- National Disaster Response Force (NDRF)
-
The DM[clarification needed] Act, 2005 has made the statutory provisions for the constitution of the National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) for the purpose of specialized response to natural and man-made disasters.[1][2] According to Section 45 of the Act, the Force has to function under the general superintendence, direction and control of the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) and under command and supervision of Director General, NDRF. Though the units of this Force were nominated in 2003, it is only after the establishment of NDMA that their training and equipping were vigorously pursued. In lieu with the Section 44 (i) of the Act that states NDRF a specialist force, the force is gradually emerging as the most visible and vibrant multi-disciplinary, multi-skilled, high-tech force of the NDMA capable of dealing with all types of natural and man-made disasters.
Contents
Present organisation
At present, National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) is about constituted of eight battalions, two each from the BSF, CRPF, CISF and ITBP. Each battalion will provide 18 self-contained specialist search and rescue teams of 45 personnel each including engineers, technicians, electricians, dog squads and medical/paramedics. The total strength of each battalion is approximately 1,149.
All the eight battalions are being equipped and trained to combat all natural disasters including four battalions in combating nuclear, biological and chemical disasters.
Raising of two more NDRF battalions at Patna, Bihar and Guntur, Andhra Pradesh has been approved by the Government and NDMA has initiated necessary actions for the same.
Deployment
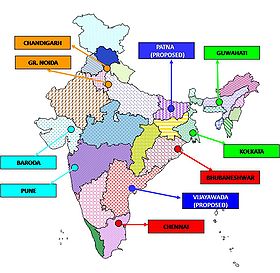
These NDRF battalions are located at nine different locations in the country based on the vulnerability profile to cut down the response time for their deployment. During the preparedness period/in a threatening disaster situation, proactive deployment of these forces will be carried out by the NDMA in consultation with state authorities. The present location of NDRF Bns are as follows:
S. No. NDRF Bn State CPF 1 NDRF Bn, Greater Noida Uttar Pradesh ITBP 2 NDRF Bn, Bhatinda Punjab ITBP 3 NDRF Bn, Kolkata West Bengal BSF 4 NDRF Bn, Guwahati Assam BSF 5 NDRF Bn, Mundali Orissa CISF 6 NDRF Bn, Arakkonam Tamilnadu CISF 7 NDRF Bn, Pune Maharashtra CRPF 8 NDRF Bn, Gandhinagar Gujarat CRPF 9 NDRF Bn, Patna (under-raising) Bihar BSF 10 NDRF Bn, Guntur (under-raising) Andhra Pradesh CRPF Functional parameters
The vision of the National Disaster Management Authority is to build a safer and disaster resilient India by developing a holistic, proactive, multi-disaster and technology driven strategy for Disaster Management. This has to be achieved through a culture of prevention, mitigation and preparedness to generate a prompt and efficient response at the time of disasters. This national vision inter alia, aims at inculcating a culture of preparedness among all stakeholders.[3]
NDRF has been proved its importance in achieving this vision by highly skilled rescue and relief operations, regular and intensive training and re-training, familiarization exercises within the area of responsibility of respective NDRF Bns, carrying out mock drills and joint exercises with the various stakeholders.
Disaster response
NDRF shifting school children to safer places during Cyclone Aila. NDRF rescue and relief operation, Karnataka.
NDRF rescue and relief operation, Karnataka.
