- Discovery and development of TRPV1 antagonists
-
Chronic pain remains a recognized unmet medical need. Consequently, the search for new analgesic agents is being intensively studied by the pharmaceutical industry. The TRPV1 receptor is an ion channel that has been implicated in mediation of many types of pain and therefore studied most extensively. The first competitive antagonist, capsazepine, was first described in 1990, since then development of novel TRPV1 antagonists has come a long way. This effort has led to the identification of several TRPV1 antagonists that have entered clinical trials as analgesic agents. Should these new chemical entities relieve symptoms of chronic pain then this class of compounds may offer one of the first novel mechanisms for the treatment of pain, in many years.[1][2]
Contents
History
Capsaicin, the active ingredient in chilli pepper was first isolated over a century ago. In 1919 the exact chemical structure of capsaicin was determined and the complete synthesis of the compound was achieved a decade later. Capsaicin has been used as an analgesic for decades, but the therapeutic potential of capsaicin was first recognized as early as 1850.[3] The effects of the pungent chemical, capsaicin, is mediated through the ligand gated ion channel TRPV1. This knowledge set the stage for further research of the function of the TRPV1 receptor and preclinical studies showed evidence of its importance in numerous human diseases.[1][4] These are the first agents acting by this mechanism that made their way into clinic for evaluation of their use as possible analgesics and therefore important targets for drug development. Many discoveries are yet to be made, both in terms of the range of potential therapeutic applications in addition to analgesia for TRPV1 antagonists and it was only in the last decade where there has been a full understanding of the molecular mechanism. In the years to come it will be clearer if TRPV1 antagonists can fulfill their potential.[1][5][6]
Vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1/TRPV1 receptor)
The vanilloid receptor (TRPV1) is one of six sub-members that belong to the transient receptor potential channel (TRP) superfamily. TRPV1 was the first mammalian member to be discovered and is a non-selective cation channel permeable for calcium. The receptor is made of four identical subunits each with six transmembrane segments, S1-S6, and between fifth and sixth segment is an aqueous pore. This region forms the channel conductive pore and contains the N- and C-termini on the cytosolic side of the cell membrane.[7] Capsaicin and RTX, elicit burning pain by activating a non-selective cation channel expressed on sensory nerve endings. When capsaicin was found to have analgesic effects in preclinical studies much emphasis was put into the research of the receptor/channel that capsaicin binds to and activates.[8][9] Besides being activated by capsaicin, TRPV1 also responds to a wide range of exogenous and endogenous chemical ligands as well as physical stimuli such as heat over 42°C and changes in more diverse activators such as protons (acid, pH<6). TRPV1 is also subject to regulation by changes in membrane potential and this intrinsic voltage-dependence is thought to underlie the gating mechanism of this non-selective cation channel which leads to the influx of sodium and calcium ions. Importantly, TRPV1 activity is also subject to regulation by a host of intracellular signaling cascades such as G-protein coupled receptor signaling, that are implicated in the responses to algogenic agents, inflammatory mediators and injury.[1]
Mechanism of action
