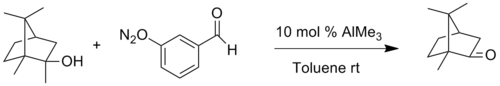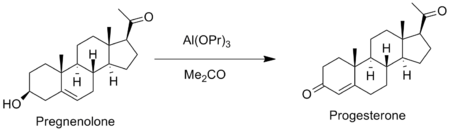- Oppenauer oxidation
-
Oppenauer oxidation, named after Rupert Viktor Oppenauer,[1] is a gentle method for selectively oxidizing secondary alcohols to ketones.
The reaction is the opposite of Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reduction. The alcohol is oxidized with aluminium isopropoxide in excess acetone. This shifts the equilibrium toward the product side.
The oxidation is highly selective for secondary alcohols and does not oxidize other sensitive functional groups such as amines and sulfides.[2] Though primary alcohols can be oxidized under Oppenauer conditions, primary alcohols are seldom oxidized by this method due to the competing aldol condensation of aldehyde products. The Oppenauer oxidation is still used for the oxidation of acid labile substrates. The method has been largely displaced by oxidation methods based on chromates (e.g. PCC) or dimethyl sulfoxide (e.g. Swern oxidation) or Dess-Martin oxidation due to its use of relatively mild and non-toxic reagents (e.g. the reaction is run in acetone/benzene mixtures). The Oppenanuer oxidation is commonly used in various industrial processes such as the synthesis of steroids, hormones, alkaloids, terpenes, etc.
Contents
Mechanism
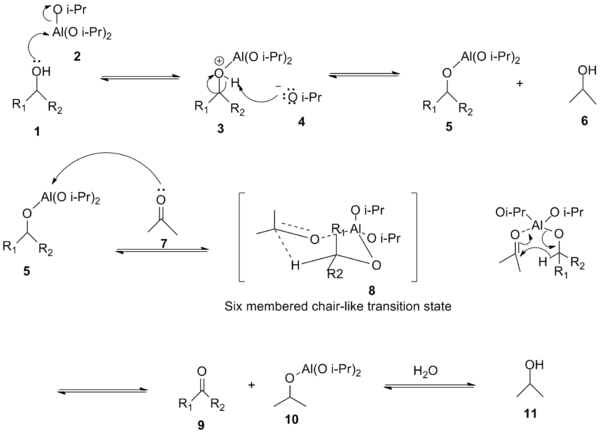
In the first step of the mechanism, the alcohol (1) coordinates to the aluminum to form a complex (3), which then, in the second step, gets deprotonated by an alkoxide ion (4) to generate an alkoxide intermediate (5). In the third step, both the oxidant acetone (7) and the substrate alcohol are bound to the aluminum. The acetone is coordinated to the aluminum which activates it for the hydride transfer from the alkoxide. The aluminium-catalyzed hydride shift from the α-carbon of the alcohol to the carbonyl carbon of acetone proceeds over a six-membered transition state (8). The desired ketone (9) is formed after the hydride transfer.[3]
Advantages of Use
An advantage of the Oppenauer oxidation is its use of relatively inexpensive and non-toxic reagents. Reaction conditions are mild and gentle since the substrates are generally heated in acetone/benzene mixtures. Another advantage of the Oppenauer oxidation which makes it unique to other oxidation methods such as Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) and Dess-Martin periodinane is that secondary alcohols are oxidized much faster than primary alcohols, thus chemoselectivity can be achieved. Furthermore, there is no over oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids as opposed to another oxidation methods such the Jones oxidation.[3]
Modifications
Wettstein-Oppenauer Reaction
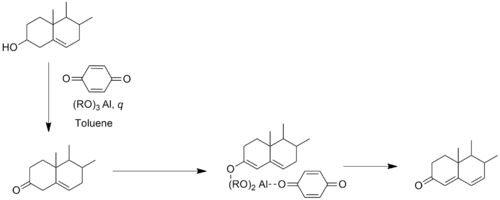
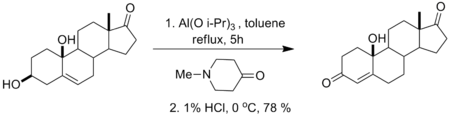
In the Wettstein-Oppenauer reaction, discovered by Wettstein in 1945, Δ 5-3b-hydroxy steroids are oxidized to Δ 4,6-3-ketosteroids with benzoquinone as the hydrogen acceptor. This reaction is useful in that it affords a one-step preparation of Δ 4,6-3-ketosteroids.[4]
Woodward Modification
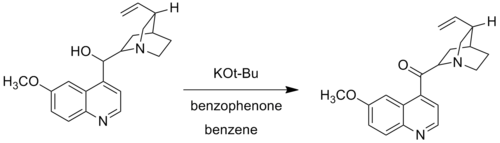
In the Woodward modification, Woodward substituted potassium tert-butoxide for the aluminum alkoxide. The Woodward modification of the Oppenauer oxidation is used when certain alcohol groups do not become oxidized under the standard Oppenauer reaction conditions. For example, Wooward used potassium tert-butoxide and benzophenone for the oxidation of quinine to quininone, as the traditional aluminum catalytic system failed to oxidize quinine due to the complex formed by coordination of the Lewis-basic nitrogen to the aluminum centre.[5]
Other Modifications
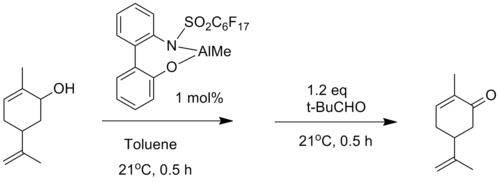
Several modified aluminum alkoxide catalysts have been also reported. For example, a highly active aluminum catalyst was reported by Maruoka and co-workers which was utilized in the oxidation of carveol to carvone (a member of a family of chemicals called terpenoids) in excellent yield (94%).[6]
In another modification [7] the catalyst is trimethylaluminium and the aldehyde 2-nitrobenzaldehyde is used as the oxidant, for example, in the oxidation of isoborneol to camphor.
