- Charles Alston
-
Charles Alston 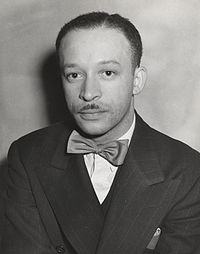
Charles Alston in 1939Birth name Charles Henry Alston Born November 28, 1907
Charlotte, North CarolinaDied April 27, 1977 (aged 69)
New York CityNationality American Field Muralism, Painting, Illustration, Sculpture Training Columbia University, Teacher's College Movement Abstract expressionism Patrons Lemoine Pierce Influenced by Aaron Douglas Influenced Jean Lacy, Jacob Lawrence Charles Henry Alston (November 28, 1907 – April 27, 1977) was an African-American painter, sculptor, illustrator, muralist and teacher who lived and worked in the New York City neighborhood of Harlem. Alston was active in the Harlem Renaissance; Alston was the first African American supervisor for the Works Progress Administration's Federal Art Project. Known for his murals at the Harlem Hospital and the Golden State Mutual Life Insurance Building. In 1990 Alston's bust of Martin Luther King, Jr. became the first image of an African American displayed at the White House.
Contents
Personal life
Early life
Charles Henry Alston was born on November 28, 1907 in Charlotte, North Carolina to Reverend Primus Priss Alston and Anna Elizabeth Miller Alston, and was the youngest of five children.[1][2][3] Only three survived past infancy: His sister Rousmaniere, and his brothers Wendell and Charles.[1][4] His father was born into slavery in 1851 in Pittsboro, North Carolina; after the Civil War, he graduated from St. Augustine's College and became a prominent minister and founder of St. Michael's Episcopal Church. He was described as a "race man": an African American who dedicated his skills to the furtherance of the black race.[1][2][3] Reverend Alston met his wife when she was a student at his school. Charles was nicknamed "Spinky" by his father, and kept the nickname as an adult. In 1910, when Charles was three, his father died suddenly of a cerebral hemorrhage. Locals described him in admiration as the "Booker T. Washington of Charlotte".[1][3]
In 1913 Anna Alston married Harry Bearden. Through the marriage, the future artist Romare Bearden became Charles’ cousin. The two Bearden families lived across the street from each other; the friendship between Romare and Charles would last a lifetime.[1][3][4] As a child Alston was inspired by his older brother Wendell's drawings of trains and cars, which the young artist copied.[1][5] Charles also played with clay, creating a sculpture of North Carolina. As an adult he reflected on his memories of sculpting with clay as a child: "I’d get buckets of it and put it through strainers and make things out of it. I think that's the first art experience I remember, making things."[1] His mother was a gifted embroiderer and took up painting at the age of 75. His father was gifted at drawing as well, wooing Alston's mother with small sketches in the medians of letters he wrote her.[1][3]
In 1915 the family moved to New York, as many African-American families did during the Great Migration.[1][2][3][6] Alston's step-father, Henry Bearden, left before his wife and children to secure a job overseeing elevator operations and the newsstand staff at the Bretton Hotel in the Upper West Side. The family lived in Harlem and was considered middle-class. During the Great Depression, the people of Harlem suffered economically. The "stoic strength" seen within the community was later expressed in Charles’ fine art.[1] At Public School 179 in Manhattan, the boy's artistic abilities were recognized and he was asked to draw all of the school posters during his years there.[3]
Higher education
Alston graduated from DeWitt Clinton High School, where he was nominated for academic excellence and was the art editor of the school's magazine, The Magpie. He was a member of the Arista - National Honor Society and also studied drawing and anatomy at the Saturday school of the National Academy of Art .[1][2][3] In high school he was given his first oil paints and learned about his aunt Bessye Bearden's art salons, which stars like Duke Ellington and Langston Hughes attended. After graduating in 1925, he attended Columbia University, turning down a scholarship to the Yale School of Fine Arts.[1][2][3][5] Alston entered the pre-architectural program only to lose interest upon seeing the lack of success many African American architects had in the field. After also experimenting with pre-med, he decided that math, physics and chemistry "was not just my bag" and he entered the fine arts program. During his time at Columbia he joined Alpha Phi Alpha, worked on the university's Columbia Daily Spectator and drew cartoons for the school's magazine Jester.[1][3] He also hung out in Harlem restaurants and clubs, where his love for jazz and black music would be fostered. In 1929 he graduated and received a fellowship to study at Teachers College, where he obtained his Master's in 1931.[1][3]
Later life
For the years 1942–1943 Alston was stationed in the army at Fort Huachuca in Arizona. Upon returning to New York on April 8, 1944, he married Dr. Myra Adele Logan, an intern at the Harlem Hospital. They met when he was working on a mural project at the hospital. Their home, including his studio, as on Edgecombe Avenue near Highbridge Park. The couple lived close to family; at their frequent gatherings Alston enjoyed cooking and Myra played piano. During the 1940s Alston also took occasional art classes studying under Alexander Kostellow.
