- Interlobular arteries
-
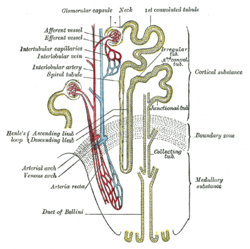
Artery: Interlobular arteries Scheme of renal tubule and its vascular supply. Latin arteriae corticales radiatae, arteriae interlobulares renis Gray's subject #253 1224 Supplies Afferent arterioles, glomeruli Source arcuate arteries of the kidney Vein Interlobular veins The first set of renal bloodvessels, the interlobular arteries (or cortical radiate arteries, or cortical radial arteries), are given off at right angles from the side of the arcuate arteries looking toward the cortical substance, and pass directly outward between the medullary rays to reach the fibrous tunic, where they end in the capillary network of this part.
These vessels do not anastomose with each other, but form what are called end-arteries.
In their outward course they give off lateral branches; these are the afferent vessels for the renal corpuscles; they enter the capsule, and end in the glomerulus.
From each tuft the corresponding efferent vessel arises, and, having made its egress from the capsule near to the point where the afferent vessel enters, breaks up into a number of branches, which form a dense plexus within Bowman's capsule.
External links
- Histology at BU 16015loa - "Urinary System: kidney, H&E, interlobular artery and vein"
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Anatomy: urinary system (TA A08, TH H3.06, GA 11.1215) Abdomen Layers(Renal artery) → Segmental arteries → Interlobar arteries → Arcuate arteries → Interlobular arteries → Afferent arteriolesRenal tubuleFiltrationPelvis Apex • Uvula • Neck • Median umbilical ligament • Muscular layer (Trigone • Detrusor) • Mucosa • SubmucosaCategories:- Cardiovascular system stubs
- Kidney anatomy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.