- Criticism of the Book of Mormon
-
Part of a series on The Book of Mormon 
Origin Angel Moroni · Golden plates
Joseph Smith · Oliver Cowdery
Book of Mormon witnesses Reformed EgyptianHistorical authenticity
and criticismAnachronisms · Archaeology
Genetics · Linguistics
Limited geography modelProphets and People Jesus
Abinadi · Ammon
Alma (elder) · (younger)
King Benjamin
Brother of Jared
Samuel the Lamanite
Captain Moroni · Enos
Helaman · Lehi · Nephi
Mormon · Moroni Book of Mormon Portal
Book of Mormon PortalThe Book of Mormon, published in 1830 by American religious leader Joseph Smith (who claimed it to be a translation of an ancient Native American record), is the subject of criticism relating to its origin, text, and historical accuracy.
Contents
Ancient origin
Main articles: Origin of the Book of Mormon and Book of Mormon witnessesCritics reject Smith's explanation of the origin of the Book of Mormon. Joseph Smith said that the Book of Mormon was originally an ancient native-American record written on golden plates, and that God gave him the power to translate it into English. Critics note that there is no physical proof of the existence of golden plates; Smith said that the angel Moroni reclaimed the plates once he had completed the translation. Smith acquired affidavits from 11 men, known as the Book of Mormon witnesses, claiming that they had been shown the plates; their testimony is typically published at the beginning of the Book of Mormon. While none of these men ever retracted their statement, critics nevertheless discount these testimonies for varying reasons, primarily because most of these men were closely interrelated.
Critics deny that the Book of Mormon is of ancient origin. They assert that portions of the Book of Mormon were plagiarized from modern publications of Smith's time, including the King James Bible,[1][2] The Wonders of Nature,[3][4] View of the Hebrews,[5][6][7] and an unpublished manuscript written by Solomon Spalding.[8][9][10] Critics have varying theories about the true authorship of the Book of Mormon, but most conclude that Smith fabricated it himself, or possibly with the aid of Oliver Cowdery.
Text and language
Main articles: Reformed Egyptian and Linguistics and the Book of MormonCritics view the language patterns, phrases, and names in the Book of Mormon as evidence that it is not authentic.
Joseph Smith claimed that he translated the Book of Mormon from a language called Reformed Egyptian. Archaeologists and Egyptologists, however, have found no evidence that this language ever existed. Furthermore, the Book of Mormon implies that at least some native Americans came from the Jerusalem area; however, Native American linguistic specialists have not found any native American language that appears to be related to languages of the ancient Near East.
Critics claim that language patterns in the Book of Mormon indicate that it is merely a repetition of rhetorical patterns found in the Old Testament. They point out that the Book of Mormon contains many words and phrases that are not consistent with the time frame or location of the stories included in the book. Supporters of the Book of Mormon note its repeated use of chiasmus—a figure of speech utilizing inverted parallelism—and claim it is evidence to support the book's ancient origin. Critics argue that while chiasmus appears in short form within ancient classical works of Rome, the complex stylization of these passages found in the Book of Mormon is more similar to that found in works of the Renaissance and into the 18th/19th centuries. There is no evidence of chiasmus in the ancient literature of the Near East or within the known rhetoric of ancient Native American cultures.
Some critics theorize that Smith derived the account of the golden plates from treasure-hunting stories of William Kidd. Critics base this theory on the similarity of the names from Smith's account—Moroni and Cumorah—to the location Moroni, Comoros, related to Kidd's hunt for treasure. Apologists argue that it was unlikely that Smith had access to this material.
Further information: Angel Moroni #Theorized origin of the name and Cumorah #Alternative origin of the nameHistorical accuracy
Main article: Historicity of the Book of MormonCritics discredit the historical accuracy of the Book of Mormon. They note various issues, including anachronisms, geographical inconsistencies, and lack of genetic evidence.
