356,396 X Los Lagos
Región de Los LagosPuerto Montt 48,584.5 716,739 XI Aisén
Región Aisén del General Carlos Ibáñez del CampoCoihaique 108,494.4 91,492 XII Magallanes and Antártica Chilena
Región de Magallanes y de la Antártica ChilenaPunta Arenas 132,297.2 150,826 RM Santiago Metropolitan
Región Metropolitana de SantiagoSantiago 15,403.2 6,061,185 Note: Populations are from the 2002 Census.[2]
See also
- ISO 3166-2:CL
- Provinces of Chile
- Communes of Chile
- Patagonia
References
- ^ La Nación
- ^ "About Chile". Government of Chile Foreign Investment Committee. http://www.cinver.cl/english/chile/chile.asp. Retrieved 13 March 2010.
Regions of Chile Spanish terms for country subdivisions National · Federal Regional · Metropolitan Comarca · Comuna · Distrito · Municipalidad · Municipio · Merindad · Corregimiento · Delegación · Parroquia · AnteiglesiaUrban · Rural Aldea · Alquería · Asentamiento · Barrio · Colonia · Fraccionamiento / Comisaría · Pedanía · Pueblos jóvenes · Ranchería · Vereda · Pueblo · Villa · Ciudad (Ciudad Autónoma)Historical subdivisions in italics.First-level administrative divisions of South American countries Table of administrative country subdivisions by countryCategories:- Regions of Chile
- Subdivisions of Chile
- Lists of country subdivisions
- Country subdivisions of the Americas
- First-level administrative country subdivisions
- Chile-related lists
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
