- Difenacoum
-
Difenacoum 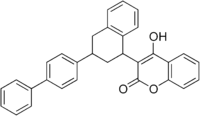 2-hydroxy- 3-[3-(4- phenylphenyl)- 1-tetralinyl]- 4-chromenoneOther namesDiphenacoum
2-hydroxy- 3-[3-(4- phenylphenyl)- 1-tetralinyl]- 4-chromenoneOther namesDiphenacoumIdentifiers CAS number 56073-07-5 PubChem 41735 KEGG C16807 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C1C(CC2=CC=CC=C2C1C3=C(OC4=CC=CC=C4C3=O)O)C5=CC=C(C=C5)C6=CC=CC=C6
Properties Molecular formula C31H24O3 Molar mass 444.52 g/mol Density 1.27 (98.7% w/w) Melting point 21 1.0 - 215.0°C (98.7% wlw)
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Difenacoum is a coumarin derivative. It has anticoagulant effects and is used as a rodenticide.
Uses
Difenacoum is sold as blue-green pellets intended to be ingested by pests such as rats and mice.
Safety and toxicity
Because other species of mammals and birds may prey upon affected rodents, there is a risk of secondary or tertiary exposure[1]. Using radiolabled isotopes, difenacoum (and/or its metabolites) has been shown to be distributed across many organ tissues upon oral ingestion, with the highest concentrations occurring in the liver and pancreas[1].
Difenacoum has been shown to be highly toxic to some species of freshwater fish and green algae despite the fact that difenacoum is weakly soluble in aqueous solutions[1].
References
Pest control: rodenticides Anticoagulants/
vitamin K antagonistscoumarins/4-Hydroxycoumarins: 1st generation (Warfarin, Coumatetralyl) • 2nd generation (Brodifacoum, Difenacoum, Flocoumafen)
1,3-Indandiones: Chlorophacinone • Pindone • Diphacinone
other: DifethialoneConvulsants Calciferols Inorganic compounds Organochlorine Organophosphorus PhosacetimMetabolic poisons Bromethalin • Fluoroacetamide • 1,3-Difluoro-2-propanol (Gliftor) • Sodium fluoroacetateOther α-Naphthylthiourea • Norbormide • Pyrinuron • Scilliroside
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
