- Photopsin
-
Photopsins (also known as iodopsins) are the photoreceptor proteins found in the cone cells of the retina that are the basis of color vision. Photopsins are very close analogs of the visual purple rhodopsin that is used in night vision. Photopsins consist of a protein called opsin and a bound chromophore, the retinal.
Contents
Function
Opsins are Gn-x protein-coupled receptors of the retinylidene protein family. Isomerization of 11-cis-retinal into all-trans-retinal by light induces a conformational change in the protein that activates photopsin and promotes its binding to G protein transducin, which triggers a second messenger cascade.
Types
Different opsins differ in a few amino acids and absorb light at different wavelengths as retinal-bound pigments.
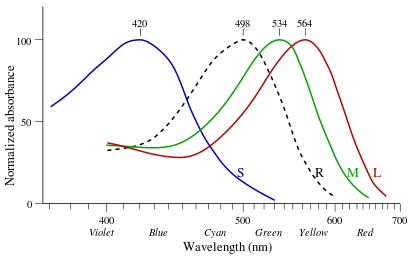
Cone type Name Range Peak wavelength[1][2] S (OPN1SW) - "tritan", "cyanolabe" β 400–500 nm 420–440 nm M (OPN1MW) - "deutan", "chlorolabe" γ 450–630 nm 534–545 nm L (OPN1LW) - "protan", "erythrolabe" ρ 500–700 nm 564–580 nm In humans there are three different iodopsins (rhodopsin analogs) that form the protein-pigment complexes photopsin I, II, and III. They are called erythrolabe, chlorolabe, and cyanolabe, respectively.[3] These photopsins have absorption maxima for yellowish-green (photopsin I), green (photopsin II), and bluish-violet light (photopsin III).
History
George Wald got the 1967 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his experiments in the 1950s that showed the difference in absorbance by these photopsins (see image).
See also
- Rhodopsins, the pigment for monochromatic (scotopic) dark vision.
- Melanopsin, the pigment which is used to control pupil sizes and the sleep/wake cycle
- Visual cycle, the chemistry of phototransduction
- Color blindness
References
- ^ Wyszecki, Günther; Stiles, W.S. (1982). Color Science: Concepts and Methods, Quantitative Data and Formulae (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley Series in Pure and Applied Optics. ISBN 0-471-02106-7.
- ^ R. W. G. Hunt (2004). The Reproduction of Colour (6th ed.). Chichester UK: Wiley–IS&T Series in Imaging Science and Technology. pp. 11–12. ISBN 0-470-02425-9.
- ^ Rushton, W. A. H. (1 June 1966). "Densitometry of pigments in rods and cones of normal and color defective subjects" (PDF). Investigative Ophthalmology 5 (3): 233–241. PMID 5296487. http://www.iovs.org/cgi/content/abstract/5/3/233. Retrieved 2006-11-14.
External links
- Rhodopsin and the eye, an excellent summary with pictures.
Opsin (retinylidene protein) Crystallin Other M: EYE
anat(g/a/p)/phys/devp/prot
noco/cong/tumr, epon
proc, drug(S1A/1E/1F/1L)
Categories:- G protein coupled receptors
- Sensory receptors
- Cell biology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.