- Military Police of Paraná State
-
Military Police of Paraná State
Polícia Militar do ParanáAbbreviation PMPR Badge of the Military Police of Paraná State. Motto Your protection is our commitment. Sua proteção é nosso compromisso. Agency overview Formed 10 August 1854.[1] Legal personality Governmental: Government agency Jurisdictional structure Operations jurisdiction* State of Paraná, Brazil Map of police jurisdiction. Size 199,314.9 km² (76,955.9 sp mi) Population 10,387,378 (2006) General nature Operational structure Headquarters Curitiba Website Official website Footnotes * Divisional agency: Division of the country, over which the agency has usual operational jurisdiction. The Military Police are reserve and ancillary forces of the Brazilian Army, and part of the System of Public Security and Brazilian Social Protection.[2] Its members are called Military's States.[3]
The primary mission of PMPR is the ostensible and preventive policing for the maintenance of public order in the State of Paraná.Contents
History
The Military Police of Paraná was created as a unit of Skirmishers on August 10, 1854, under the name of the Police Force, like a military company. This origin is due to military necessity of the Empire of Brazil in reinforcing the troops of the Army in emergency situations. With the Proclamation of the Republic of Brazil has adopted a Constitution based on the United States where the states have a large autonomy. With that the police have become small regional armies.
The history of PMPR shows an honorable participation in the events that marked Brazilian national life at that time.
- War of the Triple Alliance
- Federalist Revolution
- Contestado War
- Revolt of 1924
- Revolution of 1930
- Revolution of 1932
This dangerous situation for the national unity remained until the end of the World War II, with the deposition of the dictatorial government of Getúlio Vargas. It was only from 1946 that the military police who have purchased the configuration now, a kind of gendarmerie which is subject to the States.
Historic Designations
- 1854 - Police Force.
- 1874 - Police Corps.
- 1891 - Military Police Corps.
- 1892 - Security Regiment.
- 1917 - Military Force.
- 1932 - Public Force.
- 1939 - Police Force.
- 1946 - Military Police.
Organization
The PMPR is operationally organized into battalions, companies, and platoons; and administratively, in departments. The battalions are based in major urban centers, and their companies and platoons are distributed according to population density in cities.
The Military Police of Paraná is present in all cities of the State.Battalions of Military Police

Vehicle for transport of prisoners - 1909. 
Parade of Independence of Brazil - 1938. 
School Patrol - 2008. - 1st Battalion of Military Police - Ponta Grossa;
- 2nd Battalion of Military Police - Jacarezinho;
- 3rd Battalion of Military Police - Pato Branco;
- 4th Battalion of Military Police - Maringá;
- 5th Battalion of Military Police - Londrina;
- 6th Battalion of Military Police - Cascavel;
- 7th Battalion of Military Police - Cruzeiro do Oeste;
- 8th Battalion of Military Police - Paranavaí;
- 9th Battalion of Military Police - Paranaguá;
- 10th Battalion of Military Police - Apucarana;
- 11th Battalion of Military Police - Campo Mourão;
- 12th Battalion of Military Police - Curitiba;
- 13th Battalion of Military Police - Curitiba;
- 14th Battalion of Military Police - Foz do Iguaçu;
- 15th Battalion of Military Police - Rolândia;
- 16th Battalion of Military Police - Guarapuava;
- 17th Battalion of Military Police - São José dos Pinhais;
- 18th Battalion of Military Police - Cornélio Procópio;
- 19th Battalion of Military Police - Toledo;
- 20th Battalion of Military Police - Curitiba;
- 21st Battalion of Military Police - Francisco Beltrão;
- 1st Independent Company of Military Police - Lapa;
- 2nd Independent Company of Military Police - Rio Negro;
- 3rd Independent Company of Military Police - Telêmaco Borba;
- 4th Independent Company of Military Police - Londrina;
- 5th Independent Company of Military Police - Umuarama;
- 6th Independent Company of Military Police - Ivaiporã;
- 7th Independent Company of Military Police - Arapongas;
- 8th Independent Company of Military Police - Irati.
Special Units
- Regiment of Mounted Police;
- Battalion of Control of Urban Traffic;
- Battalion of Highway Patrol;
- Battalion of Security Prison;
- Battalion of Environmental Police;
- Battalion of School Patrol;
- Battalion of Events (sports competitions, festivals, street protest, etc.);
- Battalion of Special Operations;
- Independent Company of Security Police;
- Independent Company of Border Police.
Administrative Commands
- Medical Department;
- Hospital of Military Police;
- Veterinary Center;
- Department of Teaching;
- Academy of Military Police;
- School of Military Police;
- Department of Logistic Support;
- Department of Personnel;
- Department of Finance.