In the previous years, NDRF has proved its efficacy with its commendable performance during various disasters including the drowning cases, building collapses, landslides, devastating floods and Cyclones. NDRF has saved 133,192 human lives and retrieved 276 dead bodies of disaster victims in 73 response operations in the country. Some of the major response operations of NDRF as below:
2007
- Flood in Bhavnagar, Gujarat – July 3-05, 2007 –Rescued 291 people; distributed 3,750 food packets
- Flood in Rajkot, Gujarat – July 3-05, 2007 –Rescued 291 people; distributed 3,750 food packets
2008
- Building collapse (Hotel Shakunt) in Ahmedabad, Gujarat - Feb 03-05, 2008 – Saved 10 people & recovered 06 dead bodies
- Flood in Lakhimpur, Assam – June 14-July 20, 2008 – Rescued 2,500 civilians
- Flood in Dhemaji, Assam – June 16- July 31, 2008 –Rescued 600 people
- Flood in Lakhimpur, Assam – July 21-Aug 04, 2008 – Evacuated 2,000 people
- Kosi breach in Bihar – Aug 20, 2008 –Saved over 105,000 people including women, children & aged; distributed medicines and water bottles
- Flood in Lakhimpur, Assam – Aug 31- Sep 09, 2008 –Saved 750 people
- Flood in Puri, Cuttack, Kendrapara & Jagatsinghpur, Orissa – Sept, 2008 – Saved over 1,000 people
- Flood in Kamrup, Assam – Sep 28, 2008 –Saved 350 people
- Flood in Tiruvarur, Tamil Nadu – Nov 26-30, 2008 – Saved 773 people
- Flood in Chennai, Tamil Nadu – Nov 26-Dec 02, 2008 – Rescued 1,550 people
2009
- Cyclone Aila (24 Pargana North & South, West Bengal) – May 25- June 10, 2009 –Rescued 2,000 people; distribution of medicine to 30,000 victims & food packets to 16,000 homeless victims
- Flood in Barpeta, Assam – May 27, 2009 – Saved 300 people
- Flood in Junagarh and Porbandar, Gujarat – July 16–29, 2009 – Saved 2,225 people
- Flood in Kasarkode, Kannur and Ernakulam, Kerala – July 17–24, 2009 – Saved 180 people
- Flood in Sitamarhi, Bihar (Bagmati breach) – Aug 02-09, 2009 – Rescued 1,034 people; distributed medicines to 831 victims
- Flood in Howrah & Hooghly, West Bengal – Sep 08-14, 2009 – Rescue 675 people
- Andhra Pradesh & Karnataka Floods – Oct 2009 – Saved 10,659 people
2010
- Building collapse at Bellary, Karnataka – Jan 27, 2010 – Saved 20 human lives and recovered 27 dead bodies
- Flood in Guwahati, Assam – April 20–25, 2010 – Saved 300 human lives
- Cyclone LAILA in Andhra Pradesh & Karnataka – May 18, 2010
During the Kosi breach in Bihar in August 2008, which was decleared national calamity by Prime Minister Shri Manmohan Singh,[4][5][6][7] NDRF personnel actively engaged themselves in rescue operations and relief duties on a war footing in districts Supaul, Madhepura, Araria and Purnia. About 780 NDRF personnel trained in flood rescue operations along with 153 high capacity inflatable boats and other rescue equipments were deployed in the flood affected areas. The swift and highly skilled operations of NDRF saved more than 100,000 people trapped in swirling waters of river Kosi.[8] NDRF personnel distributed relief supplies including drinking water to the stranded flood victims.[9] Medical camps were also established to provide medical care to the flood affected people. Impressed with prompt and efficient response of NDRF, Chief Minister of Bihar Shri Nitish Kumar approached Prime Minister Shri Manmohan Singh for a NDRF Bn to be stationed in Bihar[10] and offered 65 acres (260,000 m2) of land at Bihta near Patna.
NDRF commendable rescue operations were no less appreciated during the 2008 floods in Orissa, Maharashtra, Kerala and Assam.
On May 25, 2009 Cyclone Aila hit West Bengal coast with a fury unprecedented in recent history. It took at least 94 lives, seven of them in Kolkata, and affected over 40 lakh people. More than six lakh houses were destroyed completely or damaged partially.[11] NDRF promptly responded to the devastating situation and 600 personnel of NDRF with 84 boats and other rescue equipments started rescue and relief operations at cyclone affected areas of district 24 Pargana North and South of West Bengal.[12][13][14] During the operations NDRF personnel rescued around 2,000 trapped persons and distributed 50 truckloads of relief materials to the affected people.
On Oct 01, 2009 in the wake of worsening flood situations in the States of Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka, the State Government of both the states sent their requests for deployment of National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) for rescue and relief operations. NDMA mobilized 963 flood rescue trained personnel (including some deep divers) and 308 inflatable motorized boats from 05 NDRF Bns located at Arakkonam (Chennai), Pune, Mundali (Orissa), Greater Noida and Bhatinda. and airlifted on Oct 02-03, 2009 in Air Force IL-76 and AN-32 aircraft from nearest Air Force bases and Civil Airports. The rescue personnel deployed in 04 districts of Andhra Pradesh (Kurnool, Vijayawada, Mehboob Nagar and Nandhiyal) and 04 districts of Karnataka (Bagalkote, Raichur, Gadag and Bijapur) and immediately started rescue and relief operations in the flood affected districts of both the states.[15][16][17]
NDRF rescued tens of thousands persons marooned in the floods at these two States and distributed over 40 quintals of food and drinking water. The medical teams of NDRF at these districts administering medical first response and distributing medicines to the flood victims.