Anachronisms
Main article: Book of Mormon anachronismsCritics point out that the Book of Mormon contains references to various plants and animals (horses, swine, etc) that did not exist in the Americas at the time of the story. Critics also point out that the Book of Mormon contains references to various technologies (chariots, steel, etc) that did not exist in the Americas at the time of the story.
Apologists offer varying views on these anachronisms, typically countering them in one of two ways. One claim is that archaeological evidence may exist that has not yet been found. Another is that Joseph Smith used English words in a generic way, sometimes referring to an item other than that which the direct English word would imply.
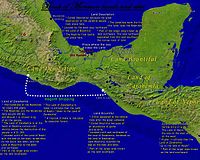
Geography
Main article: Archaeology and the Book of MormonCritics point out that there are many inconsistencies and implausibilities in the story of the Israelites coming from the Mid-East to the Americas, and in the geographical descriptions of the lands in the Americas in which the stories take place.
Native Americans and genetics
Main article: Genetics and the Book of MormonThe Book of Mormon suggests that the Native Americans are descended from people who came to the Americas by boat from the Middle East. However, scientists have used techniques involving genetic markers to conclude that Native American genes are of Asian, not Middle Eastern in origin. Apologists argue that the Middle Eastern genes in Native Americans may have been diluted beyond what can now be detected; there is currently no way to verify this claim with genetic evidence.
Divine nature of the book
 Egyptologists' translations of these fragments of the Joseph Smith Papyri do not coincide with Smith's translation.
Egyptologists' translations of these fragments of the Joseph Smith Papyri do not coincide with Smith's translation. Further information: Book of Abraham and Book of Mormon #Textual criticism
Further information: Book of Abraham and Book of Mormon #Textual criticismCritics reject the belief that the Book of Mormon is of divine origin; they discredit the book's divine origin by discrediting Joseph Smith. Critics point out that Joseph Smith also translated the Book of Abraham. Unlike the Book of Mormon, fragments of the documents from which Smith translated the Book of Abraham are available for inspection; Egyptologists find no resemblance between the original text and Smith's translation, casting doubt on Smith's claimed divine gift of translation.
Critics also discredit the divine origin of the Book of Mormon by noting the numerous revisions that have been made to the text. [5] [6] [11] [12][13][14][15] Though most changes are small spelling and grammar corrections,[16] critics claim that even these are significant in light of Smith's claims of divine inspiration.[17] Critics assert that some of these changes were systematic attempts to hide the book's flaws.[18][19]
See also
- Criticism of Mormon sacred texts
- Criticism of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
- Criticism of Mormonism
- Book of Mormon anachronisms
References
- Smith, Andrew F. (1971), The Saintly Scoundrel: The Life and Times of Dr. John Cook Bennett, Urbana and Chicago: University of Illinois Press, p. 141, ISBN 9780252022821, http://books.google.com/?id=BWM7yHuIyAUC&pg=PA113&vq=abortion&dq=The+Saintly+Scoundrel:+The+Life+and+Times+of+Dr.+John+Cook+Bennett.
- Tanner, Jerald and Sandra (1979), The Changing World of Mormonism, Moody Press, ISBN 0802412343
- Tanner, Jerald and Sandra (1987), Mormonism - Shadow or Reality?, Utah Lighthouse Ministry, ISBN 9993074438
- Twain, Mark (1872), Roughing It
- Wymetal, Wilhelm Ritter von (1886), Joseph Smith, the Prophet, His Family, and His Friends: A Study Based on Facts and Documents, Salt Lake City, UT: Tribune Printing and Publishing Company, pp. 60–61, http://olivercowdery.com/smithhome/1886WWyl.htm#pg061a.
