- Temperateness
-
Part of the Nature series on
WeatherCalendar seasons Spring · Summer
Tropical seasonsStorms Thunderstorm · Supercell
Downburst · Lightning
Tornado · Waterspout
Tropical cyclone (Hurricane)
Extratropical cyclone
Winter storm · Blizzard · Ice storm
Dust storm · Firestorm · CloudPrecipitation Drizzle · Rain · Snow · Graupel
Freezing rain · Ice pellets · HailTopics Meteorology · Climate
Weather forecasting
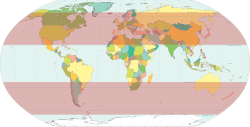
Heat wave · Air pollutionWeather portal In geography, temperate or tepid latitudes of the globe lie between the tropics and the polar circles. The changes in these regions between summer and winter are generally relatively moderate, rather than extreme hot or cold. However, in certain areas, such as Asia and central North America, the variations between summer and winter can be extreme because these areas are far away from the sea, causing them to have a continental climate. In regions traditionally considered tropical, localities at high altitudes (e.g. parts of the Andes) may have a temperate climate. The north temperate zone extends from the Tropic of Cancer (at about 23.5 degrees north latitude) to the Arctic Circle (at approximately 66.5 degrees north latitude). The south temperate zone extends from the Tropic of Capricorn (at approximately 23.5 degrees south latitude) to the Antarctic Circle (at approximately 66.5 degrees south latitude).
Within these borders there are many climate types, which are generally grouped into six categories: oceanic (maritime), mediterranean, humid subtropical, continental, arid and semi-arid.
The maritime climate is affected by the oceans, which help to sustain somewhat stable temperatures throughout the year. In temperate zones the prevailing winds are from the west, thus the western edge of temperate continents most commonly experience this maritime climate. Such regions include Western Europe, and western North America at latitudes between 40° and 60° north (65°N in Europe).
Continental, semi-arid and arid climates are usually situated inland, with warmer summers and colder winters. Heat loss and reception are aided by extensive land mass. In North America, the Rocky Mountains act as a climate barrier to the maritime air blowing from the west, creating a semi-arid and continental climate to the east. In Europe, the maritime climate is able to stabilize inland temperature, because the major mountain range – the Alps – is oriented east-west (the area east of the long Scandinavian mountain range is an exception).
The vast majority of the world's human population resides in temperate zones, especially in the northern hemisphere because of the mass of land. However the population in the temperate zones are somewhat decreasing, due to low birth rates and a growing migration trend from the temperate zone to the tropics.[citation needed]
For the history of the term, see geographical zone
See also
- Middle latitudes
- Habitat (ecology)
- Subtropical
- Geographical zone
Seasons Temperate seasons Tropical climate seasons Specific Class A Class B Class C Class D Class E Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.