- alpha-Naphthylthiourea
-
α-Naphthylthiourea 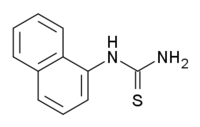 naphthalen-1-ylthiourea
naphthalen-1-ylthioureaIdentifiers Abbreviations ANTU CAS number 86-88-4 
PubChem 736366 ChemSpider 643492 
KEGG C19136 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C=CC=C2NC(=S)N
S=C(N)Nc2cccc1ccccc12
Properties Molecular formula C11H10N2S Molar mass 202.28 g/mol Hazards Main hazards Toxic  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references α-Naphthylthiourea (ANTU, Dirax) is an organosulfur compound. It is a derivative of thiourea and used as a rodenticide. It acts by inducing pulmonary edema and has relatively selective toxicity for rats.[1]
Safety
Currently, the substance is banned for use in plant protection by the UK government.[2]
References
- ^ Sipahi EY, Ozel Tekin I, Comert M, Barut F, Ustun H, Sipahi TH. Oxidized low-density lipoproteins accumulate in rat lung after experimental lung edema induced by alpha- naphthylthiourea (ANTU). Pharmacological Research. 2004 Dec;50(6):585-91. PMID 15501696
- ^ http://www.pesticides.gov.uk/approvals.asp?id=55
Pest control: rodenticides Anticoagulants/
vitamin K antagonistscoumarins/4-Hydroxycoumarins: 1st generation (Warfarin, Coumatetralyl) • 2nd generation (Brodifacoum, Difenacoum, Flocoumafen)
1,3-Indandiones: Chlorophacinone • Pindone • Diphacinone
other: DifethialoneConvulsants Calciferols Inorganic compounds Organochlorine Organophosphorus PhosacetimMetabolic poisons Bromethalin • Fluoroacetamide • 1,3-Difluoro-2-propanol (Gliftor) • Sodium fluoroacetateOther α-Naphthylthiourea • Norbormide • Pyrinuron • Scilliroside
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. - C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C=CC=C2NC(=S)N
