- Aroma compound
-
"Fragrance" redirects here. For other uses, see Fragrance (disambiguation)."Odorants" redirects here. For the punk rock band, see The Odorants.Not to be confused with Aromaticity.
An aroma compound, also known as odorant, aroma, fragrance or flavor, is a chemical compound that has a smell or odor. A chemical compound has a smell or odor when two conditions are met: the compound needs to be volatile, so it can be transported to the olfactory system in the upper part of the nose, and it needs to be in a sufficiently high concentration to be able to interact with one or more of the olfactory receptors.
Aroma compounds can be found in food, wine, spices, perfumes, fragrance oils, and essential oils. For example, many form biochemically during ripening of fruits and other crops. In wines, most form as byproducts of fermentation. Odorants can also be added to a dangerous odorless substance, like propane, natural gas, or hydrogen, as a warning. Also, many of the aroma compounds play a significant role in the production of flavorants, which are used in the food service industry to flavor, improve, and generally increase the appeal of their products.
Contents
Aroma compounds classified by structure
Esters
Compound name Fragrance Natural occurrence Chemical structure Methyl formate Ethereal Methyl acetate Sweet, nail polish
SolventMethyl butyrate
Methyl butanoateFruity, Apple
PineappleEthyl acetate Sweet, solvent Wine Ethyl butyrate
Ethyl butanoateFruity, Orange
PineappleIsoamyl acetate Fruity, Banana
PearBanana plant Pentyl butyrate
Pentyl butanoateFruity, Pear
ApricotPentyl pentanoate Fruity, Apple Octyl acetate Fruity, Orange Linear terpenes
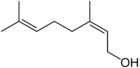
Compound name Fragrance Natural occurrence Chemical structure Myrcene Woody, complex Verbena, Bay Geraniol Rose, flowery Geranium, Lemon Nerol Sweet rose, flowery Neroli, Lemongrass Citral, lemonal
Geranial, neralLemon Lemon myrtle, Lemongrass Citronellal Lemon Lemongrass Citronellol Lemon Lemongrass, rose
PelargoniumLinalool Floral, sweet
Woody, LavenderCoriander, Sweet basil
LavenderNerolidol Woody, fresh bark Neroli, ginger
JasmineCyclic terpenes
Compound name Fragrance Natural occurrence Chemical structure Limonene Orange Orange, lemon Camphor Camphor Camphor laurel Terpineol Lilac Lilac, Cajuput alpha-Ionone Violet, woody Violet Thujone Minty Cypress, lilac
JuniperAromatic
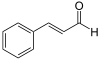
Compound name Fragrance Natural occurrence Chemical structure Benzaldehyde Almond Bitter almond Eugenol Clove Clove Cinnamaldehyde Cinnamon Cassia
CinnamonEthyl maltol Cooked fruit
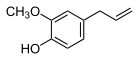
Caramelized sugarVanillin Vanilla Vanilla Anisole Anise Anise Anethole Anise Anise
Sweet basilEstragole Tarragon Tarragon Thymol Thyme Thyme Amines
Compound name Fragrance Natural occurrence Chemical structure Trimethylamine Fishy
AmmoniaPutrescine
DiaminobutaneRotting flesh Rotting flesh Cadaverine Rotting flesh Rotting flesh Pyridine Fishy Belladonna Indole Fecal
FloweryFeces
JasmineSkatole Fecal Feces Other aroma compounds
Alcohols
- Furaneol (strawberry)
- 1-Hexanol (herbaceous, woody)
- cis-3-Hexen-1-ol (fresh cut grass)
- Menthol (peppermint)
Aldehydes
- Acetaldehyde (pungent)
- Hexanal (green, grassy)
- cis-3-Hexenal (green tomatoes)
- Furfural (burnt oats)
- Hexyl cinnamaldehyde
Esters
- Fructone (fruity, apple-like)
- Hexyl acetate (apple, floral, fruity)
- Ethyl methylphenylglycidate (strawberry)
Ketones
- Dihydrojasmone (fruity woody floral)
- Oct-1-en-3-one (blood, metallic, mushroom-like)[1]
- 2-Acetyl-1-pyrroline (fresh bread, jasmine rice)
- 6-Acetyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridine (fresh bread, tortillas, popcorn)
Lactones
- gamma-Decalactone intense peach flavor
- gamma-Nonalactone coconut odor, popular in suntan lotions
- delta-Octalactone creamy note
- Jasmine lactone powerful fatty fruity peach and apricot
- Massoia lactone powerful creamy coconut
- Wine lactone sweet coconut odor
- Sotolon (maple syrup, curry, fenugreek)
Thiols
- Ethanethiol, commonly called Ethyl mercaptan (added to propane or other liquefied petroleum gases used as fuel gases)
- Grapefruit mercaptan (grapefruit)
- Methanethiol, commonly called Methyl mercaptan (Durian or leek)
- 2-Methyl-2-propanethiol, commonly called tertiary-butyl mercaptan is added as a blend of other components to natural gas used as fuel gas.
Miscellaneous compounds
- Methylphosphine and dimethylphosphine (garlic-metallic, two of the most potent odorants known)[1]
- Nerolin (orange flowers)
- Tetrahydrothiophene (added to natural gas)
- 2,4,6-Trichloroanisole (cork taint)
- Substituted pyrazines
Aroma compound receptors
Animals which are capable of smell detect aroma compounds with olfactory receptors. Olfactory receptors are cell membrane receptors on the surface of sensory neurons in the olfactory system which detect air-borne aroma compounds.
In mammals, olfactory receptors are expressed on the surface of the olfactory epithelium in the nasal cavity.
Safety
'Fragrance' was voted Allergen of the Year in 2007 by the American Contact Dermatitis Society. The composition of fragrances are usually not disclosed in the label of products, hiding the actual chemicals of the formula, which raises concerns between some consumers.[2]
References
- ^ a b D. Glindemann, A. Dietrich, H. Staerk, P. Kuschk, (2005). "The Two Odors of Iron when Touched or Pickled: (Skin) Carbonyl Compounds and Organophosphines". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 45 (42): 7006–7009. doi:10.1002/anie.200602100. PMID 17009284.
- ^ Toxic chemicals linked to birth defects are being found at alarming levels in women of childbearing age
See also
Categories:- Organic chemistry
- Olfaction
- Flavors
- Perfume ingredients
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.