- Monoacylglycerol lipase
-
monoglyceride lipase Identifiers Symbol MGLL Entrez 11343 HUGO 17038 OMIM 609699 RefSeq NM_007283 UniProt Q99685 Other data EC number 3.1.1.23 Locus Chr. 3 p13-q13.33 Monoacylglycerol lipase, also known as MAG lipase, MAGL, MGL or MGLL is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the MGLL gene.[1][2][3] MAGL is a 33-kDa, membrane-associated member of the serine hydrolase superfamily and contains the classical GXSXG consensus sequence common to most serine hydrolases. The catalytic triad has been identified as Ser122, His269, and Asp239.[2][4]
Contents
Function
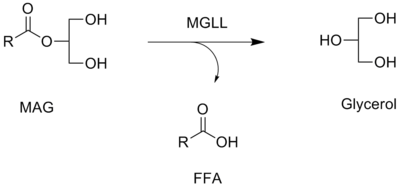
Monoacylglycerol lipase functions together with hormone-sensitive lipase (LIPE) to hydrolyze intracellular triglyceride stores in adipocytes and other cells to fatty acids and glycerol. MGLL may also complement lipoprotein lipase (LPL) in completing hydrolysis of monoglycerides resulting from degradation of lipoprotein triglycerides.[5]
Monoacylglycerol lipase is a key enzyme in the hydrolysis of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol.[6][7] It converts monoacylglycerols to the free fatty acid and glycerol. The contribution of MAGL to total brain 2-AG hydrolysis activity has been estimated to be ~85%,[8] and this in vitro estimate has been confirmed in vivo by the selective MAGL inhibitor JZL184.[9]
Inhibitors and assay
The enzyme was reported to be inhibited by URB754; however this inhibitor has subsequently been shown to be inactive and its reported activity due to contamination.[10] While the compound N-arachidonoyl maleimide (NAM) inhibits MAGL,[11] NAM is not selective due to its chemically reactive maleimide functional group, which can also react with other thiol-containing small molecules and proteins (e.g., glutathione).
JZL184 is the first efficacious and selective inhibitor of MAGL that can elevate brain 2-AG levels in vivo.[9] JZL184 has >300-fold selectivity for MAGL over other brain serine hydrolases, including FAAH.
MAGL activity is commonly detected by measuring free fatty acid release from a monoacylglycerol substrate using a liquid chromatography mass spectrometry system or the radiolabelled substrate 2-oleoyl-[3H]-glycerol.
Reaction
References
- ^ Wall EM, Cao J, Chen N, Buller RM, Upton C (December 1997). "A novel poxvirus gene and its human homolog are similar to an E. coli lysophospholipase". Virus Res. 52 (2): 157–67. doi:10.1016/S0168-1702(97)00122-6. PMID 9495531.
- ^ a b Karlsson M, Contreras JA, Hellman U, Tornqvist H, Holm C (October 1997). "cDNA cloning, tissue distribution, and identification of the catalytic triad of monoglyceride lipase. Evolutionary relationship to esterases, lysophospholipases, and haloperoxidases". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (43): 27218–23. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.43.27218. PMID 9341166.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: monoglyceride lipase". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=11343.
- ^ Tornqvist H, Belfrage P (February 1976). "Purification and some properties of a monoacylglycerol-hydrolyzing enzyme of rat adipose tissue". J. Biol. Chem. 251 (3): 813–9. PMID 1249056. http://www.jbc.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=1249056.
- ^ Karlsson M, Reue K, Xia YR, Lusis AJ, Langin D, Tornqvist H, Holm C (July 2001). "Exon-intron organization and chromosomal localization of the mouse monoglyceride lipase gene". Gene 272 (1–2): 11–8. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00559-5. PMID 11470505.
- ^ Dinh TP, Carpenter D, Leslie FM, Freund TF, Katona I, Sensi SL, Kathuria S, Piomelli D (August 2002). "Brain monoglyceride lipase participating in endocannabinoid inactivation". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (16): 10819–24. doi:10.1073/pnas.152334899. PMC 125056. PMID 12136125. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=125056.
- ^ Makara JK, Mor M, Fegley D, Szabó SI, Kathuria S, Astarita G, Duranti A, Tontini A, Tarzia G, Rivara S, Freund TF, Piomelli D (September 2005). "Selective inhibition of 2-AG hydrolysis enhances endocannabinoid signaling in hippocampus". Nat. Neurosci. 8 (9): 1139–41. doi:10.1038/nn1521. PMID 16116451.
- ^ Blankman JL, Simon GM, Cravatt BF (December 2007). "A Comprehensive Profile of Brain Enzymes that Hydrolyze the Endocannabinoid 2-Arachidonoylglycerol". Chem. Biol. 14 (12): 1347–56. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2007.11.006. PMC 2692834. PMID 18096503. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2692834.
- ^ a b Long JZ, Li W, Booker L, Burston JJ, Kinsey SG, Schlosburg JE, Pavón FJ, Serrano AM, Selley DE, Parsons LH, Lichtman AH, Cravatt BF (November 2008). "Selective blockade of 2-arachidonoylglycerol hydrolysis produces cannabinoid behavioral effects". Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 (1): 37–44. doi:10.1038/nchembio.129. PMC 2605181. PMID 19029917. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2605181.
- ^ Saario SM, Palomäki V, Lehtonen M, Nevalainen T, Järvinen T, Laitinen JT (August 2006). "URB754 has no effect on the hydrolysis or signaling capacity of 2-AG in the rat brain". Chem. Biol. 13 (8): 811–4. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.07.008. PMID 16931330.
- ^ Burston JJ, Sim-Selley LJ, Harloe JP, Mahadevan A, Razdan RK, Selley DE, Wiley JL (November 2008). "N-Arachidonyl Maleimide Potentiates the Pharmacological and Biochemical Effects of the Endocannabinoid 2-Arachidonylglycerol through Inhibition of Monoacylglycerol Lipase". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 327 (2): 546–53. doi:10.1124/jpet.108.141382. PMC 2605346. PMID 18682568. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2605346.
External links
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
3.1.21-31: Endonucleaseeither deoxy- or ribo-Categories:- Genes on chromosome 3
- Enzyme stubs
- Enzymes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.