- Dihydropteroate synthase
-
Dihydropteroate synthase 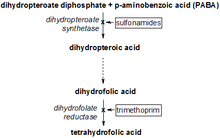
Tetrahydrofolate synthesis pathway Identifiers EC number 2.5.1.15 CAS number 9055-61-2 Databases IntEnz IntEnz view BRENDA BRENDA entry ExPASy NiceZyme view KEGG KEGG entry MetaCyc metabolic pathway PRIAM profile PDB structures RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum Gene Ontology AmiGO / EGO Search PMC articles PubMed articles Pterin binding enzyme Identifiers Symbol Pterin_bind Pfam PF00809 InterPro IPR000489 PROSITE PDOC00630 SCOP 1ajz Available protein structures: Pfam structures PDB RCSB PDB; PDBe PDBsum structure summary Dihydropteroate synthetase is an enzyme classified under EC 2.5.1.15. It produces dihydropteroate in bacteria, but it is not expressed in most eukaryotes including humans. This makes it a useful target for sulfonamide antibiotics, which compete with the PABA precursor.
- (2-amino-4-hydroxy-7,8-dihydropteridin-6-yl)methyl diphosphate + 4-aminobenzoate (PABA)
 diphosphate + dihydropteroate.
diphosphate + dihydropteroate.
All organisms require reduced folate cofactors for the synthesis of a variety of metabolites. Most microorganisms must synthesize folate de novo because they lack the active transport system of higher vertebrate cells that allows these organisms to use dietary folates. Proteins containing this domain include dihydropteroate synthase (EC 2.5.1.15) as well as a group of methyltransferase enzymes including methyltetrahydrofolate, corrinoid iron-sulphur protein methyltransferase (MeTr) Q46389 that catalyses a key step in the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway of carbon dioxide fixation.
Dihydropteroate synthase (EC 2.5.1.15) (DHPS) catalyses the condensation of 6-hydroxymethyl-7,8-dihydropteridine pyrophosphate to para-aminobenzoic acid to form 7,8-dihydropteroate. This is the second step in the three-step pathway leading from 6-hydroxymethyl-7,8-dihydropterin to 7,8-dihydrofolate. DHPS is the target of sulphonamides, which are substrate analogues that compete with para-aminobenzoic acid. Bacterial DHPS (gene sul or folP)[1] is a protein of about 275 to 315 amino acid residues that is either chromosomally encoded or found on various antibiotic resistance plasmids. In the lower eukaryote Pneumocystis carinii, DHPS is the C-terminal domain of a multifunctional folate synthesis enzyme (gene fas)[2].
References
- ^ Crawford IP, Slock J, Stahly DP, Six EW, Han CY (1990). "An apparent Bacillus subtilis folic acid biosynthetic operon containing pab, an amphibolic trpG gene, a third gene required for synthesis of para-aminobenzoic acid, and the dihydropteroate synthase gene". J. Bacteriol. 172 (12): 7211–7226. PMID 2123867.
- ^ Volpe F, Dyer M, Scaife JG, Darby G, Stammers DK, Delves CJ (1992). "The multifunctional folic acid synthesis fas gene of Pneumocystis carinii appears to encode dihydropteroate synthase and hydroxymethyldihydropterin pyrophosphokinase". Gene 112 (2): 213–218. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(92)90378-3. PMID 1313386.
External links
Transferases: alkyl and aryl (EC 2.5) 2.5.1 Dimethylallyltranstransferase - Thiaminase I - Methionine adenosyltransferase - Riboflavin synthase - Dihydropteroate synthase - Spermidine synthase - Glutathione S-transferase - Farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase - Spermine synthase - Alkylglycerone phosphate synthase - Farnesyltransferase - Geranylgeranyltransferase type 1 - Porphobilinogen deaminaseB enzm: 1.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8/10/11/13/14/15-18, 2.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8, 2.7.10, 2.7.11-12, 3.1/2/3/4/5/6/7, 3.1.3.48, 3.4.21/22/23/24, 4.1/2/3/4/5/6, 5.1/2/3/4/99, 6.1-3/4/5-6 Metabolism of vitamins, coenzymes, and cofactors Fat soluble vitamins Alpha-tocopherol transfer proteinliver (Sterol 27-hydroxylase or CYP27A1) · renal (25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 1-alpha-hydroxylase or CYP27B1) · degradation (1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 24-hydroxylase or CYP24A1)Water soluble vitamins Thiamine (B1)Niacin (B3)Pantothenic acid (B5)Folic acid (B9)Dihydropteroate synthase · Dihydrofolate reductase · Serine hydroxymethyltransferase
Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductaseRiboflavin (B2)Nonvitamin cofactors M: NUT
cof, enz, met
noco, nuvi, sysi/epon, met
drug(A8/11/12)
This article includes text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR000489
This enzyme-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. - (2-amino-4-hydroxy-7,8-dihydropteridin-6-yl)methyl diphosphate + 4-aminobenzoate (PABA)