Firefighters Corps
The Corps of Firefighters was created in 1912.[4] The Corporation is militarized like the Sapeurs-pompiers of France, and is subject to the structure of PMPR. One groupment is equivalent to a battalion, and a subgroupment is equivalent to a company. The groupments and subgroupments are based in major urban centers. In the smaller towns, fire fighting is carried out by small detachment of volunteer firefighters.
- 1st Groupment of Firefighters - Curitiba;
- 2nd Groupment of Firefighters - Ponta Grossa;
- 3rd Groupment of Firefighters - Londrina;
- 4th Groupment of Firefighters - Cascavel;
- 5th Groupment of Firefighters - Maringá;
- 6th Groupment of Firefighters - São José dos Pinhais;
- 7th Groupment of Firefighters - Curitiba;
- 1st Independent Subgroupment of Firefighters - Foz de Iguaçu;
- 2nd Independent Subgroupment of Firefighters - Paranaguá;
- 3rd Independent Subgroupment of Firefighters - Ivaiporã;
- 4th Independent Subgroupment of Firefighters - Pato Branco;
- 5th Independent Subgroupment of Firefighters - Francisco Beltrão;
- 6th Independent Subgroupment of Firefighters - Guarapuava;
- 7th Independent Subgroupment of Firefighters - Apucarana;
- 8th Independent Subgroupment of Firefighters - Umuarama;
- Center for Teaching and Training - Piraquara.
Fire apparatus
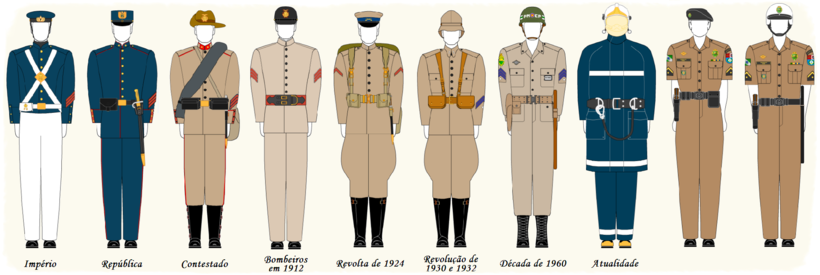
Uniforms
From 1854 until the early years of the Republic, the PMPR used the dark blue in their uniforms. In 1912[5] was adopted the khaki color, which by tradition is still in use today. The firefighters wear the same uniforms of the Military Police, just adding their badges and insignias.
Ranks
The PMPR has the same hierarchical classification[6] of the Brazilian Army, with another type of insignias.[7]
Colonel Lieutenant
ColonelMajor Captain First
LieutenantSecond
LieutenantAspirant Sub-Lieutenant First
SergeantSecond
SergeantThird
SergeantCorporal Private of
First ClassSee also


Mounted police of PMPR - 2010. - Paraná State
- Military Police of Brazil
- Brazilian Federal Police
- Federal Highway Police
- Brazilian Civil Police
References
- ^ Law 07, August 10, 1854.
- ^ Article 144 of Constitution of Brazil.
- ^ Article 42 of Constitution of Brazil.
- ^ Law 1.133, March 23, 1912.
- ^ Decree 774, August 31, 1912.
- ^ Ordinance of the Ministry of the Army 340, October 4, 1971.
- ^ Decree 3,568, March 02, 2001.
Sources
- Campanha do Contestado - Volume 1, 2 e 3; de Demerval Peixoto; Edição Farol do Saber - Prefeitura Municipal de Curitiba; 1995.
- De Catanduvas ao Oiapoque; de Milton Ivan Heller; Instituto Histórico e Geográfico do Paraná; 2007; ISBN 85-7662-027-8.
- Episódios da História da PMPR - Volume I ao VII; do Capitão João Alves da Rosa Filho; Edição da Associação da Vila Militar; 2000.
- O Paraná na Guerra do Paraguai; de David Carneiro; Edição Farol do Saber - Prefeitura Municipal de Curitiba; 1995.
- O Paraná na História Militar do Brasil; de David Carneiro; Edição Farol do Saber - Prefeitura Municipal de Curitiba; 1995.
- Os Voluntários da Pátria na Guerra do Paraguai - Volume 2, Tomo I e IV; do General Paulo de Queiroz Duarte; Edição da Bibliex; 1983.
External links
Law enforcement in Brazil Federal State Civil Police Military Police Local See also Categories:- Paraná (state)
- Military police of the states of Brazil
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.