TRPV1 is primarily expressed on, small myelinated and unmyelinated medium size, sensory neurons in dorsal root and trigeminal ganglia, where sensory neurons cluster. TRPV1 receptors are also found in muscles, joints, the urinary bladder and kidneys. The functional activity of TRPV1 has been demonstrated, within the central nervous system, in the spinal cord and specific sites in the brain including the hypothalamus, cerebellum, locus coeruleus, periaqueductal grey and cortex. Activation of TRPV1 sets off an influx of calcium and sodium ions which in turn initiates a cascade of events that result in membrane depolarization, neuronal firing and transduction of neural impulses. TRPV1 phosphorylates as a response to several algesic agents, resulting in a lower threshold of channel activation. Some substances such as bradykinin, nerve growth factor and protons have been reported to sensitize the TRPV1 receptor. Activation of TRPV1 results in the release of pro-nociceptive peptides, which decreases when treated with TRPV1 antagonists. In general, most channel antagonists bind in the pore region, interacting with residues from all four monomers of the tetrameric channel.[2][10][11]
Binding
Ligands of the TRPV1 receptor seem to act from the intracellular side. This is a unique property of TRPV1, where ligands of other ligand-gated channels bind from the extracellular space. Capsaicin is highly lipophilic and can pass the plasma membrane easily. It is generally accepted that capsaicin acts on and binds to the TRPV1 receptor from the intracellular side prior to activation. The critical sites for capsaicin binding are Arg 114 and Glu 761 at the N- and C-termini of the receptor, respectively. Because these two amino acids are charged and located in the cytosolic part of TRPV1 receptor, the two regions are likely to be implicated in hydrophilic interaction of TRPV1 with vanilloids such as capsaicin and RTX. In addition to these sites in N- and C-termini of TRPV1, a region in the intracellular linker sited in the transmembrane domain, called ‘the TM3 region’, has been shown to be critical for hydrophobic interaction with vanilloids. The TM3 region is considered to be necessary for binding to vanilloids. It is surrounded by the hydrophobic environment because of its placement in the plasma membrane. Now it is recognized as an important link in hydrophobic interaction with capsaicin. The binding sites Arg 114 and Glu 761 and the TM3 region in TRPV1, together consist of a binding pocket to vanilloids.[10][2]
Drug design
Agonists
Capsaicin (fig. 2), a naturally occurring vanilloid, is the best known TRPV1 agonist. Resiniferatoxin (RTX) is another naturally occurring vanilloid that exhibits TRPV1 agonistic activity. It is more potent than capsaicin and is currently in development as a sensory neuron desensitizing agent.[7] Initially, agonists were the major focus of the TRPV1 ligand development due to the analgesic effect resulting from desensitization of the receptor. However, because of an initial burning effect of all natural vanilloid receptor agonists, including capsaicin, therapy becomes complicated and perhaps ineffective. Attempts to make synthetic agonists with good separation between excitatory effects and the analgesic effects have not been successful. To avoid this persisting side effects of TRPV1 agonists, a focused consideration has been given to competitive antagonists as novel analgesic drugs.[9]
Antagonists
Intense efforts have been carried out to design both competitive and non-competitive TRPV1 antagonists. Antagonists that bind to the agonist binding site, and lock the channel in the closed, nonconductive state are competitive antagonists. In contrast, antagonists that interact with additional binding sites on the receptor structure preventing receptor opening by the agonist or blocking its aqueous pore are non-competitive antagonists. Non-competitive antagonists acting as open channel blockers are therapeutically attractive because of their recognition of over-activated TRPV1 channels, which can reduce the potential of unwanted side effects.[7]
Pharmacophore
