- Diglyme
-
Diglyme 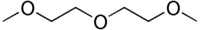 DiglymeSystematic name1-methoxy-2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethaneOther names2-Methoxyethyl ether; Di(2-methoxyethyl) ether; Diethylene glycol dimethyl ether
DiglymeSystematic name1-methoxy-2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethaneOther names2-Methoxyethyl ether; Di(2-methoxyethyl) ether; Diethylene glycol dimethyl etherIdentifiers CAS number 111-96-6 
PubChem 8150 ChemSpider 13839575 
UNII M4BH3X0MVZ 
EC number 203-924-4 DrugBank DB02935 ChEBI CHEBI:46784 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - COCCOCCOC
Properties Molecular formula C6H14O3 Molar mass 134.18 g/mol Density 0.937 g/mL Melting point -64 °C
Boiling point 162 °C
Solubility in water miscible Hazards EU classification Toxic (T)
Flammable (F)R-phrases R60, R61, R10, R19 S-phrases S53, S45 Flash point 57°C  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Diglyme, or bis(2-methoxyethyl) ether, is a solvent with a high boiling point. It is an organic compound which is the dimethyl ether of diethylene glycol. (The name "diglyme" is a portmanteau of "diglycol methyl ether.") It is a clear, colorless liquid with a slight ether-like odor. It is miscible with water, alcohols, diethyl ether, and hydrocarbon solvents.
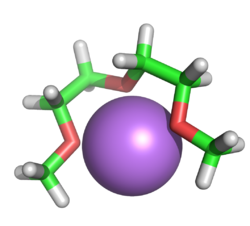 A lithium cation being chelated by a diglyme molecule
A lithium cation being chelated by a diglyme molecule
Diglyme is mainly used as a solvent in organic reactions. It has the ability to chelate small cations, leaving anions more active. Therefore, reactions involving organometallic reagents, such as Grignard reactions or metal hydride reductions, may have significantly enhanced reaction rates.
Diglyme is also used as a solvent in hydroboration reactions with diborane.
Its stability, even at high pH values, makes it an excellent solvent for reactions with strong bases or reactions that require high temperatures.
References
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 3148.
Categories:- Ethers
- Ether solvents
- Chelating agents
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
