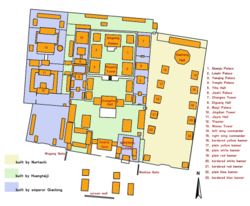
- Mukden Palace
-
Imperial Palaces of the Ming and Qing Dynasties in Beijing and Shenyang * UNESCO World Heritage Site
Country  China
ChinaType Cultural Criteria i, ii, iii, iv Reference 439 Region ** Asia-Pacific Inscription history Inscription 1987 (11th Session) Extensions 2004 * Name as inscribed on World Heritage List
** Region as classified by UNESCOThe Mukden Palace (simplified Chinese: 盛京宫殿; traditional Chinese: 盛京宮殿; pinyin: Shèngjīng Gōngdiàn) or Shenyang Gugong (simplified Chinese: 沈阳故宫; traditional Chinese: 瀋陽故宮; pinyin: Shěnyáng Gùgōng), also known as the Shenyang Imperial Palace, is the former imperial palace of the early Qing Dynasty of China.
It was built in 1625 and the first three Qing emperors lived there from 1625 to 1644. It is located in the center of the city of Mukden, Manchuria (Shenyang, China).
History
Early construction began in 1625 by Nurhaci. By 1631, additional structures were added under Emperor Huang Taiji.
The Mukden Palace was built to resemble the Forbidden City in Beijing. However, the palace also exhibits hints of Manchurian and Tibetan styles.
After the Qing Dynasty replaced the Ming Dynasty in 1644 in Beijing, the Mukden palace lost its status as the official residence of the Emperor. Instead, the Mukden Palace became a regional palace.
In 1780, Emperor Qianlong further expanded the palace. Successive Qing dynasty emperors usually stayed at Mukden Palace for some time each year.
Museum
In 1955, Mukden Palace was converted into the Shenyang Palace Museum.
In 2004, it was included on the UNESCO World Heritage List as an extension of the Imperial Palace of the Ming and Qing Dynasties site in Beijing.
References
Liaoning topics Shenyang (capital) General Geography Education Visitor attractions Mukden Palace • Early Qing Tombs • Wunu Mountain City • Anshan Jade Buddha • Bijia Mountain • DalianWorld Heritage Sites in China East Classical Gardens of Suzhou · Fujian Tulou · Lushan National Park · Mount Huang (Huangshan) · Mount Sanqing (Sanqingshan) · Mount Tai (Taishan) · Mount Wuyi (Wuyishan) · Temple and Cemetery of Confucius and Kong Family Mansion, Qufu · Ancient villages in Southern Anhui - Xidi and Hongcun · West Lake Cultural Landscape of Hangzhou
South Central Ancient Building Complex in the Wudang Mountains · Historic Centre of Macau · Kaiping Diaolou and Villages · Longmen Grottoes · Historic Monuments of Dengfeng, including the Shaolin Monastery and Gaocheng Observatory · Wulingyuan Scenic and Historic Interest Area · Yin Xu
Southwest Dazu Rock Carvings · Historic Ensemble of the Potala Palace, including the Jokhang and Norbulingka · Huanglong Scenic and Historic Interest Area · Jiuzhaigou Valley Scenic and Historic Interest Area · Old Town of Lijiang · Mount Emei Scenic Area, including Leshan Giant Buddha Scenic Area · Mount Qingcheng and the Dujiangyan Irrigation System · Sichuan Giant Panda Sanctuaries · Three Parallel Rivers of Yunnan Protected Areas
North Mount Wutai (Wutaishan) · Chengde Mountain Resort and its outlying temples including the Putuo Zongcheng Temple, Xumi Fushou Temple and the Puning Temple · Imperial Palaces of the Ming and Qing Dynasties in Beijing and Shenyang · Peking Man Site at Zhoukoudian · Ancient City of Pingyao · Summer Palace, an Imperial Garden in Beijing · Temple of Heaven: an Imperial Sacrificial Altar in Beijing · Yungang Grottoes
Northeast Capital Cities and Tombs of the Ancient Koguryo Kingdom · Imperial Palaces of the Ming and Qing Dynasties in Beijing and Shenyang
Northwest Multiple regions
Coordinates: 41°47′46″N 123°26′58″E / 41.79611°N 123.44944°ECategories:- Buildings and structures in Shenyang
- Palaces in China
- Qing Dynasty
- Manchu people
- World Heritage Sites in China
- Chinese architectural history
- Royal residences in China
- People's Republic of China building and structure stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.