The pharmacophore model for TRPV1 antagonists consists of three essential features: a hydrogen-bond acceptor, a hydrogen-bond donor, and a ring feature. In addition, the TRPV1 antagonists have been superimposed in such a way that they could fit in the volume of the TRPV1 pore. When the homology model is considered, appropriate interaction sites are found in the receptor pore. The hydrogen-bond acceptor on the ligand is proposed to interact with Tyr 667 (helix S6) on the receptor as a hydrogen-bond donor, and the hydrogen-bond donor on the ligand is proposed to interact with Tyr 667 on the opposite monomer of the tetramer on the receptor as a hydrogen-bond acceptor. The ring feature of the pharmacophore is proposed to fit in the hydrophobic space formed by the aromatic rings of the four Tyr 667 residues of the four monomers. Consistent with the critical role played by Tyr 667 in the interaction with key elements of the TPRV1 antagonist pharmacophore, site-directed mutagenesis studies have shown that exchanging this tyrosine for alanine in the rat TRPV1 receptor abolishes functional activity of TRPV1. The lipophilic end in antagonist is varied in character and volume and interacts with the lower end of transmembrane helices S5 and S6. Because the intracellular ends of these helices extend past the membrane, they are likely to be flexible and may be part of the channel opening and closing process. The combined use of a pharmacophore model, assembled from highly optimized TRPV1 antagonists, with a homology model of the protein has enhanced understanding of the observed structure–activity relationships of many series of current TRPV1 antagonists, and should be useful in the discovery of new classes of antagonists.[2]
Structure activity relationship
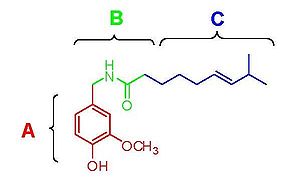
Capsaicin (fig. 2) has three functional regions: an aromatic A region where a parent homovanillyl (3-methoxy 4-hydroxybenzyl) group is optimal, a B region known as the ester or amide linker and the aliphatic C region where a lipophilic octanyl moiety is associated with the highest potency. The homovanillyl motif and amide bond regions contain dipolar groups which are implicated in hydrogen bonding interactions.[12]
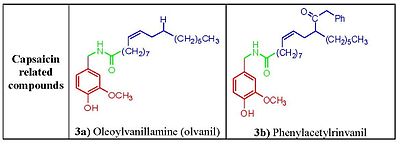
Phenolic hydroxide and amide moieties appear to be vital for inducing capsaicin responses. Removal of the phenolic hydroxide or amide bond in capsaicin analogues leads to reduction of potency. The phenolic hydroxide and amide moieties in capsaicin share potential multiple hydrogen bond interactions with the TRPV1 receptor. Capsaicinoids and capsinoids are characterized by an oxygenated aromatic moiety bound via an amide(capsaicinoids) or ester (capsinoids) linker to a lipophilic acyl group. The vanillyl and carbonyl linker contain polar groups capable of forming hydrogen bonds essential for activity, whereas the lipophilic moiety interacts with a corresponding cleft of the vanilloid binding site on TRPV1. Replacement of the medium-sized branched fatty acid of capsaicin with longer fatty acids is damaging for activity,[13] but the presence of unsaturations restores and potentiates activity e.g. oleoylvanillamine (olvanil)(fig. 3a), is 10-fold more potent than capsaicin in TRPV1 activation assays.[14]
1,3-Di(arylalkyl)thioureas
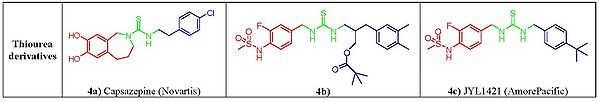
Capsazepine (fig. 4a), the first competitive vanilloid antagonist,[15][10] reported by Novartis group, was
