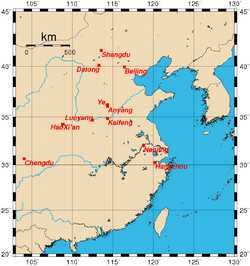
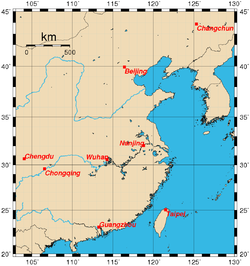
- Historical capitals of China
-
The Chinese phrase Four Great Ancient Capitals of China (simplified Chinese: 中国四大古都; traditional Chinese: 中國四大古都; pinyin: Zhōngguó Sì Dà Gǔdū) traditionally refers to Beijing (the current capital of the People's Republic), Nanjing, Luoyang, and Chang'an (Xi'an).
Due to additional evidence discovered since the 1930s, other historical capitals have been included in the list. The later phrase Seven Ancient Capitals of China includes Kaifeng (added in the 1920s as the fifth ancient capital), Hangzhou (the sixth, added in the 1930s), and Anyang (a proposal by numerous archaeologists in 1988, after which it finally became the seventh ancient capital). In 2004, the China Ancient Capital Society officially added Zhengzhou as an eighth due to archaeological finds from the early Shang Dynasty there.
Contents
List of historical capitals of China
In alphabetical order:
- Anyang was the capital during the Yin period of the Shang Dynasty (estimated between 1600 BC and 1046 BC): called Yin (殷, pinyin: Yīn).
- Beijing (formerly Romanized as Peking, from Chinese Postal Map Romanization (CPMR); briefly known as Peip'ing in Wade-Giles (WG) or Běipíng in pinyin (py)) was and has been the capital of various Chinese governments including (sorted chronologically):
-
- State of Yan (Yen in WG) in Spring and Autumn Period (722-481 BC): called Ji (薊, pinyin: Jì).
-
- Liao Dynasty (907-1125), as a secondary capital: called Yanjing (燕京, pinyin: Yānjīng, "capital of Yan").
-
- Jin Dynasty (1115-1234) from Emperor Shizong until 1215: called Zhongdu (中都, pinyin: Zhōngdū, "central capital").
-
- Yuan Dynasty (1271 to 1368): called Dadu (大都, pinyin: Dàdū, "great capital") in Chinese, Daidu (a direct transliteration from Chinese[1]) in Mongolian and Khanbaliq ("city of the Khan") in the Turkic languages. This was reported as "Cambuluc" by Marco Polo.
-
- Ming Dynasty from the time of the Ming Yongle Emperor (r. 1402/1424) until 1644 called Jīngshī (京師,"capital").
-
- Qing Dynasty from the fall of the Ming in 1644 to the end of the dynasty in 1912.
-
- The Beiyang Government of the Republic of China.
-
- The current capital of the People's Republic of China.
- Chengdu (WG: Ch'eng-tu) was the capital of the Shu Kingdom during the period of the Three Kingdoms. It was briefly the seat of Chiang's ROC government during the Chinese civil war with the Communist Party of China.
- Chongqing (CPMR: Chungking) was the provisional capital of the government of Chiang Kai-shek during World War II (Second Chinese-Japanese War), and was briefly the seat of Chiang's ROC government during the Chinese civil war with the Communist Party of China.
- Guangzhou (formerly Romanized Canton from CPMR)
-
- Republic of China: it was seat of the National Government before the Northern Expedition, and was briefly the seat of Chiang's ROC government during the Chinese civil war with the Communist Party of China.
- Hangzhou (also Hangchou or Hangchow) was the capital of:
-
- The Wuyue Kingdom (904-978), during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period.
-
- China during the Southern Song Dynasty: called Lin'an (臨安 Lín'ān).
- Fenghao was the capital during the Western Zhou Dynasty, located near present day Xi'an.
- Kaifeng was the capital of various Chinese governments including (sorted chronologically):
-
- Later Liang Dynasty during the Period of Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms.
-
- Later Jin Dynasty during the Period of Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms.
-
- Later Han Dynasty during the Period of Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms.
-
- Later Zhou Dynasty during the Period of Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms.
-
- Northern Song Dynasty: called Dongjing (東京 Dōngjīng).
- Luoyang was the capital of various Chinese governments including (sorted chronologically):
-
- Eastern Zhou Dynasty
-
- Eastern Han Dynasty from 25 to 220
-
- Kingdom of Wei during the Three Kingdoms.
-
- Western Jin Dynasty
-
- Northern Wei Dynasty since 493, moved its capital from Datong.
-
- Later Tang Dynasty during the Period of Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms.
- Nanjing (formerly Romanized Nanking (CPMR) or Nanching in WG) was the capital of various Chinese governments including (sorted chronologically):
-
- all of the Six Dynasties: called Jianye (建業 Jiànyè) or Jiankang (建康 Jiànkāng). The Six Dynasties are:
-
-
- Kingdom of Wu during the Three Kingdoms.
