- dnaA
-
Chromosomal replication initiator protein dnaA Identifiers Symbol dnaA Entrez 948217 UniProt P03004 Other data Bac_DnaA_C 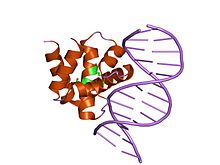
crystal structure of dnaa domainiv complexed with dnaabox dna Identifiers Symbol Bac_DnaA_C Pfam PF08299 Pfam clan CL0123 InterPro IPR013159 SCOP 1j1v Available protein structures: Pfam structures PDB RCSB PDB; PDBe PDBsum structure summary Bac_DnaA 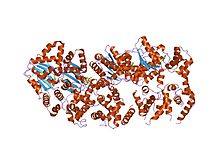
structure of amppcp-bound dnaa from aquifex aeolicus Identifiers Symbol Bac_DnaA Pfam PF00308 Pfam clan CL0023 InterPro IPR013317 PROSITE PDOC00771 SCOP 1j1v Available protein structures: Pfam structures PDB RCSB PDB; PDBe PDBsum structure summary dnaA is a replication initiation factor which promotes the unwinding or denaturation of DNA at oriC (around 240bp in Escherichia coli), during DNA replication in prokaryotes.
The formation of the oriC/DnaA complex and DNA unwinding requires ATP hydrolysis[1].
The oriC site in E. coli has three AT rich 13 base pair regions (DUE's elements) followed by five 9 bp regions. Around 10 dnaA molecules bind to the 9 bp regions, which wrap around the proteins causing the DNA at the AT-rich region to unwind. The denatured AT-rich region allows for the recruitment of DnaB (helicase) complexes with DnaC (helicase loader). DnaC helps the helicase to bind to and to properly accommodate the ssDNA at the 13 bp region, this is accomplished by ATP hydrolysis after which DnaC is released. Single-strand binding protein's (SSBs) stabilize the single DNA strands in order to maintain the replication bubble. DnaB is a 5'->3' helicase, so it travels on the lagging strand. It associates with DnaG (a primase) to form the only primer for the leading strand and to add RNA primers on the lagging strand. The interaction between DnaG and DnaB is necessary to control the longitude of Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand. DNA polymerase III is then able to start DNA replication.
DnaA contains two conserved regions: the first is located in the central part of the protein and corresponds to the ATP-binding domain, the second is located in the C-terminal half and could be involved in DNA-binding.
External links
References
- Voet, Donald; Voet, Judith; Pratt, Charlotte (2001). Fundamentals of Biochemistry. Wiley.
- Nelson, David L.; Cox, Michael M. (2008). "Principles of Biochemistry". Freeman.
This article includes text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR013159
This article includes text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR013317
Categories:- Genetics stubs
- Biochemistry stubs
- Biomolecules
- DNA replication
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