On Jan 26, 2010 a five-storied under-construction residential building collapsed at Bellary, Karnataka with about 50 people trapped under the huge debris. 3 rescue teams (102 personnel) of NDRF Bn Pune promptly airlifted to Bellary and NDRF personnel carried out round the clock operation with the help of search & rescue equipments and dogs for 09 days.In the meticulously carried out operation under huge debris the NDRF managed to rescue 20 live persons. The last person was rescued on the 9th day. NDRF also retrieved 27 dead bodies trapped under debris.[18][19][20][21]
Training
In future, the key to efficient disaster response will depend primarily on effectiveness of training and re-training of Specialised Disaster Response Forces. With this vision, a detailed “Training Regime for Disaster Response” has been prepared by NDMA/NDRF identifying the specific disaster response training courses and devising a unified, structured and uniform course module as well as syllabus for these training courses. The proposition behind a unified, structured, uniform course module and syllabus is that first the entire NDRF battalions will successfully attain these courses and subsequently the State Disaster Response Forces (SDRF) and other stakeholders will be trained on the same lines. The need of uniformly structured course module emerged out of the fact that if all the NDRF battalions and other ‘first responders’ undergo the same training exercise, the coordination between different stakeholders would be expedient and well planned at the time of any major disaster where different NDRF battalions, SDRF battalions and other stakeholders will be working together in close coordination with each other.
Already Trained Trained in 2009-10 Total CBRN 2,976 480 3,456 Heli-Borne Training 2,700 1,500 4,200 Natural Disasters 5,071 950 6,021 Water Rescue 3,520 1,600 5,120 Foreign Trained 54 07 61 After its constitution in 2005, NDRF with its swift and highly-skilled rescue operations has emerged as most visible and vibrant force of the NDMA. NDRF personnel are invariably trained in courses like Flood Rescue, Collapsed Structure Search and Rescue, Medical First Responders, Rope Rescue, Nuclear, Biological and Chemical Emergencies; Dignified Disposal of Dead Bodies etc. NDRF personnel are trained in prestigious institutes like NISA, DRDO, BARC, CME, Army, Navy and Air Force as well in foreign countries like USA, Singapore, China, Finland, Korea, Switzerland etc.
Training Abroad
- INSARAG Asia Pacific Exercise, China, August 4–7, 2006
- OPCW Chemical Emergency Course, Finland, August 21–25, 2006
- UNDAC Induction Course, Korea, Sept 17-29, 2006
- INSARAG Asia Pacific Exercise, Mongolia, July 31 – August 2, 2007
- UNDAC Induction Course, Malaysia, July 10 – 14, 2007
- INSARAG Meeting, Korea, Oct 03-06, 2007
- UNDAC Induction Course, New Zealand, Oct 14-16, 2007
- INSARAG Asia Pacific Exercise, Switzerland, Nov 17-20, 2008
- Management of Dead Bodies, Geneva, Switzerland, Feb 04-08, 2008
- Singapore Civil Defence Academy, Singapore, March 10–27, 2008
- INSARAG Asia Pacific Exercise, Philippines, April 15–17, 2008
- APCSS, Honolulu, Hawai, USA, May 29-June 27, 2008
- Advanced Search & Rescue Course, Florida, USA, Sep 1-5, 2008
- Chemical Exercise, OPCW, Tehran, Iran, Nov 01-05, 2008
- INSARAG Asia Pacific Exercise, Nepal, April 21–24, 2009
- APCSS, Honolulu, Hawai, USA, Aug 20-Sep 22, 2009
- Bioterrorism Table top Exercise, Montreux, Switzerland, Sep 07-08, 2009
Training of SDRF
While the NDRF is being trained, re-trained and equipped as a specialist force for level three disasters, it is equally important to ensure capacity building of state police personnel who are invariably the first responders in any natural or man-made disasters. To ensure this, a two-pronged strategy is being suggested to the states: firstly, to train state police personnel in the basics of disaster management and secondly, to train at least one battalion equivalent out of their state armed police units as State Disaster Response Force (SDRF) on lines of the NDRF. In addition to police personnel, the SDRFs may be constituted from existing resources of the Fire Services, Home Guards and Civil Defence. NDRF Bns and their training institutions will assist the States/UTs in this effort. The State/ UTs will also be encouraged to set up DM training facilities in their respective Police Training Colleges and include this subject in their basic and in-service courses.
