- Outline of ecology
-
See also: Glossary of ecology
Ecology, or ecological science, is the scientific study of the distribution and abundance of living organisms and how the distribution and abundance are affected by interactions between the organisms and their environment. The environment of an organism includes both physical properties, which can be described as the sum of local abiotic factors such as solar insolation, climate and geology, as well as the other organisms that share its habitat.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to ecology:
Essence of ecology
- Main article: Ecology
-
- Food web –
Subdisciplines of ecology, and subdiscipline classification
Ecology is a broad discipline comprising many sub-disciplines. The field of ecology can be sub-divided according to several classification schemes:
By level of complexity or scope
Arranged from lowest to highest complexity:
- Ecophysiology/Behavioral ecology – examine adaptations of the individual to its environment.
- Population ecology – studies the dynamics of populations of a single species.
- Community ecology – (or synecology) focuses on the interactions between species within an ecological community.
- Ecosystem ecology – studies the flows of energy and matter through the biotic and abiotic components of ecosystems.
- Systems ecology – is an interdisciplinary field focusing on the study, development, and organization of ecological systems from a holistic perspective.
- Landscape ecology – examines processes and relationship across multiple ecosystems or very large geographic areas.
By organisms under study
- Animal ecology –
- Biogeography – the study of the geographic distributions of species ;
- Insect ecology –
- Microbial ecology – the ecology of micro-organisms;
- Paleoecology – which seeks to understand the relationships between species in fossil assemblages;
- Plant ecology –
By biome under study
- Benthic ecology – study of sea-floor organisms, and their interaction with each other and with the environment
- Desert ecology –
- Forest ecology –
- Grassland ecology –
- Marine ecology – and aquatic ecology, where the dominant environmental milieu is water;
- Urban ecology – the study of ecosystems in urban areas.
By geographic or climatic area under study
- Arctic ecology –
- Polar ecology –
- Tropical ecology –
By spatial scale under study
- Global ecology – which examines ecological phenomena at the largest possible scale, addressing macroecological questions;
- Landscape ecology – which studies the interactions between discrete elements of a landscape;
- Landscape limnology – the spatially-explicit study of aquatic ecosystems (e.g., rivers, lakes, and wetlands) as they interact with the aquatic, terrestrial, and human components of landscapes to determine the effects of pattern on ecosystem processes across spatial scales;
- Spatial ecology – which identifies spatial patterns and their relationships to ecological events;
- Macroecology – the study of large scale phenomena;
- Microecology – the study of small scale phenomena;
- Microbial ecology –
- Molecular ecology –
By ecological aspects or phenomena under investigation
- Chemical ecology – which deals with the ecological role of biological chemicals used in a wide range of areas including defense against predators and attraction of mates;
- Ecophysiology – which studies the interaction of physiological traits with the abiotic environment;
- Ecotoxicology – which looks at the ecological role of toxic chemicals (often pollutants, but also naturally occurring compounds);
- Evolutionary ecology – or ecoevolution which looks at evolutionary changes in the context of the populations and communities in which the organisms exist;
- Fire ecology – which looks at the role of fire in the environment of plants and animals and its effect on ecological communities;
- Functional ecology – the study of the roles, or functions, that certain species (or groups thereof) play in an ecosystem;
- Genetic ecology –
- Soil ecology – the ecology of the pedosphere;
By technique used for investigation
- Field ecology –
- Quantitative ecology –
- Theoretical ecology – the development of ecological theory, usually with mathematical, statistical and/or computer modeling tools;
By philosophical approach
- Ecosophy –
- Applied ecology – the practice of employing ecological principles and understanding to solve real world problems (includes agroecology and conservation biology);
- Conservation ecology – which studies how to reduce the risk of species extinction;
- Deep ecology –
- Restoration ecology – which attempts to understand the ecological basis needed to restore impaired or damaged ecosystems;
Ecology-involved interdisciplinary fields
- Agroecology – provides an interdisciplinary framework with which to study the activity of agriculture.
- Biogeochemistry – effect of biota on global chemistry, and the cycles of matter and energy that transport the Earth's chemical components in time and space.
- Ecological design –
- Ecological economics –
- Ecological engineering –
- Festive ecology –
- Human ecology – the interaction of human beings and their living and non-living environments and the effects of human decisions on those environments.
- Ecological anthropology –
- Social ecology –
- Ecological health –
- Environmental psychology –
- Industrial ecology –
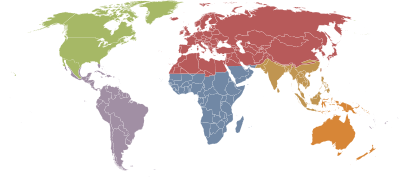
Biogeographic regions
Ecozone
Main article: EcozoneThe World Wildlife Fund (WWF) developed a system of eight biogeographic realms (ecozones):
- Nearctic 22.9 mil. km² (including most of North America)
- Palearctic 54.1 mil. km² (including the bulk of Eurasia and North Africa)
- Afrotropic 22.1 mil. km² (including Sub-Saharan Africa)
- Indomalaya 7.5 mil. km² (including the South Asian subcontinent and Southeast Asia)
- Australasia 7.7 mil. km² (including Australia, New Guinea, and neighbouring islands). The northern boundary of this zone is known as the Wallace line.
- Neotropic 19.0 mil. km² (including South America and the Caribbean)
- Oceania 1.0 mil. km² (including Polynesia, Fiji and Micronesia)
- Antarctic 0.3 mil. km² (including Antarctica).
Ecoregions
Main article: EcoregionEcozones are further divided into ecoregions. The World has over 800 terrestrial ecoregions. See Lists of ecoregions by country.
History of ecology
- Main article: History of ecology
General ecology concepts
-
-
- Pioneer species –
- Ruderal –
- Supertramp –
-
- Autotroph –
- Bacteria –
- Bioinvader –
- Biomass –
- Biotic material –
- Carbon cycle –
- Climate –
- Ecological selection –
- Gaia hypothesis –
- Natural resource –
- Monoculture –
- inorganic substances–
-
- Detritus –
- Biodegradable –
-
- Neutralism –
- Amensalism –
- Ecological facilitation –
Ecology lists
- Main article: List of ecology topics
See also
- Biology
- Outline of biology
- Index of biology articles
External links
- What is Ecology?
- Fundamentals of Ecology Textbook-style investigation to the economy of nature, breaks down in 4 chapters from Population to Ecosystem.
- Ecology (Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy)
Outlines General reference · Culture and the arts · Geography and places · Health and fitness · History and events · Mathematics and logic · Natural and physical sciences · People and self · Philosophy and thinking · Religion and belief systems · Society and social sciences · Technology and applied sciencesCategories:- Outlines
- Ecology
- Ecology lists
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.