- Mu (rocket family)
-
The Mu, also known as M, was a series of Japanese solid-fuelled carrier rockets, which were launched from Uchinoura between 1966 and 2006. Originally developed by Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Mu rockets were later operated by Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency following its merger with ISAS.
Early Japanese carrier rockets
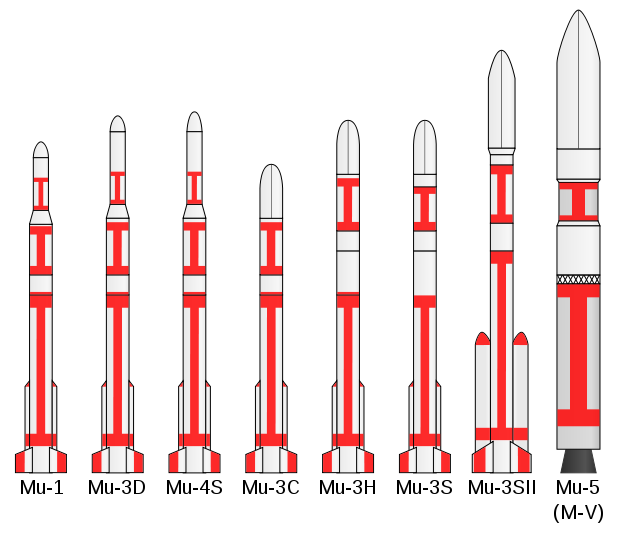
The first Mu rocket, the Mu-1 made a single, sub-orbital, test flight, on 31 October 1966. Subsequently a series of rockets were produced, designated Mu-3 and Mu-4. In 1969 a suborbital test launch of the Mu-3D was conducted. The first orbital launch attempt for the Mu family, using a Mu-4S, was conducted on 25 September 1970, however the fourth stage did not ignite, and the rocket failed to reach orbit. On 16 February 1971, Tansei 1 was launched by another Mu-4S rocket. Two further Mu-4S launches took place during 1971 and 1972. The Mu-4S was replaced by the Mu-3C, was launched four times between 1974 and 1979, with three successes and one failure, and the Mu-3H, which was launched three times in 1977 and 1978. The Mu-3S was used between 1980 and 1984, making four launches. The final member of the Mu-3 family was the Mu-3SII, which was launched eight times between 1985 and 1995. The Mu-3 was replaced in service by the M-V.
M-V
Main article: M-VThe M-V, or Mu-5, was introduced in 1997 and retired in 2006. Seven launches, six of which were successful, were conducted. Typically, the M-V flew in a three-stage configuration, however a four-stage configuration, designated M-V KM was used 3 times, with the MUSES-B (HALCA) satellite in 1997, Nozomi (PLANET-B) spacecraft in 1998, and the Hayabusa (MUSES-C) spacecraft in 2003. The three-stage configuration had a maximum payload of 1,800 kg (4,000 lb) for an orbit with altitude of 200 km (120 mi) and inclination of 30°, and 1,300 kg (2,900 lb) to a polar orbit (90° inclination), with an altitude of 200 km (120 mi). The M-V KM could launch 1,800 kg (4,000 lb) to an orbit with 30° inclination and 400 km (250 mi) altitude.
The three stage M-V had a total launch mass of 137,500 kg (303,000 lb), whilst the total mass of a four-stage M-V KM was 139,000 kg (310,000 lb).
External links
Expendable launch systems Current Ariane 5 · Atlas V · Delta (II · IV) · Dnepr-1 · GSLV · H-IIA · H-IIB · Kaituozhe-1 · Kosmos-3M · Long March (1D · 2C · 2D · 2F · 3A · 3B · 3C · 4B · 4C) · Minotaur (I · IV) · Naro-1 · Paektusan · Pegasus · Proton (K · M) · PSLV · Rokot · Safir · Shavit · Shtil' · Start-1 · Strela · Soyuz (U · FG · 2) · Taurus · Unha · VLS-1 · Volna · Zenit (2 · 2M · 3SL · 3SLB)
Planned Angara · Athena (Ic · IIc) · GSLV III · Haas · Long March (5 · 6 · 7) · Minotaur V · RPS-420 · Rus-M · Soyuz-1 · Simorgh · TSLV · Taurus II · Tsyklon-4 · Vega · Zenit-3F
Previous Ariane (1 · 2 · 3 · 4) · ASLV · Athena (I · II) · Atlas (B · D · E/F · G · H · I · II · III · LV-3B · SLV-3 · Able · Agena · Centaur) · Black Arrow · Caleb · Conestoga · Delta (A · B · C · D · E · G · J · L · M · N · 0100 · 1000 · 2000 · 3000 · 4000 · 5000 · III) · Diamant · Energia · Europa · Falcon 1* · Feng Bao 1 · H-I · H-II · J-I · Juno I · Juno II · Kosmos (1 · 2I · 3) · Lambda (4S) · Long March (1 · 2A · 2E · 3 · 4A) · Mu (4S · 3C · 3H · 3S · 3SII · V) · N1 · N-I · N-II · Pilot · R-7 (Luna · Molniya (M) · Polyot · Soyuz (L · M · U2) · Soyuz/Vostok · Sputnik · Voskhod · Vostok (L · K · 2 · 2M)) · Saturn (I · IB · V · INT-21) · Scout · SLV · Sparta · Thor (Able · Ablestar · Agena · Burner · Delta · DSV-2U) · Thorad-Agena · Titan (II GLV · IIIA · IIIB · IIIC · IIID · IIIE · 34D · 23G · CT-3 · IV) · Tsyklon (2 · 3) · Vanguard
- - Falcon 1 designed for partial reuse, however recovery failed on the first three flights and remaining vehicles were flown expendably
Japanese orbital launch systems JAXA Active Planned EpsilonISAS Retired NASDA Retired Other Cancelled GX*Retired - - Based around licence produced US rockets
Categories:- Space launch vehicles of Japan
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.