- Barbituric acid
-
Barbituric acid 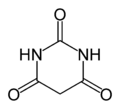
 pyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trioneOther names2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-Pyrimidinetrione, 2,4,6-Trioxohexahydropyrimidine, 2,4,6-Trihydroxypyrimidine, 2,4,6-Trioxypyrimidine, 2,4,6-Pyrimidinetriol, 2,4,6-Pyrimidinetrione, Pyrimidinetriol, 2,4,6-Trihydroxy-1,3-diazine, N,N′-Malonylurea, Malonylurea, 6-Hydroxyuracil, 6-Hydroxy-Hydrouracil, N,N′-(1,3-dioxo-1,3-propanediyl)urea
pyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trioneOther names2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-Pyrimidinetrione, 2,4,6-Trioxohexahydropyrimidine, 2,4,6-Trihydroxypyrimidine, 2,4,6-Trioxypyrimidine, 2,4,6-Pyrimidinetriol, 2,4,6-Pyrimidinetrione, Pyrimidinetriol, 2,4,6-Trihydroxy-1,3-diazine, N,N′-Malonylurea, Malonylurea, 6-Hydroxyuracil, 6-Hydroxy-Hydrouracil, N,N′-(1,3-dioxo-1,3-propanediyl)ureaIdentifiers CAS number 67-52-7 
PubChem 6211 ChemSpider 5976 
UNII WQ92Y2793G 
EC number 200-658-0 KEGG C00813 
ChEBI CHEBI:16294 
ChEMBL CHEMBL574699 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C1NC(=O)NC(=O)C1
Properties Molecular formula C4H4N2O3 Molar mass 128.09 g mol−1 Appearance White crystals Melting point 245 °C
Boiling point 260 °C
Solubility in water 142 g/l (20 °C) Hazards MSDS External MSDS R-phrases R36/38, R43 S-phrases S22, S26, S28 NFPA 704  acid (verify) (what is:
acid (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
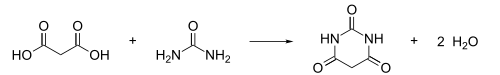
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Barbituric acid or malonylurea or 6-hydroxyuracil is an organic compound based on a pyrimidine heterocyclic skeleton. It is an odorless powder soluble in water. Barbituric acid is the parent compound of barbiturate drugs, although barbituric acid itself is not pharmacologically active. The compound was discovered by the German chemist Adolf von Baeyer on December 4, 1864, the feast of Saint Barbara (who gave the compound its namesake), by combining urea and malonic acid in a condensation reaction.[1] Malonic acid has since been replaced by diethyl malonate,[2] as using the ester avoids the problem of having to deal with the acidity of the carboxylic acid and its unreactive carboxylate.
The α-carbon has a reactive hydrogen atom and is quite acidic (pKa = 4.01) even for a diketone species (cf. dimedone with pKa 5.23 and acetylacetone with pKa 8.95) because of the additional aromatic stabilisation of the carbanion. Using the Knoevenagel condensation reaction, barbituric acid can form a large variety of barbiturate drugs that behave as central nervous system depressants.
Barbituric acid is used in synthesis of riboflavin[citation needed].
As of 2007, more than 2550 barbiturates and related compounds have been synthesised, with 50 to 55 in clinical use around the world at present. The first to be used in medicine was barbital (Veronal) starting in 1903, and the second, phenobarbitone a.k.a. phenobarbital was first marketed in 1912.
See also
References
- ^ Baeyer, Adolf (1864). "Untersuchungen über die Harnsäuregruppe". Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie 131 (3): 291. doi:10.1002/jlac.18641310306.
- ^ J. B. Dickey & A. R. Gray (1943), "Barbituric acid", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv2p0060; Coll. Vol. 2: 60
Categories:- Pyrimidines
- Barbiturates
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.