- Benzophenone
-
Benzophenone 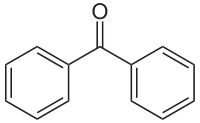

 diphenylmethanoneOther namesphenyl ketone; diphenyl ketone; benzoylbenzene
diphenylmethanoneOther namesphenyl ketone; diphenyl ketone; benzoylbenzeneIdentifiers CAS number 119-61-9 
PubChem 3102 ChemSpider 2991 
UNII 701M4TTV9O 
DrugBank DB01878 KEGG C06354 
ChEBI CHEBI:41308 
ChEMBL CHEMBL90039 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C(c1ccccc1)c2ccccc2
Properties Molecular formula C13H10O Molar mass 182.217 g/mol Appearance White solid Density 1.11 g/cm3, solid Melting point 47.9 °C
Boiling point 305.4 °C
Solubility in water Insoluble Solubility Benzene, THF, ethanol, propylene glycol Hazards MSDS External MSDS by JT Baker Main hazards Harmful (XN) NFPA 704  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Benzophenone is the organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CO, generally abbreviated Ph2CO. Benzophenone is a widely used building block in organic chemistry, being the parent diarylketone.
Contents
Uses
Benzophenone can be used as a photo initiator in UV-curing applications such as inks, imaging, and clear coatings in the printing industry. Benzophenone prevents ultraviolet (UV) light from damaging scents and colors in products such as perfumes and soaps. It can also be added to the plastic packaging as a UV blocker. Its use allows manufacturers to package the product in clear glass or plastic. Without it, opaque or dark packaging would be required.
In biological applications, benzophenones have been used extensively as photophysical probes to identify and map peptide–protein interactions[1] .
Synthesis
Benzophenone can be prepared by the reaction of benzene with carbon tetrachloride followed by hydrolysis of the resulting diphenyldichloromethane,[2] or by Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of a Lewis acid (e.g. aluminium chloride) catalyst. The industrial synthesis relies on the copper-catalyzed oxidation of diphenylmethane with air.[3]
Organic chemistry
Benzophenone is a common photosensitizer in photochemistry. It crosses from the S1 state into the triplet state with nearly 100% yield. The resulting diradical will abstract a hydrogen atom from a suitable hydrogen donor to form a ketyl radical.
Benzophenone radical anion
Sodium reduces benzophenone to the deeply colored radical anion, diphenylketyl:
- Na + Ph2CO → Na+Ph2CO·−
This ketyl is used in the purification of hydrocarbon solvents, because it reacts with water and oxygen to give non-volatile products.[4] The ketyl is soluble in the organic solvent being dried, so it reacts quickly with residual water and oxygen. In comparison, sodium is insoluble, and its heterogeneous reaction is much slower. The ketyl radical generally appears blue or purple, depending on the solvent.
Commercially significant derivatives
Substituted benzophenones such as oxybenzone and dioxybenzone are used in some sunscreens. The use of benzophenone-derivatives which structurally resemble a strong photosensitizer has been strongly criticized (see sunscreen controversy).[5]
p,p'-bis(N,N-dimethylamino)benzophenone or Michler's ketone has dimethylamino substituents at each para position.
The high-strength polymers PEEK, polyetherether ketones, are prepared from derivatives of benzophenone.
See also
References
- ^ Dorman, Gyorgy; Prestwich, Glenn D. (1 May 1994). "Benzophenone Photophores in Biochemistry". Biochemistry 33 (19): 5661–5673. doi:10.1021/bi00185a001.
- ^ Marvel, C. S.; Sperry, W. M. (1941), "Benzophenone", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv1p0095; Coll. Vol. 1: 95
- ^ Hardo Siegel, Manfred Eggersdorfer "Ketones" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry Wiley-VCH, 2002 by Wiley-VCH, Wienheim. DOI: 10.1002/14356007.a15_077
- ^ W. L. F. Armarego and C. Chai (2003). Purification of laboratory chemicals. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0750675713.
- ^ Knowland, John; McKenzie, Edward A.; McHugh, Peter J.; Cridland, Nigel A. (1993). "Sunlight-induced mutagenicity of a common sunscreen ingredient". FEBS Letters 324 (3): 309–313. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(93)80141-G. PMID 8405372.
Notes
- Merck Index, 11th edition, 1108.
Gallery
-
Toluene is refluxed with sodium and benzophenone to produce dry, oxygen-free toluene.
-
A solvent pot contains dibutyl ether dried over sodium and benzophenone, which gives it its purple color.
Categories:- Desiccants
- Printing materials
- Endocrine disruptors
- Aromatic ketones
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.







