- Chloroprene
-
Chloroprene 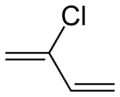
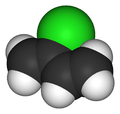 2-Chlorobuta-1,3-dieneOther namesChloroprene, 2-chloro-1,3-butadiene
2-Chlorobuta-1,3-dieneOther namesChloroprene, 2-chloro-1,3-butadieneIdentifiers CAS number 126-99-8 
ChemSpider 29102 
KEGG C19208 
ChEBI CHEBI:39481 
ChEMBL CHEMBL555660 
RTECS number EL9625000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - Cl/C(=C)/C=C
Properties Molecular formula C4H5Cl Molar mass 88.5365 g/mol Appearance Colorless liquid. Density 0.9598 g/cm3, liquid. Melting point -130 °C, 143 K, -202 °F
Boiling point 59.4 °C, 333 K, 139 °F
Solubility in water 0.026 g/100 mL, liquid. Hazards R-phrases R45, R11, R20/22,
R36/37/38, R48/20S-phrases S53, S45 Main hazards Highly flammable, toxic. NFPA 704 Flash point -15.6°C Related compounds Related Dienes Butadiene
IsopreneRelated compounds Vinyl chloride  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Chloroprene is the common name for the organic compound 2-chlorobuta-1,3-diene, which has the formula CH2=CCl-CH=CH2. This colorless liquid is the monomer for the production of the polymer polychloroprene, a type of synthetic rubber. Polychloroprene is better known to the public as Neoprene, the trade name given by DuPont.
Contents
Production of chloroprene
Chloroprene is produced in three steps from 1,3-butadiene: (i) chlorination, (ii) isomerization of part of the product stream, and (iii) dehydrochlorination of 3,4-dichloro-1-butene.
Chlorine adds to 1,3-butadiene to afford a mixture of 3,4-dichloro-1-butene and 2,3-dichloro-2-butene. The 2,3-chloro isomer is subsequently isomerized to 3,4 isomer, which in turn is treated with base to induce dehydrochlorination to 2-chlorobuta-1,3-diene. This dehydrohalogenation entails loss of a hydrogen atom in the 3 position and the chlorine atom in the 4 position thereby forming a double bond between carbons 3 and 4. In 1983, approximately 2,000,000 kg were produced in this manner.[1] The chief impurity in chloroprene prepared in this way is 1-chlorobuta-1,3-diene, which is usually separated by distillation.
Acetylene process
Until the 1960s, chloroprene production was dominated by the “acetylene process,” which was modeled after the original synthesis of vinylacetylene.[2] In this process, acetylene is dimerized to give vinyl acetylene, which is then combined with hydrogen chloride to afford 4-chloro-1,2-butadiene (an allene derivative), which in the presence of cuprous chloride, rearranges to the targeted 2-chlorobuta-1,3-diene:[1]
- HC≡C-CH=CH2 + HCl → H2C=C=CH-CH2Cl
- H2C=C=CH-CH2Cl → H2C=CCl-CH=CH2
This process is very energy-intensive and has high investment costs. Furthermore, the intermediate vinyl acetylene is unstable.
This "acetylene process" has been replaced by a process which adds Cl2 to one of the double bonds in 1,3-butadiene instead, and subsequent elimination produces HCl instead, as well as chloroprene.
References
- ^ a b Manfred Rossberg, Wilhelm Lendle, Gerhard Pfleiderer, Adolf Tögel, Eberhard-Ludwig Dreher, Ernst Langer, Heinz Rassaerts, Peter Kleinschmidt, Heinz Strack, Richard Cook, Uwe Beck, Karl-August Lipper, Theodore R. Torkelson, Eckhard Löser, Klaus K. Beutel, “Chlorinated Hydrocarbons” in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2006 John Wiley-VCH: Weinheim.DOI: 10.1002/14356007.a06_233.pub2
- ^ Wallace H. Carothers, Ira Williams, Arnold M. Collins, and James E. Kirby (1937). "Acetylene Polymers and their Derivatives. II. A New Synthetic Rubber: Chloroprene and its Polymers". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 53 (11): 4203–4225. doi:10.1021/ja01362a042.
External links
Categories:- Dienes
- Monomers
- Organochlorides
- Hazardous air pollutants
- IARC Group 2B carcinogens
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

