- Constellation Observing System for Meteorology, Ionosphere, and Climate
-
COSMIC 
Operator COSMIC Major contractors Orbital Sciences Corporation Mission type Meteorology, Ionosphere, Climatology, and Space weather research. Satellite of Earth Launch date 15/04/06 at 01:40 GMT Launch vehicle Minotaur Mission duration 5 years COSPAR ID 2006-011A Homepage COSMIC at UCAR Mass 155 lb Orbital elements Eccentricity 0 Inclination 72 degrees Apoapsis 500km (original) 800km (final) Periapsis 500km (original) 700km (final) Constellation Observing System for Meteorology, Ionosphere, and Climate[citation needed] (COSMIC) is a program designed to provide advances in meteorology, ionospheric research, climatology, and space weather by using GPS satellites in conjunction with low Earth orbiting (LEO) satellites. The term "COSMIC" may refer to either the organization itself or the constellation of satellites (also known as FORMOSAT-3, 福爾摩沙衛星三號, in Taiwan). The constellation is a joint U.S.-Taiwanese project with major participants including the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR), the National Science Foundation, the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL), the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) on the U.S. side and the National Space Organization (NSPO) on the Taiwanese side.
The total cost of the project is US$100 million, 80% of which is being provided by NSPO, and the remainder by various U.S. agencies.[1]
After experiencing several delays, the launch of the COSMIC satellite constellation atop a Minotaur launch vehicle from Vandenberg AFB occurred at 01:40 GMT, on April 15, 2006, despite heavy fog.[2] The satellites, which orbit at an altitude of 500 miles, required over a year to move into the correct positions to provide full global coverage.
Contents
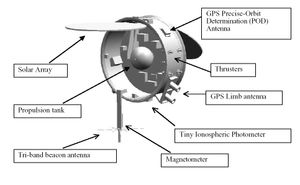
Instruments
The COSMIC satellites are be equipped with three primary forms of instrumentation for remote sensing, including:
- GPS Occultation Experiment
- Tri-band beacon (TBB)
- Tiny Ionospheric Photometer (TIP)
Sources: [3]
Deployment
All 6 microsatellites were launched on a single launch vehicle and deployed into a single parking orbit after launch. The spacecraft were then deployed into separate orbital planes through the use of precession due to the oblateness of the Earth and raised to a final orbital altitude over the course of several months. Scientific data were collected during the deployment process, along with experimental validation and calibration.
Status
Currently only four of the microsatellites remain fully functional. The FM2's power system lost 50% of its output in February 2007, while FM3's solar panel also malfunctioned since August 2007. As a result, both satellites are operating in a degraded state, capable of returning data only during specific solar angles. The FM6 went out of control on September 2007, but control was restored by November 16 of the same year.[4][5] FM3 had severe power problem since July 6 2010. It is declared no function since them. FM4, FM5, and FM6 has battery aging problem. So right now FM1 is the only FM remains fully functional.
Orbital information
Parking orbit
- Altitude: 500 km
- Inclination: 72 degrees
- Eccentricity: 0 degrees
Final orbital configuration
- Altitude: 700 – 800 km
- Inclination: 72 degrees
- Eccentricity: 0 degrees
- Spacing between right ascension of ascending node: 24 degrees
- Spacing in mean anomaly between adjacent orbital planes: 45 degrees
See also
- CHAMP
- Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE)
- List of spaceflights (2006)
Notes & references
- ^ "COSMIC: About". UCAR COSMIC. http://www.cosmic.ucar.edu/about.html. Retrieved 2006-04-18.
- ^ Ray, Justin (2006-04-14). "Launch Coverage for Minotaur Rocket' COSMIC Mission". Spaceflight Now. http://www.space.com/missionlaunches/sfn_minotaur_cosmic_cntdwn.html.
- ^ "New Satellite System Will Use GPS Signals To Track Hurricanes, Climate Change, and Space Weather" (Press release). UCAR. 2006-04-12. http://www.ucar.edu/news/releases/2006/cosmic.shtml.
- ^ COSMIC Current Status
- ^ [1] COSMIC Homepage
External links
- Official site
- COSMIC Mission Profile by NASA's Solar System Exploration
- University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR)
- UCAR Office of Programs (UOP)
- National SPace Organization (NSPO) - COSMIC's Taiwanese counterpart.
- ScienceNOW: The Little Satellite Fleet That Could,
- http://www.agu.org/pubs/crossref/2007/2006JA012240.shtml
Comparison of COSMIC ionospheric measurements with ground-based observations and model predictions: Preliminary results 12 December 2006
Meteorological remote sensing systems in Earth orbit Concepts Current projects A-train satellitesOther satellitesCBERS · COSMIC (FORMOSAT-3) · COSMO-SkyMed · DMSP · DMC · Elektro-L · Envisat · EROS · ERS · Fengyun · FORMOSAT-2 · GOES · IKONOS · Landsat · MetOp · Meteor · Meteosat · MTSAT · NOAA-N' · QuickBird · RADARSAT-1 · RADARSAT-2 · SMOS · SPOT · TerraSAR-X · THEOSFormer projects CompletedFailed← 2005 · Orbital launches in 2006 · 2007 → New Horizons | Daichi | EchoStar X | Himawari 7 | Akari · Cute-1.7+APD | Arabsat-4A | SpainSat-1 · Hot Bird 7A | ST-5 | FalconSAT-2 | Soyuz TMA-8 | JCSAT-5A | COSMIC | Astra 1KR | Progress M-56 | EROS-B | Yaogan 1 | Kosmos 2420 | GOES 13 | Satmex 6 · Thaicom 5 | Resurs-DK1 | KazSat-1 | Galaxy 16 | USA-187 · USA-188 · USA-189 | Progress M-57 | Kosmos 2421 | USA-184 | STS-121 (MPLM) | Kwangmyŏngsŏng-2 | INSAT-4C | Genesis I | Kosmos 2422 | BelKA · Baumanets · PicPot · SACRED · ION · Rincon 1 · ICECube-1 · KUTESat Pathfinder · SEEDS · nCube-1 · HAUSAT-1 · MEROPE · CP-2 · AeroCube-1 · CP-1 · Mea Huaka'i · ICECube-2 | Arirang-2 | Hot Bird 8 | JCSAT-10 · Syracuse 3B | Koreasat 5 | Shijian 8 | STS-115 (ITS P3/4) | IGS-3A | Chinasat-22A | Kosmos 2423 | Soyuz TMA-9 | Hinode · HIT-SAT · SSSAT | USA-190 | DirecTV-9S · Optus D1 · LDREX | MetOp-A | Progress M-58 | Shijian 6C · Shijian 6D | STEREO | Sinosat-2 | XM-4 | USA-191 | Badr-4 | USA-192 | Feng Yun 2D | WildBlue 1 · AMC-18 | STS-116 (ITS P5 · SpaceHab LSM · ANDE-MAA · ANDE-FACL · RAFT1 · MARScom · MEPSI-2) | MEASAT-3 | USA-193 | TacSat-2 · GeneSat | Kiku 8 | SAR-Lupe 1 | Meridian 1 | Kosmos 2424 · Kosmos 2425 · Kosmos 2426 | COROTPayloads are separated by bullets ( · ), launches by pipes ( | ). Manned flights are indicated in bold text. Uncatalogued launch failures are listed in italics. Payloads deployed from other spacecraft are denoted in brackets.Categories:- Earth observation satellites
- Taiwanese space program
- 2006 in spaceflight
- Spacecraft launched by Minotaur rockets
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.