- Labia
-
This article is about the part of the female external genitalia. For other uses, see Labium.
The labia are anatomical structures that are part of the female genitalia; they are the major externally visible portions of the vulva. In humans, there are two pairs of labia: the outer labia, or labia majora are larger and fattier, while the labia minora are folds of skin often concealed within the outer labia. The labia surround and protect the clitoris and the openings of the vagina and urethra.
Contents
Etymology
Labium (plural labia) is a Latin-derived term meaning "Lip". Labium and its derivatives (including labial, labrum) are used to describe any lip-like structure, but in the English language, labium often specifically refers to parts of the vulva.
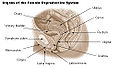
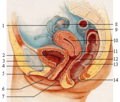
Anatomy and medical
The labia majora are lip-like structures consisting mostly of skin and adipose tissue, which extend on either side of the vulva to form the pudendal cleft through the middle.
When standing or with the legs together, they usually entirely or partially cover the other parts of the vulva. Protection is the main function. The labia majora are homologous to the scrotum in males.
The labia minora (obsolete: nymphae) are two soft folds of skin between the labia majora and to either side of the opening of the vagina. The clitoris is anterior to the vulva where the labia minora meet superiorly. The visible tip of the clitoris, the clitoral glans, is entirely or partially covered by a "hood" of tissue (the clitoral hood).
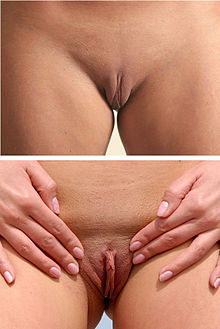
The coloration, size and general appearance of the labia can vary extensively from woman to woman.[1] In some women the labia minora are almost non-existent, and in others they can be fleshy and protuberant. Usually, but not always, they are symmetrical. Some differences are purely personal, while others may be genetically linked; a striking example of the latter is the elongated labia minora of the Khoisan peoples, whose "khoikhoi aprons" can hang down up to 10 cm (four inches) past their labia majora when they are standing.
During sexual arousal, the labia minora become engorged with blood, typically swelling slightly and darkening or reddening in color.
- frontal view
- detailed view
Social and cultural considerations
In many cultures and locations all over the world, the labia, as part of the genitalia, are considered private, or intimate parts, whose exposure (especially in public) is governed by fairly strict socio-cultural mores. In many cases, public exposure is limited, and often prohibited by law.[2][3]
Labiaplasty is a controversial plastic surgery procedure that involves the creation or reshaping of the labia. The clinical procedure of labiaplasty alters the appearance of the labia, for cosmetic or medical reasons.
In some cultures, any of several areas of the female genitals are surgically altered or removed for religious, cultural, or hygienic purposes. Terms for these types of procedures include female circumcision, Pharaonic circumcision, intubation, infibulation, and female genital mutilation or cutting.[4][5] In many parts of the world the practice is believed to have ancient origins, but even in countries where it has been widespread in the past, it is now mostly illegal.
Labia piercing is a cosmetic piercing, usually with a special needle under sterile conditions, of either the inner labia (labia minora) or the outer labia (labia majora). Jewelry is worn in the resulting opening.
Additional images
See also
- Penis
- Vulva
- Pudendal cleft
- Labia stretching
- Labia piercing
- Lip
- WikiSaurus:labia — the WikiSaurus list of synonyms and slang words for the labia in many languages
References
- ^ Femalia. Joani Blank. 978-0940208155
- ^ 617.23, Minnesota Statute
- ^ 18-4116 — INDECENT EXPOSURE - Idaho 18-4116 — INDECENT EXPOSURE - Idaho Code :: Justia
- ^ http://www.emro.who.int/publications/Book_Details.asp?ID=58%7CWorld Health Organization website
- ^ Female Genital Mutilation (FGM) - Terminology and the main types of FGM
External Links
 Media related to Labia (genitalia) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Labia (genitalia) at Wikimedia Commons
Female reproductive system (TA A09.1–2, TH H3.07.01, GA 11.1254) Internal Adnexacorpus (hemorrhagicum, luteum, albicans) · Theca of follicle (externa, interna) · Follicular antrum (Follicular fluid) · Corona radiata · Zona pellucida · Membrana granulosa · Perivitelline spaceOtherProper of ovary · Suspensory of ovarycorpus/body (Uterine cavity, Fundus) · cervix/neck (External orifice, Canal of the cervix, Internal orifice, Supravaginal portion of cervix, Vaginal portion of cervix, Cervical ectropion) · Uterine hornsGeneralExternal Mons pubis · Labia majora (Anterior commissure, Posterior commissure) · Pudendal cleft · Labia minora (Frenulum of labia minora, Frenulum of clitoris) · Vulval vestibule · Interlabial sulci · Bulb of vestibule · Vaginal orifice
vestibular glands/ducts (Bartholin's glands/Bartholin's ducts, Skene's glands/Skene's ducts)Other Categories:- Female reproductive system
- Sexual anatomy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.