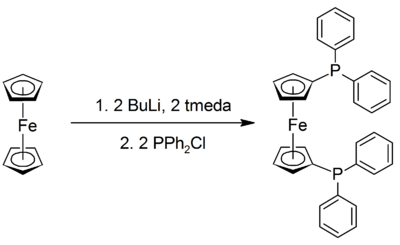- 1,1'-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene
-
1,1'-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene 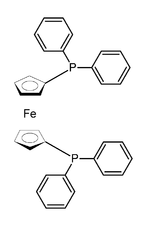
 1,1'- bis( diphenylphosphanyl) ferroceneOther names1,1'- Bis( diphenylphosphino) ferrocene, 1,1'- Ferrocenediyl- bis(diphenylphosphine), Dppf, 1,1'- Ferrocenebis (diphenylphosphine)
1,1'- bis( diphenylphosphanyl) ferroceneOther names1,1'- Bis( diphenylphosphino) ferrocene, 1,1'- Ferrocenediyl- bis(diphenylphosphine), Dppf, 1,1'- Ferrocenebis (diphenylphosphine)Identifiers CAS number 12150-46-8 PubChem 635956 ChemSpider 21865114 
ChEBI CHEBI:30743 Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- C1=CC=C(C=C1)P([C-]2C=CC=C2)C3=CC=CC=C3 .C1=CC=C(C=C1)P([C-]2C=CC=C2)C3=CC=CC=C3.[Fe+2]
c1ccc(cc1)P(c2ccccc2)C34C5[Fe]3678912(C5C6C74)C3C8C9C1(C23)P(c1ccccc1)c1ccccc1
- InChI=1S/2C17H14P.Fe/c2*1-3-9-15(10-4-1)18(17-13-7-8-14-17)16-11-5-2-6-12-16;/h2*1-14H;

Key: HPXNTHKXCYMIJL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI=1/2C17H14P.Fe/c2*1-3-9-15(10-4-1)18(17- -13-7-8-14-17)16-11-5-2-6-12-16;/h2*1-14H;/q2*-1;+2
Key: HPXNTHKXCYMIJL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI=1/2C17H14P.Fe/c2*1-3-9-15(10-4-1)18(17-13-7-8-14-17)16-11-5-2-6-12-16;/h2*1-14H;/rC34H28FeP2/c1-5-13-21(14-6-1)36(22-15-7-2-8-16-22)33-29-25-26-30(33)35(25,26,29,33)27-28(35)32(35)34(35,31(27)35)37(23-17-9-3-10-18-23)24-19-11-4-12-20-24/h1-20,25-32H
Key: HPXNTHKXCYMIJL-KDKHWAOJAX
Properties Molecular formula C34H28FeP2 Molar mass 554.391 Melting point 181-183 °C
Hazards R-phrases R25 S-phrases S28A S45 Main hazards Toxic  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references 1,1'-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene, commonly abbreviated dppf, is a substituted phosphine commonly used, as are other phosphines, as a ligand in organometallic chemistry. It contains a ferrocene moiety in its backbone, and is closely related to other bridged diphenylphosphines such as 1,1-bis(diphenylphosphino)methane (dppm) and 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe).
Contents
Preparation
This compound is commercially available. It may be prepared by the lithiation of ferrocene with n-butyllithium in the presence of TMEDA, followed by reaction with chlorodiphenylphosphine:[1]
Reactions
Dppf readily forms complexes with various metals;[2] the palladium derivative, (dppf)PdCl2 is especially popular for palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions. It is easily prepared in the usual manner, by reaction of dppf with the acetonitrile or benzonitrile complexes of palladium dichloride:[2]
- dppf + PdCl2(RCN)2 → (dppf)PdCl2 + 2 RCN (RCN = acetonitrile or benzonitrile)
See also
- Diphosphines
- borrowing hydrogen catalysis
References
- ^ Ian R. Butler (2010). "3.15 The Use of Organolithium Reagents in the Preparation of Ferrocene Derivatives". In J. Derek Woollins (Google Books excerpt). Inorganic Experiments. pp. 175–179. ISBN 9783527324729. http://books.google.com/books?id=IlL_qLqj_nUC&pg=PA173.
- ^ a b Nataro, Chip; Fosbenner, Stephanie M. (2009). "Synthesis and Characterization of Transition-Metal Complexes Containing 1,1’-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene". J. Chem. Ed. 86: 1412. doi:10.1021/ed086p1412.
Categories:- Organoiron compounds
- Metallocenes
- Tertiary phosphines
- C1=CC=C(C=C1)P([C-]2C=CC=C2)C3=CC=CC=C3 .C1=CC=C(C=C1)P([C-]2C=CC=C2)C3=CC=CC=C3.[Fe+2]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.