aimed at assessing the effect of conformational constraint on the lipophilic C-region of capsaicin. In capsazepine the amide bond of the capsaicin is replaced by a thiourea moiety and a propylidene linker between the aromatic vanillyl 2-carbon A ring and the B-linker amide nitrogen forces the aromatic ring in an orthogonal orientation with respect to the thiourea bond.[16] This constraint has long been considered as the distinctive characteristic of vanilloid antagonism.[17] Capsazepine competes for the capsaicin-binding site on TRPV1 however, due to low metabolic stability and poor pharmacokinetic properties the compound did not reach into clinical development.[18] It was observed later on that this tether was not critical for activity as powerful antagonists free from this structural feature were developed, with 1,3-di(arylalkyl)thioureas emerging as one of the most promising non-vanilloid class of TRPV1 antagonist showing excellent therapeautical potential in pain regulation. Within these compounds, the replacement of the guaiacyl moiety of capsaicinoids with a 3-fluoro-4-sulfonylamido group found critical to revert activity. This, lead to the design of C-region moiety mimicked on RTX, led to compound seen in figure 4b,that showed excellent analgesic activity in mice.[19][20] An alternative optimization of the lipophilic C region led to JYL1421 (fig. 4c), another promising clinical candidate.[21]
Di(arylalkyl)- and Aryl(arylakyl)ureas
Several capsaicin analogs of the urea type were developed by acylation of homovanillylamine and related amines with different 4-(α-pyridyl)piperidine-1-acyl chlorides. The presence of a polar amino moiety in the hydrophobic C region of capsacinoids was crucial to couple potency and hydrophilicity, mimicking similar observations that led to the discovery of phenylacetylrinvanil (fig. 3b) from olvanil(fig. 3a). Phenylacetylrinvanil is the most potent capsaicinoid reported to date, ~500-fold more potent than capsaicin.[22] Several other ureas emerged as remarkably active TRPV1 antagonists. Compared with capsazepine, the piperazinyl urea (fig. 5a and 5b) showed a higher selectivity profile against a wide variety of enzymes and channels[23] whereas the related very potent and specific TRPV1 antagonist A-425619 (fig. 5c) could reduce pain associated with inflammation and tissue injury in rats.[24] Further research has led to a variety of small-molecule antagonists of TRPV1, including the ureas SB-705498 (fig. 5d), SB-452533 (fig. 5e)[16,17] and ABT-102(fig. 5f), compounds that have entered clinical trials.[25]
Cinnamides
N-Arylcinnamides have emerged as potent and important class of TRPV1 antagonists, Compound SB-366791, (fig. 6a) shows competitive and specific activity in both human and rat TRPV1 receptors overall profile of receptor selectivity much better than that of capsazepine.[26][27] Within this series of compounds, AMG9810 (fig. 6b) exhibited high antagonist potency showing good oral bio-availability in rats and a promising pharmacokinetic profile, boding well for clinical efficacy.[28] Another potent blocker from this group is AMG0347(fig. 6c)that was shown in a postoperative pain trial to be able to decrease capsaicin-induced heat and mechanical hyperalgesia and to block central TRPV1 receptors.[29]
Carboxamides
Several TRPV1 antagonists of the carboxamide type have been discovered. They are structurally quite heterogenous, as exemplified by comparison of the nicotinamide derivative SB-782443 (fig. 7a), the thiazolylcarboxamide (fig. 7b), and the tetrahydropyridylcarboxamide (fig. 7c).[30] SB-782443 (fig. 7a) showed excellent potency at human, guinea pig, and rat TRPV1, a favorable in vitro drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics profile, and remarkable in vivo activity in an inflammatory pain model.[31][32] Based on their in vitro profile, several compounds of this class qualified for preclinical development.[30]
Other derivatives
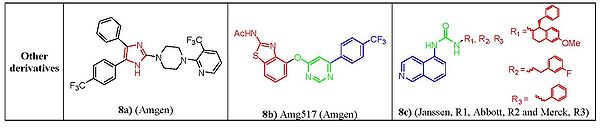
