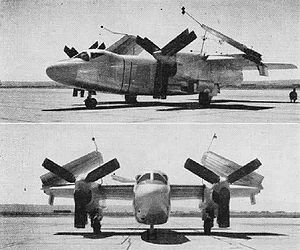
- North American XA2J Super Savage
-
XA2J "Super Savage" The XA2J-1 with folded wings Role Attack aircraft Manufacturer North American Aviation First flight 4 January 1952 Status Cancelled Produced 1 Developed from AJ Savage The North American Aviation XA2J "Super Savage" was a prototype carrier-based attack aircraft built in the early 1950s. It was developed by North American Aviation (NAA) from the smaller AJ Savage.
Contents
Development
The XA2J was intended to replace the AJ Savage which was deficient in performance and was a less than satisfactory carrier plane.[1] It was essentially an "enlarged" AJ Savage with the two reciprocating engines replaced with two Allison T40 turboprop engines and removal of the tail-mounted turbojet. Construction of two prototypes started 1 October 1948, but due to delays developing the engines, the first flight was not until 4 January 1952.[2] The competing XA3D, the prototypes of which were ordered the year after construction had begun on the XA2J prototypes, first flew in October 1952. The A3D had far superior performance, and that doomed the XA2J.
The root cause for the failure of the XA2J was the protracted development and poor reliability of the Allison T40 engines. The T40 engine was an advanced engine design of joining two T38 turboprop engines to drive two large contra-rotating propellers through a combining gearbox, proved to be very unreliable. The T40 engine was also used in the developmental A2D Skyshark, and the XF-84H Thunderscreech. After a number of engine related mishaps the XA2J project was abandoned.
Design
The XA2J was a shoulder-mounted straight wing aircraft derived from the AJ Savage.
Operators
Specifications (XA2J-1)
General characteristics
- Length: 70 ft 3 in (21.42 m)
- Wingspan: 71 ft 6 in (21.80 m)
- Height: 24 ft 2 in (7.37 m)
- Wing area: 836 ft² (77.7 m²)
- Empty weight: 35,350 lb (16,035 kg)
- Loaded weight: 46,890 lb (21,269 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 61,200 lb (27,760 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Allison T40-A-6 turboprops, 5,035 eshp (3,756 kW) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 451 mph (726 km/h)
- Range: 2,180 miles (3,508 km)
- Service ceiling: 37,500 ft (11,400 m)
- Rate of climb: 6,820 ft/min (34.7 m/s)
- Wing loading: 56 lb/ft² (274 kg/m²)
- Power/mass: 0.21 hp/lb (350 W/kg)
Armament
- 10,500 lb (4,763 kg) of disposable stores
- 2x 20 mm cannons in tail (never fitted)
See also
- Related development
References
- Notes
- ^ Miller 2001, pp. 90–9
- ^ Wagner 1982, pp. 389–490
- Bibliography
- Wagner, Ray. American Combat Planes (3rd edition). Garden City, NY: Doubleday & Company, 1982. ISBN 0-385-13120-8.
- Miller, Jerry. Nuclear Weapons and Aircraft Carriers. Washington D.C.: Smithsonian institution Press, 2001. ISBN 1-56098-944-0.
USN/USMC attack aircraft designations 1946-1962 Douglas Grumman McDonnell Douglas North American Martin Vought Lists relating to aviation General Aircraft (manufacturers) · Aircraft engines (manufacturers) · Airlines (defunct) · Airports · Civil authorities · Museums · Registration prefixes · Rotorcraft (manufacturers) · TimelineMilitary Accidents/incidents Records Categories:- Aircraft with contra-rotating propellers
- Carrier-based aircraft
- North American Aviation aircraft
- United States attack aircraft 1950–1959
- Twin-engined aircraft
- Cancelled military aircraft projects of the United States
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.