- Chalkidiki
-
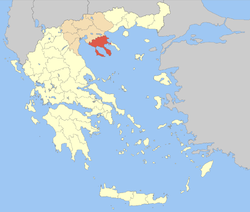
Chalkidiki
Περιφερειακή ενότητα
Χαλκιδικής— Regional unit — Municipalities of Chalkidiki Chalkidiki within Greece Coordinates: 40°20′N 23°30′E / 40.333°N 23.5°ECoordinates: 40°20′N 23°30′E / 40.333°N 23.5°E Country Greece Region Central Macedonia Capital Polygyros Government – Vice Governor Ioannis Giorgos Area – Total 2,918 km2 (1,126.6 sq mi) Population (2005) – Total 109,587 – Density 37.6/km2 (97.3/sq mi) Postal codes 63x xx Area codes 237x0, 239x0 ISO 3166 code GR-64 Car plates ΧΚ Website halkidiki.gov.gr Chalkidiki, also Halkidiki, Chalcidice or Chalkidike (Greek: Χαλκιδική, [xalciðiˈci]), is a peninsula in northern Greece, and one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Central Macedonia. The autonomous Mount Athos region is part of the peninsula, but not of the regional unit. The capital of Chalkidiki is the main town of Polygyros, located in the centre of the peninsula.
Contents
Geography
 Monastery in Mount Athos, an UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Monastery in Mount Athos, an UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The Cholomontas mountains lie in the northcentral part of Chalkidiki. Chalkidiki consists of a large peninsula in the northwestern Aegean Sea, resembling a hand with three "fingers" (though in Greek these peninsulas are often referred to as "legs") – Pallene (now Kassandra), Sithonia, and Agion Oros (the ancient Acte), which contains Mount Athos and its monasteries. Chalkidiki borders on the regional unit of Thessaloniki to the north.
Its largest towns are Nea Moudania (Νέα Μουδανιά), Nea Kallikrateia (Νέα Καλλικράτεια) and the main town of Polygyros (Πολύγυρος).
There are many summer resorts on the beaches of all three fingers where other minor towns and villages are located, such as at Yerakini (Gerakina Beach), Neos Marmaras (Porto Carras), Ouranoupolis, Nikiti, Psakoudia, Kallithea (Pallene/Pallini, Athos), Sani Resort and more.
History
The first Greek settlers in this area came from Chalcis and Eretria, cities in Euboea, around the 8th century BC who founded cities such as Mende, Toroni and Scioni;[citation needed] a second wave came from Andros in the 6th century BC.[citation needed] The ancient city of Stageira was the birthplace of the great philosopher Aristotle.
In June 2003, at the holiday resort Porto Carras located in Neos Marmaras, Sithonia, European Union leaders presented the first draft of the European constitution. See History of the European Constitution for developments after this point.
Ancient sites
- Acanthus
- Acrothoi
- Aege
- Alapta
- Aphytis
- Apollonia (Chalcidice)
- Charadrus
- Cleonae (Chalcidice)
- Galepsus
- Mekyberna
- Mende
- Neapolis, Chalcidice
- Olophyxus
- Olynthus
- Palaiochori "Neposi" castle
- Polichne
- Potidaea
- Scione
- Scolus
- Sermylia
- Stageira
- Spartolus
- Thyssus
- Torone
Administration
The regional unit Chalkidiki is subdivided into five municipalities. These are (number as in the map in the infobox):[1]
- Aristotelis (2)
- Kassandra (4)
- Nea Propontida (3)
- Polygyros (1)
- Sithonia (5)
Prefecture
As a part of the 2011 Kallikratis government reform, the regional unit Chalkidiki was created out of the former prefecture Chalkidiki (Greek: Νομός Χαλκιδικής). The prefecture had the same territory as the present regional unit. At the same time, the municipalities were reorganised, according to the table below.[1]
New municipality Old municipalities Seat Aristotelis Arnaia Ierissos Panagia Stagira-Akanthos Kassandra Kassandra Kassandreia Pallini Nea Propontida Kallikrateia Nea Moudania Moudania Triglia Polygyros Polygyros Polygyros Anthemountas Zervochoria Ormylia Sithonia Sithonia Nikiti Toroni Provinces
- Province of Chalkidiki - Polygyros
- Province of Arnaia
Note: Provinces no longer hold any legal status in Greece.
Television
- TV Halkidiki - Nea Moudania
- Super TV - Nea Moudania
Transport
- GR-18, NW, W, SW, Cen., NE
- Chalkidiki has no railroads or airports.
- A bus system, KTEL, serves major municipalities.