Nonclassic antagonists lack the urea, thiourea, or amide groups typical of the classic TRPV1 ligands. Two major structural types of nonclassic antagonists have been discovered. First there are the imidazole derivatives. Starting from a 4,6-disubstituted benzimidazole lead structure, a series of 4,5-biarylimidazoles capable to block both capsaicin and acid-induced calcium influx in TRPV1-expressing Chinese hamster ovary cells. Imidazole (fig. 8a) was identified as a highly potent and orally bioavailable TRPV1.[33] Another class are the diaryl ethers and amines. Compounds from a quinazoline series can be considered as conformationally restricted analogs of a biarylamide series. In terms of activity 5-isoquinoline was found the most active among and ranked in the order of 5-isoquinoline > 8-quinoline> 8-quinazoline> 8-isoquinoline≥ cinnoline> phthalazine> quinoxaline> 5-quinoline[34] e.g. AMG517 (fig. 8b),although it lacks any recognizable carbonyl motif it still potently blocks capsaicin, proton, and heat activation of TRPV1 in vitro and shows a good tolerability profile.[35] Also, the clinical candidates from Janssen, Abott and Merck pharmaceuticals (fig. 8c) having a 5-aminoisoquinoline group as a common feature suggesting that there is a key interaction of this group at the receptor site for TRPV1 antagonist activity.[34]
Current status
Clinical trials
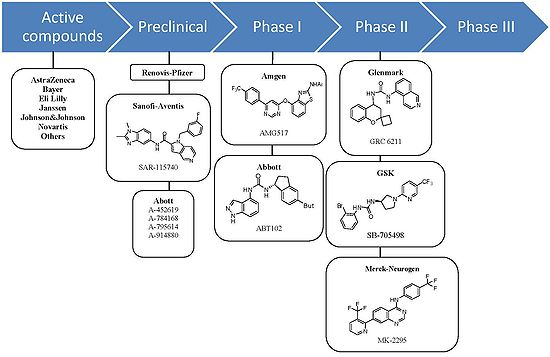
As of late 2009 no vanilloid receptor ligands are on the market but available public information suggests that quite a few are in clinical trials. Several biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies are developing TRPV1 ligands and the emphasis seems to be on both agonists and antagonists. Although the agonists appear to be further along in clinical development.[1]
Agonists NeurogesX has successfully completed three Phase III clinical studies of Qutenza (NGX-4010) that met studies primary endpoints. Qutenza is a synthetic trans-capsaicin and drug delivery is by a rapid-delivery patch application system[36] NeurogesX plans to launch Qutenza in the United States in the first half of November 2010.[37] Anesiva, another biotechnology company, has completed two Phase III trials of Adlea (ALGRX 4975), an injectable capsaicin. Adlea is promising as a pain reliever[38] and both trials showed that Adlea’s safety profile of adverse events, wound healing, and wound sensory function were similar to placebo over the study duration.[39]
Antagonists At least seven orally active TRPV1 antagonist substances have progressed into clinical development and several more are in preclinical development. The ligand GRC 6211, by Eli Lilly and Company-Glenmark is the most advanced and is currently in phase IIb clinical trials. GlaxoSmithKline, Merck-Neurogen, Amgen and AstraZeneca are all developing TRPV1 antagonist and all are developing substances that have completed phase I trials successfully.[1]
See also
- Vanilloid receptor TRPV
- Vanilloid receptor subtype 1 TRPV1
- Transient receptor potential channel
- Capsaicin
- Resiniferatoxin
- Capsazepine
References
- ^ a b c d e f Gunthorpe, M.; Chizh, B. (2009), "Clinical development of TRPV1 antagonists: targeting a pivotal point in the pain pathway", Drug Discovery Today 14: 56–67
- ^ a b c d Kym, P.R.; Kort, M.E.; Hutchins, C.W. (2009), "Analgesic potential of TRPV1 antagonists", Biochemical Pharmacology 78: 211–216
- ^ Szallasi, A.; Blumberg, P.M. (1999), "Vanilloid (Capsaicin) Receptors and Mechanisms", Pharmacological reviews 51: 1–53
- ^ Immke, D.C.; Gavva, N.R. (2006), "The TRPV1 receptor and nociception", Seminars in Cell & Developmental biology 17: 581–591
- ^ Rami, H.K.; Gunthorpe, M.J. (2004), "The therapeutic potential of TRPV1 (VR1) antagonists: clinical answers await", Drug Discovery Today: Therapeutic Strategies 1: 97–104
- ^ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedpmid19150372; see Help:Cite errors/Cite error references no text - ^ a b c Messeguer, A.; Planells-Cases, R.; Ferrer-Montiel, A. (2006), "Physiology and Pharmacology of the Vanilloid Receptor", Current Neuropharmacology. 4: 1–15
- ^ Wong, G.Y.; Gavva, N.R. (2009), "Therapeautic potential of vanilloid receptor TRPV1 angonists and antagonists as analgesics: Recent advances and setbacks", Brain Research Reviews 60: 267–277