-
-
-
- Eastern Jin Dynasty
-
-
-
- Southern Qi Dynasty
-
-
- Ming Dynasty before Yongle Emperor moved the capital to Beijing.
-
- Taiping Tianguo (Heavenly Kingdom of Great Peace and Prosperity) during the Taiping Rebellion. Known as Tianjing (天京,literally 'Heavenly Capital') between 1853 and its fall in 1864.
-
- Republic of China after the Northern Expedition until the Japanese invasion in 1937 of WWII, and after the war until Chiang Kai-Shek retreated to Taiwan in 1949.
-
- Wang Jingwei's pro-Japanese collaborationist government.
- Taipei has been the de-facto capital of the Republic of China (Taiwan) since 1949.
- Wuhan was the capital of a leftist Kuomintang government led by Wang Jingwei in opposition to Chiang Kaishek during the 1920s.
- Xanadu (Shangdu) (上都) was the summer capital of Kublai Khan's empire.
- Xi'an (WG: Hsi'an; called Chang'an in ancient times) was the capital of various Chinese governments including (sorted chronologically):
-
- Western Zhou Dynasty, also see Fenghao.
-
- State of Qin in the Spring and Autumn Period and the Qin Dynasty 221 BC-207 BC: Xi'an is located near the former Qin capital Xianyang (咸陽 Xiányáng).
-
- Western Han Dynasty from 206 BC to AD 9
-
- Xin Dynasty from 8 to 23
-
- Eastern Han Dynasty
-
- Western Jin Dynasty
-
- State of Former Zhao, a state in the Sixteen Kingdoms period during the Jin Dynasty (265-420).
-
- State of Former Qin from 351 to 394, during the Sixteen Kingdoms period.
-
- State of Later Qin from 384 to 417, during the Sixteen Kingdoms period.
-
- Western Wei Dynasty
-
- Northern Zhou Dynasty
-
- Sui Dynasty from 581 to 618
-
- Tang Dynasty from 618 to 907
- Ye was the capital of Eastern Wei Dynasty and Northern Qi Dynasty.
Chronology
Government Capital Period Xia Song (崇) Gun Yangcheng (陽城) Yu[2] Chu (鉏) Yi Qiongshi (窮石) Yi, Hanzhuo Zhen (斟) Taikang Diqiu (帝丘) Xiang Yuan (原) Zhu Laoqiu (老丘) Zhu Xihe (西河) Yinjia Zhen (斟) Jie Henan (河南) Jie[3] Shang Bo (亳) Shang Tang[3] Fan (蕃) Xie Dishi (砥石) Zhaoming Shang (商) Zhaoming Shangqiu (商邱) Xiangtu Foot of Mount Tai ("泰山麓") Xiangtu Shangqiu (商邱) Xiangtu Yin (殷) Shanghou Shangqiu (商邱) Yinhou Bo ("西"亳) Tang Xiao (囂) Zhongding Xiang (相) Hedanjia Xing (邢) Zuyi Bi (庇) Zuyi Yan (奄) Nan'geng Yin (殷) Pan'geng Zhou (Western) Zongzhou (宗周, Western capital) 1046 BC—771 BC Chengzhou (成周, Eastern capital) 1046 BC—771 BC Zhou (Eastern) Chengzhou (成周) 770 BC—367 BC "Henan" (河南, capital of the Western Zhou State) 367 BC—256 BC Gong (鞏, capital of the Eastern Zhou State) 367 BC—249 BC Qin Xiquanqiu (西犬丘) Pingyang (平陽) —677 BC Yong (雍) 677 BC— Jingyang (涇陽) —383 BC Liyang (櫟陽) 383 BC—250 BC Xianyang (咸陽) 350 BC—207 BC Han (Western) Luoyang (雒陽) 202 BC Liyang (櫟陽) 202 BC—200 BC Chang'an (長安) 200 BC—8 BC Xin Chang'an (長安) 8 CE—23 CE Han (Eastern) Luoyang (雒陽) 25—190 Chang'an (長安) 191—195 Xu (許) 196—220 Wei
(Three Kingdoms)Luoyang (洛陽) 220—265 Han
(Three Kingdoms)Chengdu (成都) 221—263 Wu
(Three Kingdoms)Jianye (建業) 227—279 Jin (Western) Luoyang (洛陽) 265—313 Chang'an (長安) 313—316 Jin (Eastern) Jiankang (建康) 317—420 Wei
(Northern dynasties)Pingcheng (平城) 386—493 Luoyang (洛陽) 493—534 Ye (鄴, capital of the Eastern Wei State) 534—550 Chang'an (長安, capital of the Western Wei State) 535—557 Qi
(Northern dynasties)Ye (鄴) 550—577 Zhou
(Northern dynasties)Chang'an (長安) 557—581 Song
(Southern dynasties)Jiankang (建康) 420—479 Qi
(Southern dynasties)Jiankang (建康) 479—502 Liang
(Southern dynasties)Jiankang (建康) 502—557 Chen