In January 1977 Myra Logan died. Months later on April 27, 1977, Charles Spinky Alston died after a long bout with cancer.[1][3] His memorial service was held at St. Martins Episcopal Church on May 21, 1977 in New York City.[7]
Professional career
While obtaining his master's degree, Alston was the boys’ work director at the Utopia Children's House, started by James Lesesne Wells.[1][6] He also began teaching at the Harlem Arts Workshop, founded by Augusta Savage in the basement of what is now the Schomburg Center for Research in Black Culture.[1][3][6] Alston's teaching style was influenced by the work of John Dewey, Arthur Wesley Dow, and Thomas Munro. During this period, Alston began to teach the 10-year old Jacob Lawrence, whom he strongly influenced.[1][3][8] Alston was introduced to African art by the poet Alain Locke.[1][3][5][6] In the late 1920s Alston joined Bearden and other black artists who refused to exhibit in William E. Harmon Foundation shows, which featured all-black artists in their traveling exhibits. Alston and his friends thought the exhibits were curated for a white audience, a form of segregation which the men protested. They did not want to be set aside but exhibited on the same level as art peers of every skin color.[3]
In 1938 the Rosenwald Fund provided money for Alston to travel to the South, which was his first return there since leaving as a child. His travel with Giles Hubert, an inspector for the Farm Security Administration, gave him access to certain situations and he photographed many aspects of rural life.[1][2][6] These photographs serves as the basis for a series of genre portraits' depicting southern black life. In 1940 he completed Tobacco Farmer, the portrait of a young black farmer in white overalls and a blue shirt with a youthful yet serious look upon his face, sitting in front of the landscape and buildings he works on and in. That same year he received a second round of funding from the Rosenwald Fund to travel South, and he spent extended time at Atlanta University.[1]
During the 1930s and early 1940s, Alston created illustrations for magazines such as Fortune, Mademoiselle, The New Yorker, Melody Maker and others.[1][3] He also designed album covers for artists such as Duke Ellington and Coleman Hawkins.[3] Alston became staff artist at the Office of War Information and Public Relations in 1940, creating drawings of notable African Americans. These images were used in over 200 black newspapers across the country by the government to "foster goodwill with the black citizenry,".[6][9]
Eventually Alston left commercial work to focus on his own artwork. In 1950 he became the first African-American instructor at the Art Students League, where he remained on faculty until 1971.[1][2][6] In 1950 his Painting was exhibited at the Metropolitan Museum of Art and his artwork was one of few purchased by the museum.[6] He landed his first solo exhibition in 1953 at the John Heller Gallery, who represented artists such as Roy Lichtenstein. He exhibited there five times from 1953–1958.