Synthetic Applications
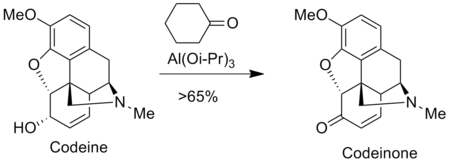
The Oppenauer oxidation is used to prepare analgesics in the pharmaceutical industry such as morphine and codeine. For instance, codeinone is prepared by the Oppenauer oxidation codeine.[8]
The Oppenauer oxidation is also used to synthesize hormones. Progesterone is prepared by the Oppenauer oxidation of pregnenolone.[9]
A slight variation of the Oppenauer oxidation is also used to synthesize steroid derivatives. For example, an efficient catalytic version of the Oppenauer oxidation which employs a ruthenium catalyst has been developed for the oxidation of 5-unsaturated 3â-hydroxy steroids to the corresponding 4-en-3-one derivative.[10]
The Oppenauer oxidation is also used in the synthesis of lactones from 1,4 and 1,5 diols.[11]
Side Reactions
A common side reaction of the Oppenauer oxidation is the base catalyzed aldol condensation of aldehyde products, which have α-hydrogens to form either ß-hydroxy aldehydes or α, ß-unsaturated aldehydes.[12]
Another side reaction is the Tischenko reaction of aldehyde products with no α-hydrogen, but this can be prevented by use of anhydrous solvents.[3] Another general side reaction is the migration of the double bond during the oxidation of allylic alcohol substrates.[13]
See also
- Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reduction
- Dess-Martin oxidation
- PCC
- Jones oxidation
- Aldol condensation
References
- ^ Oppenauer, R. V. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas 1937, 56, 137-144.
- ^ Otvos, L., Gruber, L., Meisel-Agoston,J. (1965). "The Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley-Oppenauer. Investigation of the reaction mechanism with radiocarbon. Racemization of secondary alcohols". Acta Chim. Acad. Sci. Hung. 43: pp 149–153.
- ^ a b c Corey, E.J; K.C. Nicolaou (2005). Strategic Applications of Named Reactions in Organic Synthesis. Elsevier, Inc. ISBN 978-7-03-019190-8.
- ^ Mandell, L. (1955). "The Mechanism of the Wettstein-Oppenauer Oxidation". J. Am. Chem. Soc 78: 3199–3201. doi:10.1021/ja01594a061.
- ^ Woodward, R.B,; Wendler, N.L.; Brutschy.F.J. (1945). J. Am. Chem. Soc 67: pp 1425.
- ^ OOi, T.; Miura, T.; Ichikawa, H.; Marvoka, K. (2002). Org. Lett. 4: pp 2669.
- ^ Efficient and Selective Al-Catalyzed Alcohol Oxidation via Oppenauer Chemistrysai krishna oxidation methods are sucessfuly conducted Christopher R. Graves, Bi-Shun Zeng, and SonBinh T. Nguyen J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 2006; 128(39) pp 12596 - 12597; (Communication) doi:10.1021/ja063842s
- ^ Stéphane Caron, Robert W. Dugger, Sally Gut Ruggeri, John A. Ragan, and David H. Brown Ripin (2006). "Large-Scale Oxidations in the Pharmaceutical Industry". Chem. Rev. 106: pp 2979. doi:10.1021/cr040679f. PMID 16836305.
- ^ Dewick, P (2001). Medicinal Natural Products: A Biosynthetic Approach. 2nd ed. Wiley & Sons.
- ^ Maria L.S. Almeida, Paval Kocovsky and Jan-E. Backvall. (1996). "Ruthenium-Catalyzed Oppenauer-Type Oxidation of 3â-Hydroxy Steroids. A Highly Efficient Entry into the Steroidal Hormones with 4-En-3-one Functionality". J. Org. Chem. 61: pp 6587–6590. doi:10.1021/jo960361q.
- ^ Eignerova, L.; Kasal, A. (1976). Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 41: pp 1056.
- ^ Milas, N.A; Grossi, F.X.; Penner, S.E.; Kahn, S (1948). J. Am. Chem. Soc 70: pp 1292.
- ^ Suzuki, T., Kinoshita, A., Kawada, H., Nakada, M (2003). "A new asymmetric tridentate carbazole ligand: Its preparation and application to Nozaki Hiyama allylation". Synlett: pp 570–572.
Categories:- Organic redox reactions
- Name reactions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.