Till the time, 205 police personnel from 21 states of the country have been trained.
S. No Date of Course Location No of successful Participants 1 Feb 05-April 6, 2007 FSTI, NISA Hyderabad 24 2 Nov 05 – Dec 29, 2007 FSTI, NISA Hyderabad 18 3 Oct 11 – Nov 11, 2008 Police Training Centre, Arunachal Pradesh 42 4 Nov 24, 2008 – Jan 16, 2009 FSTI, NISA Hyderabad 16 5 Jan 12 – Feb 27, 2009 CTC-II Coimbatore 17 6 Sep 05 – Nov 13, 2009 FSTI, NISA Hyderabad 23 7 Oct, 2009 ILDM, Department of Revenue, Govt of Kerala 40 8 Feb 08 – March 20, 2010 CTC-II Coimbatore 25 Total 205 Training being one of the most important attributes for an efficient force, Government of India has recognised the recommendations of the NDMA for setting up an apex National Institute of Excellence for Search and Rescue at a central place like Nagpur to provide training of trainers and to meet other national and international commitments. Also a network of ten outreach centres at the respective NDRF Bns locations are proposed to be set up.
Community Based Disaster Preparedness
Training the Teachers of Pune University.
Awareness and preparedness campaigns are key components of proactive approach on Disaster Management. In case of any disaster, the local population is the actual first responder. It may take some time for the district/ state administration to mobilize rescue teams, including police, fire personnel etc. If the local people is properly sensitized about the precautions and preventive actions to be taken in case of any calamity, the loss of life and damage to property can be drastically reduced. Thus, one of the most important tasks of NDRF is to continuously engage themselves in the Community Capacity Building and Public Awareness programmes in a big way which includes training of people (the first responders) and concerned government officials at different levels in the areas with high vulnerability. Along with Community Capacity Building and Public Awareness exercises NDRF is also actively engaged in area familiarization exercises. Such exercises provide first-hand knowledge about the topography, access route to various disaster prone areas, availability of local infrastructure/ logistics which can be used in disaster response operations.
Year wise Figure of Community Volunteers trained by NDRF
Year No. of Volunteers 2007-08 48,374 2008-09 196,477 2009-10 410,830 Total 655,681 A pilot project on Community Capacity Building and Public Awareness campaigns on floods, earthquakes and other natural disasters was organised by NDRF teams during June–July, 2007 in 14 high vulnerable districts (Araria, Saharsa, Kishanganj, Madhepura, Supaul, Khagaria, Begusarai, Darbhanga, Madhubani, Munger, Patna, Muzaffarpur, Sitamarhi and Samastipur) of Bihar. In this project, 2,200 volunteers and State Disaster Management Authority (SDMA) officials were trained by the NDRF. This capacity building programme was continued next year also.
State wise Figure of Community Volunteers trained by NDRF
S.No State No of Beneficiaries 1 Gujarat 147,018 2 North-Eastern States 93,349 3 Maharashtra 82,735 4 Rajasthan 79,524 5 Bihar 74,095 6 Karnataka 31,809 7 Haryana 31,349 8 West Bengal 21,086 9 Kerala 18,363 10 Tamil Nadu 16,110 11 Uttar Pradesh 14,490 12 Uttarakhand 9,946 13 Madhya Pradesh 9,550 14 Himachal Pradesh 7,440 15 Punjab 7,060 16 Andhra Pradesh 6,345 17 Other States 5,412 Total 655,681 In 2008, NDRF embarked in a big way upon the community capacity building and public awareness programmes in Bihar which included training of vulnerable people and officials in various districts. NDRF carried out 3 day Flood Preparedness training programme for a month in 15 vulnerable districts (Bhagalpur, East Champaran, Vaishali, Munger, Muzaffarpur, Saharsa, Madhepura, Khagaria, Begusarai, Darbhanga, Madhubani, Patna, Sitamarhi, Samastipur and Sheohar) of Bihar before monsoon season at district/Block levels. More than 15,000 village volunteers, local people, students, State Police, and also Central and State Govt. personnel participated in the programme.
NDRF also conducts regular mock exercises on various disasters like cyclone, flood, earthquake, NBC emergencies, mass causality management etc. Participation in such exercises on the one hand improve the professionalism of NDRF personnel to tackle the real emergency situations and on the other provides an opportunity to interact with various State Government officials and to develop cordial relations with them that can be of great help during response to actual disasters.