In 1956 he became the first African-American instructor at the Museum of Modern Art, where he taught for a year before going to Belgium on behalf of MOMA and the State Department. He coordinated the children's community center at Expo 58. In 1958 he was awarded a grant from and was elected as a member of the American Academy of Arts and Letters.[1][2][3]
In 1963 Alston co-founded Spiral with Romare Bearden and Hale Woodruff.[1][2][3][6] Spiral served as a collective of conversation and artistic exploration for a large group of artists who "addressed how black artists should relate to American society in a time of segregation." Artists and arts supporters gathered for Spiral, such as Emma Amos, Perry Ferguson and Merton Simpson.[1][5] [10] This group served as the 1960s version of 306, and Alston was described as an "intellectual activist." In 1968 he spoke at Columbia about his activism and in the mid-60s Spiral created an exhibition of black and white artworks. But, the exhibition was never officially sponsored by the group due to inner-group disagreements.[1]
In 1968 Alston received a presidential appointment from Lyndon Johnson to the National Council of Culture and the Arts. Mayor John Lindsay appointed him to the New York City Art Commission in 1969.[6] He was made full professor at City College of New York in 1973 where he had taught since 1968.[1][2] In 1975 he was awarded the first Distinguished Alumni Award from Teachers College.[1] The Art Student's League created a 21-year merit scholarship in 1977 under Alston's name to commemorate each year of his tenure.[3]
Painting a person and a culture
Alston shared studio space with Henry Bannarn at 306 W. 141st St, which served as an open space for artists, photographers, musicians, writers and the like. Other artists held studio space at 306, such as Jacob Lawrence, Addison Bate and his brother Leon.[1][3][6][10] During this time Alston founded the Harlem Artists’ Guild with Savage and Elba Lightfoot to work towards equality in WPA art programs in New York. During the early years of 306, Alston focused on mastering portraiture. Early works such as Portrait of a Man (1929) show Alston's detailed and realistic style depicted through pastels and charcoals, inspired by the style of Winold Reiss. In his Girl in a Red Dress (1934) and The Blue Shirt (1935), he used modern and innovative techniques for his portraits of young individuals in Harlem. Blue Shirt is thought to be a portrait of Jacob Lawrence. During this time he also created Man Seated with Travel Bag (c. 1938–40), showing the seedy and bleak environment, contrasting with work like the racially charged Vaudeville (c. 1930) and its caricature style of a man in blackface.[1]
Inspired from his trip South, Alston began his "family series" in the 1940s.[1][3] Intensity and angularity come through in the faces of the youth in his portraits Untitled (Portrait of a Girl) and Untitled (Portrait of a Boy). These works also show the influence that African sculpture had on his portraiture, showing, with Portrait of a Boy showing more cubist features. Later family portraits show Alston's exploration of religious symbolism, color, form and space. His family group portraits are often faceless, which Alston states is the way that white America views blacks. Paintings such as Family (1955) show a woman seated and a man standing with two children – the parents seem almost solemn while the children are described as hopeful and with a use of color made famous by Cézanne. In Family Group (c. 1950) Alston's use of grey and ochre tones brings together the parents and son as if one with geometric patterns connecting them together as if a puzzle. The simplicity of the look, style and emotion upon the family is reflective and probably inspired by Alston's trip south. His work during this time has been described as being "characterized by his reductive use of form combined with a sun-hued". During this time he also started to experiment with ink and wash painting seen in work like Portrait of a Woman (1955) as well as creating portraits to illustrate the music surrounding him in Harlem. Blues Singer #4 shows a female singer on stage with a white flower on her shoulder and a bold red dress, reminisecent of Ella Fitzgerald.[1][3] Girl in a Red Dress is thought to may be Bessie Smith, for whom he drew many times when she was recording and performing. Jazz was an important influence in Alston's work and socila life, representing itself in other works like Jazz (1950) and Harlem at Night.[1]
The 1960s civil rights movement influenced his work heavily with artworks influenced by inequality and race relations in the United States. One of his few religious artworks was created in 1960, Christ Head, with an angular "Modiglianiesque" portrait of Jesus Christ. Seven years later he creates You never really meant it, did you, Mr. Charlie? which, in a similar style as Christ Head shows a black man standing against a red sky "looking as frustrated as any individual can look", according to Alston.[1]
Modernism