- ^ a b Gomtsyan, A.; Bayburt, E.K.; Schmitd, R.G.; Zheng, G.Z.; Perner, R.J.; Didomenico, S.; Koenig, J.R. (2005), "Novel Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 Receptor Antagonists for the Treatment of Pain: Structure-Activity Relationship for Ureas with Quinoline, Isoquinoline, Quinazoline, Phtalazine, Quinoxaline and Cinnoline Moieties", J.Med.Chem. 48: 744–752
- ^ a b c Suh, Y.G.; Oh, U. (2005), "Activation and Activators of TRPV1 and Their Pharmaceutical Implication", Current Pharmaceutical Design 11: 2687–2698
- ^ Gunnthorpe, M.J.; Szallasi, A. (2008), "Peripheral TRPV1 Receptor As Targets for Drug Development: New Molecules and Mechanisms", Current Pharmaceutical Design 14: 32–41
- ^ Pearce, L.V.; Petukhov, P.A.; Szabo, T.; Kedei, N.; Bizik, F.; Kozikowski, A.P.; Blumberg, P.M. (2004), "Eviodiamine functions as an agonist for the vanilloid receptor TRPV1", Org.Biomol.Chem. 2: 2281–2286
- ^ Morita, A.; Iwasaki, M.A.; Kobata, K.; Higashi, T.; Oda, K.; Suzuki, A. (2006), "Lipophilicity of capsaicinoids and capsinoids influences the multiple activation process of rat TRPV1", Life Sci. 79: 2303–2310
- ^ Vriens, J.; Appendino, B.; Nilius (2009), "Pharmacology of Vanilloid Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channels", Molecular Pharmacology 75: 1262–1279
- ^ Suh, Y.G.; Lee, Y.S.; Min, K.H.; Park, O.H.; Kim, J.K.; Seung, H.S. (2005), "Novel potent antagonists of transient receptor potential channel, vanilloid subfamily member 1: structure-activity relationship of 1,3-diarylalkyl thioureas possessing new vanilloid equivalents.", J.Med.Chem. 48: 5823–5836
- ^ Szallasi, A.; Appendino, G. (2004), "Vanilloid Receptor TRPV1 Antagonists as the Next Generation Painkillers. Are We Putting the Cart before the Horse?", Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 47: 2717–2723
- ^ Tominaga, M.; Malmberg, A.B.; Rosen, T.A.; Gilbert, H.; Skinner, K.; Rau-mann, B.E. (1998), "The cloned capsaicin receptor inte-grates multiple pain-producing stimuli", Neuron 21: 531–543
- ^ Walker, K.M.; Medhurst, S.J.; Patel, S.; Panesar, M.; Fox, A.J.; McIntyre, P. (2003), "The VR1 antagonist capsazepine reverses mechanical hyperalgesia in models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain", Pharmacol.Exp.Ther 304: 56–62
- ^ Lee, J.; Kang, M.; Shin, S.U.; Kim; Kang; Lim, J.O.; et al (2003), "N-(3-acyloxy-2-benzylpropyl)-N´-[4-methylsulfonylamino)ben-zyl]thiourea analogues: novel potent and high affinity antagonists and partialantagonists of the vanilloid receptor", Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 46: 3116–3126
- ^ Lee, J.; Kang, S.U.; Kil, M.J.; Shin, M.; Lim, J.O.; Choi, H.K.; et al (2005), "Analysis of structure-activity relationships for the ‘A-region’ of N-(4-t-butylbenzyl)-N´-[4-(methylsulfonylamino)benzyl]thiourea analogues as TRPV1 antagonists", Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 15: 4136–4142
- ^ Wang, Y.; Szabo, T.; Welter, R.; Toth; Tran; Lee, J.; et al (2002), "High affinity antagonists of the vanilloid receptor", Mol. Pharmacol. 62: 947–956
- ^ Appendino, G.; DePetrocellis, A.S; Trevisani, M.; Minassi, A.; Daddario, N.; Moriello (2005), "Development of the first ultra-potent “capsaicinoid” agonist at transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) channels and its therapeutic potential", J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther 312: 561–570
- ^ Pomonis, J.D.; Harrison, J.E.; Bristol, D.R.; Valenzano, K.J.; Walker, K. (2003), "N-(4-tertiarybutylphenyl)-4-(3-cholorphyridin-2-yl)tetrahydropyrazine-1(2H)- carbox-amide (BCTC), a novel, orally effective vanilloid receptor 1 antagonist with analgesic properties: II. in vivo characterization in rat models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain", J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther 306: 387–393
- ^ McDonald, H.A.; Neelands, T.R .; Kort, M.; Han, P.; Vos, M.H.; Faltynek, C.R (2008), "Characterization of A-425619 at native TRPV1 receptors: a comarison between dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia", Eur. J. Pharmacol. 596: 62–69