Till March 31, 2010 NDRF has trained more than 6.5 lacs community volunteers throughout the country.
Workshops/Exhibitions
NDRF Bn Pune put up an exhibition of International standard at TechFest 2010 (The annual International Science and Technology Festival of IIT Mumbai) and organized demonstrations on Heli-Rescue, Collapsed Structure Search & Rescue, High-Rise Building Rescue and Dog Show between Jan 22-24, 2010 aimed at generate awareness among the visitors. TechFest 2010 was inaugurated by Gen. N. C. Vij. Hon’ble Vice Chairman, NDMA. This three day event witnessed more than 70,000 visitors, 15,000 participants, nearly 2,000 colleges and approximately 5,000 members of Industry and academia. The exhibition and demonstrations of NDRF were highly appreciated by the visitors.
Some of the important exhibitions organised by NDRF are as below:
2007
- UNOCHA, Annual USAR Team Leaders Meeting - March 13–15, 2007
- 2nd Asian Ministerial Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction – Nov, 2007
2008
- Workshop on ‘Disaster Risk Management’ at Itanagar, Aurnachal Pradesh – April 17–18, 2008
- Workshop on ‘Disaster Preparedness’ at Shillong, Meghalaya – June 10–11, 2008
- Workshop on ‘Disaster Risk Reduction’ at Agartala, Tripura – Dec 12-13, 2008
- Exhibition on Disaster Management, Army Training Command at Bhubaneswar, Orissa – Dec 13-14, 2008
2009
- A workshop cum exhibition on Disaster Management, University of Pune, Maharashtra – Jan 12-13, 2009
- Workshop on ‘Disaster Risk Reduction’ at Aizawl, Mizoram – June 11–12, 2009
2010
- TechFest 2010 (The annual International Science and Technology Festival of IIT Mumbai) – Jan 22-24, 2010
- Technika 2010, the annual technical festival of Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra –March 26, 2010
- Exhibition on Disaster Awareness, Bihar Divas at Gandhi Maidan, Patna – March 22–24, 2010
- Participation in TATPAR 2010 (Mega-Exhibition on disaster management organized by Disaster Management Department of Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai) at Shivaji Park, Mumbai – Feb 26-27, 2010
References
- ^ http://mha.nic.in/Noti-pdf/DM-No.53.pdf
- ^ PIB Press Release
- ^ http://ndma.gov.in/ndma/index.htm
- ^ http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/news/specials/Rs-1000-cr-for-flood-hit-Bihar-PM/articleshow/3418604.cms
- ^ http://www.hindu.com/2008/08/29/stories/2008082958130100.htm
- ^ http://www.mainstreamweekly.net/article937.html
- ^ http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/News/PoliticsNation/Kosi-flood-highlights-need-for-water-management-Montek-Ahluwalia/articleshow/3461829.cms
- ^ http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/News/PoliticsNation/NDRF_men_turn_saviour_for_1_lakh_in_Bihar/rssarticleshow/3456266.cms Economic Times, Sep 08, 2008
- ^ http://www.hindustantimes.com/News/bihar/Unsung-disaster-force-shines/Article1-337654.aspx Hindustan Times, Sept 14, 2008
- ^ http://www.thaindian.com/newsportal/uncategorized/flooded-bihar-to-get-disaster-response-force-base-camp_10090605.html
- ^ http://www.hindu.com/fline/fl2612/stories/20090619261213100.htm
- ^ http://www.hindu.com/2009/05/27/stories/2009052759991000.htm
- ^ http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/NEWS/City/Kolkata-/Mamata-stays-back-to-take-charge-in-city-today/articleshow/4577694.cms
- ^ http://indiatoday.intoday.in/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=43739§ionid=4&Itemid=1&issueid=107
- ^ http://www.indianexpress.com/news/ndrf-teams-head-for-ap-karnataka/525330/#
- ^ http://www.ptinews.com/news/315084_Centre-steps-up-flood-relief-ops-in-AP--Karnataka#
- ^ http://www.tribuneindia.com/2009/20091005/main3.htm
- ^ http://www.expressindia.com/latest-news/Four-killed-in-Bellary-building-collapse/571993/
- ^ http://www.hindustantimes.com/Bellary-building-collapse-rescue-operations-end/Article1-505334.aspx
- ^ http://beta.thehindu.com/news/states/karnataka/article95959.ece
- ^ http://www.ndtv.com/news/videos/video_player.php?id=1196850
Categories:- Disaster preparedness in India
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.