Experimenting with the use of negative space and organic forms in the late 1940s, by the mid-1950s Alston began creating notably modernist style paintings. Woman with Flowers (1949) has been described as a tribute to Modigliani and African art makes another strong appearance in Ceremonial (1950). Untitled works during the era show his use of color overlay using muted colors to create simple layered abstracts of still live. Symbol (1953) relates to Picasso's Guernica, which was a favorite work of Alston's.[1] His final work of the 1950s, Walking serves as a precursor to the 1960s: civil rights movement. The painting, which was inspired by the Montgomery Bus Boycott, has come to represent "the surge of energy among African Americans to organize in their struggle for full equality."[11] About the artwork, Alston is quoted "The idea of a march was growing...It was in the air...and this painting just came. I called it Walking on purpose. It wasn't the militancy that you saw later. It was a very definite walk-not going back, no hesitation."[1][12]
Black and white
The civil rights movement of the 1960s was a major influence on Alston. Considered to be one of his most powerful and impressive periods in the late 1950s he began working in black and white up until the mid-1960s. Some of the works are simple abstracts of black ink on white paper, similar to a Rorschach test. Untitled (c. 1960s) shows a boxing match in great simplicity with an attempt to express the drama of the fight through few brushstrokes. Alston worked with oil-on-Masonite during this period as well, utilizing impasto, cream and ochre to create a moody cave-like artwork. Black and White #1 (1959) is one of Alston's more "monumental" works. Gray, white and black come together to fight for space on an abstract canvas, in a softer form than the more harsh Franz Kline. Alston continued to explore the relationship between monochromatic hues throughout the series which Wardlaw describes as "some of the most profoundly beautiful works of twentieth-century American art."[1]
Murals
In the beginning Charles Alston's mural work was inspired by the work of Aaron Douglas, Diego Rivera and José Clemente Orozco, the latter who he met when they did mural work in New York.[3] In 1943 Alston was elected to the board of directors of the National Society of Mural Painters. He created murals for the Harlem Hospital, Golden State Mutual, American Museum of Natural History, Public School 154, the Bronx Family and Criminal Court and the Abraham Lincoln High School in Brooklyn, New York.[1][3]
Harlem Hospital Murals
Originally hired as an easel painter, in 1935 Alston became the first African American supervisor to work for the WPA's Federal Art Project in New York, which would also serve as his first mural work.[1][3][6][10] At this time he was awarded WPA Project Number 1262 – an opportunity to oversee a group of artists creating murals and to supervise their painting for the Harlem Hospital.[1] The first government commission ever awarded to African American artists including Beauford Delaney, Seabrook Powell and Vertis Hayes.[3] He also had the chance to create and paint his own contribution to the collection: Magic in Medicine and Modern Medicine.[1][2][6] These paintings were part of a diptych completed in 1936 depicting the history of medicine in the African American community and Beauford Delaney served as assistant.[1][10] When creating the murals Alston was inspired by the work of Aaron Douglas, who a year earlier had created the public art piece Aspects of Negro Life for the New York Public Library, and researched traditional African culture, including traditional African medicine. Magic in Medicine, which depicts African culture and holistic healing, is considered one of "America's first public scenes of Africa". All of the murals sketches submitted were accepted by the FAP, however, four were denied creation by the hospital superintendent Lawrence T. Dermody and commissioner of hospitals S.S. Goldwater due to the excessive amount of African-American representation in the works.[1][3][6][13] The artists fought the response through letter writing and four years later succeeded in gaining the right to complete the murals.[1][3] The sketches for Magic in Medicine and Modern Medicine were exhibited in the Museum of Modern Art's "New Horizons in American Art".[1][3][10]
Condition
Alston's murals were hung in the Women's Pavilion of the hospital over uncapped radiators which caused the paintings to deteriorate from the steam. Plans failed to recap the radiators. In 1959 Alston estimated, in a letter to the Department of Public Works, that the conservation would cost $1,500 but the funds were never acquired. In 1968, after Martin Luther King Jr.'s death, Alston was asked to create another mural for the hospital to be placed in a pavilion named after the assassinated civil rights leader titled Man Emerging from the Darkness of Poverty and Ignorance into the Light of a Better World". After Alston's death in 1977 a committee was formed, unable to raise funds for conservation on the original murals. In 1991 the Municipal Art Society's Adopt-a-Mural program was launched and the Harlem Hospital murals were chosen. A grant from Alston's sister Rousmaniere Wilson and step-sister Aida Bearden Winters assisted in completing a restoration of the works in 1993.[3] In 2005 Harlem Hospital announced a $2 million project to conserve Alston's murals and three other pieces in the original commissioned project as part of a $225 dollar hospital expansion.[1][3]
Golden State Mutual Murals