Notable inhabitants
- Paeonius of Mende (late 5th c. BC), sculptor
- Philippus of Mende, Plato's student, astronomer
- Nicomachus, Aristotle's father
- Aristobulus of Cassandreia (375 - 301 BC), historian, architect
- Aristotle (384 BC in Stageira-322 BC), philosopher
- Callisthenes (360-328 BC), historian
- Crates of Olynthus, Alexander's hydraulic engineer
- Andronicus the Olynthian (c.370 BC) Phrourarchus of Tyre, appointed by Antigonus
- Bubalus of Cassandreia 304 BC keles(horse) flat race Lykaia[2]
- Poseidippus of Cassandreia (3rd c.BC), comic poet
- Erginus (son of Simylus) from Cassandreia, citharede winner in Soteria c.260 BC[3]
- Athanasios Stageiritis, professor of Greek language at the Royal Academy in Vienna. Publisher of the fortnightly literary journal "Kalliope" in Vienna from 1819 to 1821
- Stamatios Chapsas, revolutionary of the Greek War of Independence (1821–1830)
- Kyrkos Papageorgakis, revolutionary of the Greek War of Independence (1821–1830)
- Archbishop Demetrios of America
- Georgios Papanikolaou (1875 in Polygyros - 1949), doctor, author, fighter of Greek Struggle for Macedonia and founder of the pan-chalcidikian association of Thessaloniki (1903)
- Sokratis Malamas (1957 in Sykia), singer
- Manolis Mitsias (1944 in Doumpia), singer
- Christos Zabounis, a pro-royalist author and editor
References
- ^ a b Kallikratis reform law textPDF
- ^ Arkadia — Lykaion — Epigraphical Database
- ^ Phokis — Delphi Epigraphical Database
See also
Area: 18,811 km² • Population : 1,874,214 (2001) • Capital: ThessalonikiRegional unit of Chalkidiki Regional unit of ImathiaAlexandreia • Naousa • VeroiaRegional unit of KilkisKilkis • PaioniaRegional unit of PellaRegional unit of PieriaDio-Olympos • Katerini • Pydna–KolindrosRegional unit of SerresRegional unit of ThessalonikiAmpelokipoi–Menemeni • Chalkidona • Delta • Kalamaria • Kordelio–Evosmos • Lagkadas • Neapoli–Sykies • Oraiokastro • Pavlos Melas • Pylaia–Chortiatis • Thermaikos • Thermi • Thessaloniki • VolviRegional governor: Panagiotis Psomiadis (el) • Website: www.pkm.gov.gr
Regional unit of ImathiaAlexandreia • Naousa • VeroiaRegional unit of KilkisKilkis • PaioniaRegional unit of PellaRegional unit of PieriaDio-Olympos • Katerini • Pydna–KolindrosRegional unit of SerresRegional unit of ThessalonikiAmpelokipoi–Menemeni • Chalkidona • Delta • Kalamaria • Kordelio–Evosmos • Lagkadas • Neapoli–Sykies • Oraiokastro • Pavlos Melas • Pylaia–Chortiatis • Thermaikos • Thermi • Thessaloniki • VolviRegional governor: Panagiotis Psomiadis (el) • Website: www.pkm.gov.grPrefectures of Greece Achaea and Elis (1833) · Achaea (1899) · Adrianople (1920)‡ · Aetolia-Acarnania (1833) · Arcadia (1833) · Argolis and Corinthia (1833) · Argolis (1899) · Argyrokastron (1915)§ · Arta (1882) · Attica and Boeotia (1833) · Attica (1899) · Boeotia (1899) · Chalkidiki (1915) · Chania (1912) · Chios (1915) · Corfu (1864) · Corinthia (1899) · Cyclades (1833) · Dodecanese (1947) · Drama (1915) · Elis (1899) · Euboea (1833) · Evros (1920) · Evrytania (1899) · Florina (1915) · Grevena (1964) · Heraklion (1912) · Imathia (1947) · Ioannina (1915) · Kallipolis (1920)‡ · Karditsa (1899) · Kastoria (1941) · Kavala (1915) · Kefallinia (1864) · Kilkis (1934) · Korytsa (1915)§ · Kozani (1915) · Lacedaemon (1899) · Laconia (1833) · Lakoniki (1899) · Larissa (1882) · Lasithi (1912) · Lefkada (1864) · Lesbos (1915) · Magnesia (1899) · Messenia (1833) · Pella (1930) · Phocis and Locris (1833) · Phocis (1899) · Phthiotis and Phocis (1845) · Phthiotis (1899) · Pieria (1947) · Piraeus (1964) · Preveza (1915) · Rethymno (1912) · Rhaedestos (1920)‡ · Rhodope (1920) · Samos (1915) · Saranta Ekklisies (1920)‡ · Serres (1915) · Sfakia (1912) · Thesprotia (1937) · Thessaloniki (1914) · Trikala (1882) · Trifylia (1899) · Xanthi (1944) · Zakynthos (1864)
From 1971, Attica Prefecture consisted of four prefecture-level units: Athens, East Attica, Piraeus, West Attica
From 1994, the prefectures of Athens and Piraeus; Drama, Kavala and Xanthi; Rhodope and Evros; were grouped intro super-prefecturesdates of first establishment in parentheses
today outside Greece: § in Northern Epirus ‡ in Eastern ThraceCategories:- Chalcidice
- Peninsulas of Greece
- Prefectures of Greece
- Tourism in Greece
- Regional units of Greece
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.