(Southern dynasties)Jiankang (建康) 557—589 Sui Dongdu (東都) 581—618 Daxing (大興, auxiliary capital) 581—618 Tang Chang'an (長安) 618—690 Zhou Chang'an (長安) 690—705 Tang Chang'an (長安) 705—904 Luoyang (洛陽) 904—907 Liang
(Five dynasties)Dongdu (東都) 907—923 Tang
(Five dynasties)Dongdu (東都) 923—936 Jin
(Five dynasties)Dongjing (東京) 936—947 Han
(Five dynasties)Dongjing (東京) 947—950 Zhou
(Five dynasties)Dongjing (東京) 951—960 Song (Northern) Dongjing (東京) 960—1127 Song (Southern) Lin'an (臨安) 1127—1279 Liao,
Empire of the KhitanShangjing (上京) 907—1120 Nanjing (南京) 1122—1123 Tokmok (虎思斡耳朵) 1134—1218 Jin Shangjing (上京) 1115—1153 Zhongdu (中都) 1153—1214 Nanjing (南京) 1214—1234 Western Xia Xingqing 1038—1227 Yuan Shangdu (上都) May 1264 — 1276 Dadu (大都) 1276 — August 1368 Shangdu (上都) August 1368 — 1369 Ming Nanjing (南京) 23 January 1368 — 2 February 1421 Beijing (北京) 2 February 1421 — 25 April 1644 Nanjing (南京) 1644 — 1645 Fuzhou (福州) 1645 — 1646 Zhaoqing (肇慶) 1646 — 25 April 1662 Later Jin Feiala (費阿拉) 1587 — 1603 Hetuala (赫圖阿拉) 1603 — 1619 Jiefan (界凡) 1619 — September 1620 Sarhu (薩爾滸) September 1620 — April 1621 Dongjing (東京) April 1621 — 11 April 1625 Shengjing (盛京) 11 April 1625 — 1636 Qing Shengjing (盛京) 1636 — 20 September 1644 Beijing (北京) 20 September 1644 — 12 February 1912[4] Republic of China Nanjing (南京) 1 January 1912 — 2 April 1912
(Provisional Government)Beijing (北京) 2 April 1912 — 30 May 1928
(Beiyang Government)[4]Fengtian (奉天) 30 May 1928 — 29 December 1928
(Beiyang Government)Guangzhou (廣州) 1 July 1925 — 21 February 1927
(Guangzhou Nationalist Government)Wuhan (武漢) 21 February 1927 — 19 August 1927
(Wuhan Nationalist Government)[5]Nanjing (南京) 18 April 1927 — 20 November 1937
(the Nanjing decade)[4]Beiping (北平) 9 September 1930 — 23 September 1930
(Beiping Nationalist Government)Taiyuan (太原) 23 September 1930 — 4 November 1930
(Beiping Nationalist Government)Guangzhou (廣州) 28 May 1931 — 22 December 1931
(Guangzhou Nationalist Government)Chongqing (重慶) 21 November 1937 — 5 May 1946
(during the Second Sino-Japanese War)[4]Nanjing (南京) 30 March 1940 — 10 August 1945
(Wang Jingwei Government)Nanjing (南京) 5 May 1946 — 23 April 1949[4] Guangzhou (廣州) 23 April 1949 — 14 October 1949
(during the Chinese Civil War)Chongqing (重慶) 14 October 1949 — 30 November 1949
(during the Chinese Civil War)Chengdu (成都) 30 November 1949 — 27 December 1949
(during the Chinese Civil War)Xichang (西昌) 27 December 1949 — 27 March 1950
(during the Chinese Civil War)Taipei (臺北) 10 December 1949 — Present People's Republic of China Beijing (北京) 10 October 1949 — Present See also
References
- ^ Denis Twitchett, Herbert Franke, John K. Fairbank, in The Cambridge History of China: Volume 6, Alien Regimes and Border States (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1994), p 454.
- ^ 李玉潔. [2003] (2003). 中國早期國家性質. 知書房出版集團. ISBN 9867938178, 9789867938176.
- ^ a b Bamboo annals Xia chapter on Xia Jie under the name Gui (癸).
- ^ a b c d e Esherick, Joseph. [2000] (2000). Remaking the Chinese City: Modernity and National Identity, 1900-1950. University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 0824825187.
- ^ Clark, Anne Biller. Clark, Anne Bolling. Klein, Donald. Klein, Donald Walker. [1971] (1971). Harvard Univ. Biographic Dictionary of Chinese communism. Original from the University of Michigan v.1. Digitized Dec 21, 2006. p 134.
Categories:- Ancient Chinese capitals
- Cities in China
- History of China
- Capitals by country
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.