In the late 1940s Alston became involved in a mural project commissioned by Golden State Mutual Life Insurance Company which asked the artists to create work involving African American contributions to the settling of California. Alston worked with Hale Woodruff on the murals in a large studio space in New York where they utilized ladders to reach the upper parts of the canvas.[1][10] The artworks, which are considered "priceless contributions to American narrative art", consists of two panels: Exploration and Colonization by Alston and Settlement and Development by Woodruff. Alston's piece covers the post-colonial period of 1527 to 1850. Images of James Beckworth, Biddy Mason, and William Leidesdorff are portrayed in the well detailed historical mural. While both artists kept in contact with African Americans on the West Coast during its creation, influencing the content and depictions. The murals, which were unveiled in 1949, have been on display in the lobby of the Golden State Mutual Headquarters.[1][10] Due to economic downturn Golden State was forced to sell their entire art collection to ward off its mounting debts and as of spring 2011 the National Museum of African American History and Culture had offered $750,000 to purchase the artworks which led to a controversy regarding the importance of the artworks which have been estimated to be worth at least $5 million. It was requested that the murals be covered by city landmark protections by the Los Angeles Conservancy. The state of California had declined philanthropic proposals to keep the murals in their original location and the Smithsonian withdrew their offer. The murals are currently awaiting their fate in California courts.[14][15]
Sculpture
Alston also created sculptures. Head of a Woman (1957) shows his move towards a "reductive and modern approach to sculpture....where facial features were suggested rather than fully formulated in three dimensions,".[1] In 1970 Alston was commissioned by the Community Church of New York to create a bust of Martin Luther King Jr. for $5,000, with limited copies produced.[16][17] In 1990 Alston's bronze bust of Martin Luther King Jr. (1970), became the first image of an African American displayed in the White House.[1][18]
Reception
Art critic Emily Genauer stated that Altson "refused to be pigeonholed", regarding his varied exploration in his artwork.[1] Patron Lemoine Pierce said of Alston's work: "Never thought of as an innovative artist, Alston generally ignored popular art trends and violated many mainstream art conventions; he produced abstract and figurative paintings often simultaneously, refusing to be stylistically consistent, and during his 40-year career he worked prolifically and unapologetically in both commercial and fine art." Romare Bearden described Alston as "...one of the most versatile artists whose enormous skill led him to a diversity of styles..." Bearden also describes the professionalism and impact that Alston had on Harlem and the African American community: "'was a consummate artist and a voice in the development of African American art who never doubted the excellence of all people's sensitivity and creative ability. During his long professional career, Alston significantly enriched the cultural life of Harlem. In a profound sense, he was a man who built bridges between Black artists in varying fields, and between other Americans."[3] Writer June Jordan described Alston as "an American artist of first magnitude, and he is a Black American artist of undisturbed integrity."[19]
Major exhibitions
- A Force for Change, group show, 2009, Spertus Museum, Chicago
- Canvasing the Movement, group show, 2009, Reginald F. Lewis Museum of Maryland African-American History & Culture[20][21]
- On Higher Ground: Selections From the Walter O. Evans Collection, group show, 2001, Henry Ford Museum, Michigan[22]
- Rhapsodies in Black: Art of the Harlem Renaissance, group show, 1998, Corcoran Gallery of Art, Washington, D.C.[23]
- In the Spirit of Resistance: African-American Modernists and the Mexican Muralist School, group show, 1996, The Studio Museum in Harlem, New York[24]
- Charles Alston: Artist and Teacher, 1990, Kenkeleba Gallery, New York[1]
- Masters and Pupils: The Education of the Black Artist in New York, 1986, Jamaica Arts Center, New York[25]
- Hundred Anniversary Exhibition of Paintings and Sculpture, 1975, Art Students League of New York, New York
- Solo exhibition, 1969, Huntington Hartford Gallery of Modern Art, New York.
- Solo exhibition, 1968, Fairleigh Dickinson University, New Jersey[1]
- A Tribute to Negro Artists in Honor of the 100th Anniversary of the Emancipation Proclamation, group show, 1963, Albany Institute of History and Art[3]
Major collections
- Hampton University[3]
- Harmon and Harriet Kelly Foundation for the Arts[1][2]
- National Association for the Advancement of Colored People[3]
- National Museum of African American History and Culture
- Whitney Museum of American Art[2]
Notes
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc Wardlaw, Alvia J. (2007). Charles Alston. Pomegranate. ISBN 978-0-7649-3766-8.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "Charles Henry Alston". Artists. Hollis Taggart Galleries. 2011. http://www.hollistaggart.com/artists/biography/charles_henry_alston/. Retrieved 9 April 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak Pierce, Lemoine (2004). "Charles Alston – An Appreciation". The International Review of African American Art (4): 33–38.