Notes
- ^ Abanes, Richard (2003), One Nation Under Gods: A History of the Mormon Church, Thunder's Mouth Press, pp. 72, ISBN 1568582838
- ^ Tanner, Jerald and Sandra (1987), Mormonism - Shadow or Reality?, Utah Lighthouse Ministry, pp. 73–80, ISBN 9993074438
- ^ Abanes, Richard (2003), One Nation Under Gods: A History of the Mormon Church, Thunder's Mouth Press, pp. 68, ISBN 1568582838
- ^ Tanner, Jerald and Sandra (1987), Mormonism - Shadow or Reality?, Utah Lighthouse Ministry, pp. 84–85, ISBN 9993074438
- ^ a b Brody, Fawn (1971), No Man Knows My History: The Life of Joseph Smith (2d ed.), New York: Alfred A. Knopf
- ^ a b Krakauer, Jon (2003), Under the Banner of Heaven: A Story of Violent Faith, New York: Doubleday
- ^ Roberts, Brigham H. (1992), Brigham D. Madsen, ed., Studies of the Book of Mormon, Salt Lake City, UT: Signature Books, ISBN 9781560850274, ISBN 1-56085-027-2, http://books.google.com/?id=EXgFAAAACAAJ&dq=Studies+of+the+Book+of+Mormon
- ^ Howe, Eber D (1834), Mormonism Unvailed, Painesville, Ohio: Telegraph Press, http://www.solomonspalding.com/docs/1834howb.htm
- ^ Spaulding, Solomon (1996), Reeve, Rex C, ed., Manuscript Found: The Complete Original "Spaulding" Manuscript, Provo, Utah: Religious Studies Center, Brigham Young University
- ^ Roper, Matthew (2005), "The Mythical "Manuscript Found"", FARMS Review (Provo, Utah: Maxwell Institute) 17 (2): 7–140, http://farms.byu.edu/display.php?table=review&id=584, retrieved 2007-01-31
- ^ Abanes, Richard (2003), One Nation Under Gods: A History of the Mormon Church, Thunder's Mouth Press, pp. 73, ISBN 1568582838
- ^ Beckwith, Francis (2002), The New Mormon Challenge, Zondervan, pp. 367–396, ISBN 0310231949
- ^ Cowan, Marvin (1997), Mormon Claims Answered
- ^ There have been numerous changes to the text of the Book of Mormon between the 1830 edition and modern LDS editions, almost four thousand changes according to one count at 3913 Changes in The Book of Mormon Jerald and Sandra Tanner
- ^ "Criticism of changes to Book of Mormon". http://www.utlm.org/onlinebooks/3913intro.htm.
- ^ The majority of these changes are spelling and grammar corrections: http://www.lightplanet.com/mormons/response/qa/bom_changes.htm
- ^ Critics claim that even changes in spelling and grammar are important when considering the claims concerning the translation which were made by Joseph Smith and the witnesses to the book (Smith claimed that the Book of Mormon was "the most correct of any book on earth," and Martin Harris said that the words which appeared on the seer stone would not disappear until they were correctly written): J. and S. Tanner, The Changing World of Mormonism, p. 132
- ^ Some critics claim that some revisions are systematic attempts to remove evidence that Joseph Smith fabricated the Book of Mormon, and other revisions were made to hide embarrassing aspects of the church's past: Abanes, Richard (2003), One Nation Under Gods: A History of the Mormon Church, Thunder's Mouth Press, pp. 59–80, ISBN 1568582838
- ^ Tanner, Jerald and Sandra (1987), Mormonism - Shadow or Reality?, Utah Lighthouse Ministry, pp. 50–96, ISBN 9993074438
The Latter Day Saint movement Fundamental ideas Mormonism · Latter Day Saint · Mormonism and Christianity · Mormon Fundamentalism · Latter Day Saint denominations · List of sects · Mormon studies
History Sacred texts Founders & leaders Doctrines & practices Views on Godhead · Views on Jesus · Priesthood · Articles of Faith · Restoration · Mormonism and Judaism · Temples
Controversies Criticism · Joseph Smith, Jr. and polygamy · Blacks and the Latter Day Saint movement · Oath of vengeance · Mountain Meadows massacre · Historicity of the Book of Mormon
See also Latter Day Saints Portal – Category Mormonism Categories:- Criticism of Mormonism
- Book of Mormon
- Pre-Columbian trans-oceanic contact
- 19th-century Christian texts
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.