- ^ Surowy, C.S.; Neelands, T.R .; Bianchi, B.R.; McGaraughty, S.; El Kouhen, R.; Han, P. (2008), "ABT-102 ((R)-(5-tert-butyl- 2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-yl)-3-(1H-indazol-4-yl)-urea) blocks polymodal activation of TRPV1 receptors in vitro and heat-evoked firing of spinal dorsal horn neurons in vivo", J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 326: 879–888
- ^ Gunthorpe, M.J.; Rami, H.K.; Jerman, J.C.; Smart, D.; Gill, C.H.; Soffin, E.M. (2004), "Identification and characterisation of SB-366791, a potent and selective vanilliod receptor (VR1/TRPV1) antagonist", Neuropharmacology. 46: 133–149
- ^ Patwardhan, A.M.; Jeske, N.A.; Price, T.J.; Gamper, N.; Akopian, A.N.; Hargreaves, K.M. (2006), "The cannabinoid WIN 55,212–2 inhibits transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) and evokes peripheral antihyperalgesia via calcineurin", Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci USA 103: 11393–11398
- ^ Doherty, E.M; Fotsch, C.; Bo, Y.; Chakrabarti, P.P.; Chen, N.; Gavva, N. (2005), "Discovery of potent, orally available vanilloid receptor-1 antagonists. Structure activity relationship of N-aryl cinnamides", Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 48: 71–90
- ^ Wu, C.; Gavva, N.R; Brennan, T.J (2008), "Effect of AMG0347, a transient receptor potentioal type V1 receptor antagonist, and morphine on pain behaviour after platarincision", Anesthesiology 108: 1100–1108
- ^ a b Westaway, S.M.; Brown, S.L; Conway, E.; Heightman, T.D.; Johnson, C.N.; Lapsley, K. (2008), "The discovery of biaryl carboxamides as novel small molecule agonists of the motilin receptor", Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 18: 6429–6436
- ^ Westaway, S.M.; Chung, Y.K.; Stevens, A.J.; Thompson, M. (2006), "N-Tetrahydroquinolinyl, N-quinolinyl andN-isoquinolinyl biaryl carboxamides as antagonists of TRPV1", Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 16: 4533–4536
- ^ Brown, B.S.; Keddy, R.; Zheng, G.Z.; Schmidt, R.G.; McDonald, H.A.; Bianchi, B.R. (2008), "Tetrahydropyridine-4-carboxamides as novel, potent transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) antagonists", Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 16: 8516–8525
- ^ Gore, V.K.; Ma, V.V.; Tamir, J.J.; Gavva; Treanor; Norman, M.H. (2007), "Structure-activity relationship (SAR) investigations of substituted imidazole analogs as TRPV1 antagonists", Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17: 5825–5830
- ^ a b Blum, C.A.; Zheng, X.; Brielmann, H.; Hodgetts, K.J.; Bakthavatchalam, R.; Chandrasekhar, J.; et al (2008), "Aminoquinazolines as TRPV1 antagonists: modulation of drug-like properties through the exploration of 2-position substitution", Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett. 18: 4573–4577
- ^ Gavva, N.R.; Bannon, A.W.; Hovland, D.N.; Lehto, S.G.; Klionsky, L.; Surapaneni, S.; et al (2007), "Repeated administration of vanilloid receptor TRPV1 antagonists attenuates hyperthermia elicited by TRPV1 blockade", J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.. 323: 128–137
- ^ http://www.neurogesex.com
- ^ http://www.bio-medicine.org
- ^ Aids, T. (2009), "Capsaicin: Risks and Benefits", US Pharm 7: 20
- ^ http://www.anesiva.com
Drug design steps in design Case studies of discovery and development of drug classes triptans · cephalosporins · antiandrogens · Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitors · nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors · melatonin receptor agonists · proton pump inhibitors · angiotensin receptor blockers · dual serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors · cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors · TRPV1 antagonistsCategories:- Analgesics
- Drug discovery
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.