- ^ a b Schwartzman, Myron (1990). Romare Bearden: His Life and Art. Abrams Books. ISBN 978-0810931084.
- ^ a b c d Murray, Al (interviewer) (19 October 1968) (mp3). Oral History Interview with Charles Alston. Archives of American Art. http://www.aaa.si.edu/collections/interviews/oral-history-interview-charles-henry-alston-11460.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Finkelman, Paul (2004). Encyclopedia of the Harlem Renaissance. Routledge. ISBN 1579584578.
- ^ Charles Henry Alston Memorial Service. 21 May 1977. Archives of American Art.
- ^ "First publication of the migration series captures A defining moment in American history.". Sentinel. 1993. http://search.proquest.com/docview/369369766?accountid=11243. Retrieved 10 April 2011.
- ^ "Charles H. Alston". Images. AAGE. http://www.aacvr-germany.org/AACVR.ORG/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=90&Itemid=60. Retrieved 9 April 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g Patton, Sharon (1998). African-American Art. Oxford. ISBN 0192842137.
- ^ Sharon J. Burton (2010). "Celebrating African American History Through Art: The Reginald F. Lewis Museum of African American History & Culture". Blog. Authentic Art Visions Blog. http://authenticartonline.com/art/tag/charles-alston. Retrieved 9 April 2010.
- ^ Henderson, Henry (1993). A History of African-American Artists: From 1792 to the Present. Pantheon. ISBN 978-0394570167.
- ^ "The Controversy". Harlem Hospital WPA Murals. Columbia University. 2006. http://www.columbia.edu/cu/iraas/wpa/controversy/index.html. Retrieved 9 April 2010.
- ^ Eve M. Kahn (17 March 2011). "Smithsonian Plan to Remove Murals From Los Angeles Lobby Is Criticized". The New York Times. http://artsbeat.blogs.nytimes.com/2011/03/17/smithsonian-plan-to-remove-murals-from-los-angeles-lobby-is-criticized/?scp=1&sq=smithsonian%20murals&st=cse. Retrieved 10 April 2011.
- ^ Eve M. Kahn (28 March 2011). "Smithsonian Won’t Buy Murals of Black Life in California". The New York Times. http://artsbeat.blogs.nytimes.com/2011/03/28/smithsonian-wont-buy-murals-of-black-life-in-california/. Retrieved 10 April 2011.
- ^ Special Committee on the Martin Luther King Bust. Minutes of the Meeting of the Special Committee on the Martin Luther King Bust. 23 June 1970. Archives of American Art.
- ^ Harrington, D. Martin Luther King Jr. Bust. Community Church of New York. 22 October 1970. Archives of American Art.
- ^ "Clinton announces first image of a Black is on display at the White House". Jet. 14 Mar 2000. http://search.proquest.com.proxygw.wrlc.org/docview/199980619?accountid=11243. Retrieved 10 April 2011.
- ^ Jordan, June. Publication proposal by June Jordan. 25 March 1970. Archives of American Art.
- ^ "January 2010 Programs". Calender of Events. Reginald F. Lewis Museum. 2010. http://www.africanamericanculture.org/januaryprograms.html. Retrieved 9 April 2010.
- ^ Samantha McCoy (2009). "Canvasing the Movement: The Lewis' Arts Wall Captures Images of Civil Rights, Past and Present". Press. Reginald F. Lewis Museum. http://www.africanamericanculture.org/PressSheets/ArtsWall-Canvasingthe%20Movement-Release.pdf. Retrieved 9 April 2010.
- ^ "Time Off: A Week of Diversions". The Wall Street Journal. 7 Feb 2001. http://search.proquest.com.proxygw.wrlc.org/docview/398825418?accountid=11243. Retrieved 10 April 2011.
- ^ Lawrence van Gelder (13 April 1998). "This Week". The New York Times. http://search.proquest.com.proxygw.wrlc.org/docview/430968853?accountid=11243. Retrieved 10 April 2011.
- ^ "Traveling Exhibit Depicts Black Life". The Sacramento Observer. 19 June 1996. http://search.proquest.com.proxygw.wrlc.org/docview/367497716?accountid=11243. Retrieved 10 April 2011.
- ^ Fraser, C. Gerald (7 December 1986). "America's black artists are seen in new light". The New York Times. http://proxygw.wrlc.org/login?url=http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=aph&AN=30794464&site=ehost-live. Retrieved 10 April 2011.
References
- Finkelman, Paul (2004). Encyclopedia of the Harlem Renaissance. London: Routledge. ISBN 1579584578.
- Henderson, Henry (1993). A History of African-American Artists: From 1792 to the Present. New York: Pantheon Books. ISBN 978-0394570167.
- Patton, Sharon (1998). African-American Art. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0192842137.
- Pierce, Lemoine (2004). "Charles Alston – An Appreciation". The International Review of African American Art (4): 33–38.
- Schwartzman, Myron (1990). Romare Bearden: His Life and Art. New York: Abrams Books. ISBN 978-0810931084.
- Wardlaw, Alvia J. (2007). Charles Alston. Petaluma, California: Pomegranate Communications. ISBN 978-0-7649-3766-8.
Further reading
- Anonymous, "First portrait of an Africa-American on display at White House" New York Amsterdam News, 2 March 2000. Article about Alston's Martin Luther King Jr. at the White House.
- Ascoli, Peter M, et all. A force for change: African American art and the Julius Rosenwald Fund. Chicago: Spertus Institute of Jewish Studies. 2009. ISBN 9780810125889 Book that documents the concept of and recipients of Rosenwald Funds.
- Barnwell, Andrea D.; Evans, Walter O.; Buick, Kristen; Mooney, Amy; Benjamin, Tritobia Hayes. The Walter O. Evans collection of African American art. Seattle:University of Washington Press. 2000. ISBN 0295979208 Features work by Alston.
- Berman, G. (1977). "The Walls of Harlem". Arts magazine, 52 (2), 122–126. Discusses the impact of 306 and related artists.
- Brigham, D.R. (2008) Breaking the 'chain of segregation': The Pyramid Club annual exhibitions. International Review of African American Art, 2–17. These exhibitions featured work by Charles Alston.
- Cameron, A. (1999). "Buenos Vecinos: African-American printmaking and the Taller de Gráfica Popular". Print Quarterly, 16 (4), 356–367. The importance of 306 and the relationship these artists had to Latin American artists.
- Coker, G. G., & Jennings, C. L. (1994). The Harmon and Harriet Kelley Collection of African American art. San Antonio: San Antonio Museum of Art. ISBN 1883502012 Exhibition catalog.
- Donaldson, J. R. (1974). Generation '306' – Harlem, New York. Northwestern University. Chicago: Northwestern University. Dissertation about 306 with input from Alston himself.
- Dunitz, R and Prigoff, J. Walls of heritage: walls of pride – African American murals. Fullbridge: Pomegranate Europe Ltd. 2001. ISBN 0764913395 Features Alston's murals.
- Glueck, Grace. "The best painter I can possibly be". New York Times, 1968. Interview with Alston.
- Henderson, H., & Coker, G. G. (1990). Charles Alston: artist and teacher. New York: Kenkeleba Gallery. Exhibition catalog.
- Langa, Helen. "Two antilynching art exhibitions: politicized viewpoints, racial perspectives, gendered constraints". American Art, 1999. 13 (1), 10–39. Politically charged article about lynching related artworks, includes Alston.
- Michael Rosenfeld Gallery. (1996). African-American art: 20th century masterworks, III. New York: Michael Rosenfeld Gallery. Exhibition catalog.
External links
 Media related to Charles Alston at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Charles Alston at Wikimedia Commons- Charles Henry Alston Papers from the Archives of American Art
- Alston's work is used to teach children about family life and race
Categories:- African American artists
- American caricaturists
- American magazine illustrators
- American muralists
- American painters
- Contemporary painters
- Modern painters
- American sculptors
- 20th-century sculptors
- Modern sculptors
- Portrait artists
- People of the New Deal arts projects
- People from Charlotte, North Carolina
- City University of New York faculty
- Art Students League of New York alumni
- Columbia University alumni
- Teachers College, Columbia University alumni
- Abstract expressionist artists
- Harlem Renaissance
- DeWitt Clinton High School alumni
- Alpha Phi Alpha
- United States Army artists
- Cancer deaths in New York
- The New Yorker cartoonists
- Artists from New York City
- Artists from North Carolina
- 1907 births
- 1977 deaths
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


