- New York State Route 63
-
NYS Route 63 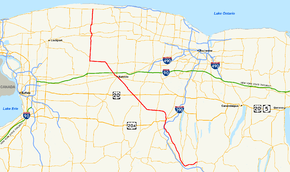
Map of western New York with NY 63 highlighted in redRoute information Maintained by NYSDOT and the village of Medina Length: 82.20 mi[2] (132.29 km) Existed: 1930[1] – present Major junctions South end: 
 NY 15 / NY 21 in Wayland
NY 15 / NY 21 in Wayland
 US 20A / NY 39 in Geneseo
US 20A / NY 39 in Geneseo
 US 20 in Pavilion
US 20 in Pavilion

 NY 5 / NY 33 in Batavia
NY 5 / NY 33 in Batavia
 NY 31 in Medina
NY 31 in MedinaNorth end:  NY 18 in Yates
NY 18 in YatesLocation Counties: Steuben, Livingston, Wyoming, Genesee, Orleans Highway system Numbered highways in New York
Interstate • U.S. • N.Y. (former) • Reference • County←  NY 62A
NY 62ANY 63A  →
→New York State Route 63 (NY 63) is a state highway in the western part of New York in the United States. The southern terminus of the route is at an intersection with NY 15 and NY 21 in the village of Wayland in Steuben County. Its northern end is at a junction with NY 18 in the town of Yates in Orleans County, 2 miles (3.2 km) south of the Lake Ontario shoreline. NY 63, which follows more of a southeast–northwesterly alignment for much of its routing, passes through the city of Batavia and enters or comes near several villages, including Dansville and Medina.
NY 63 was assigned as part of the 1930 renumbering of state highways in New York, but to a largely different routing than it follows today. The original alignment of NY 63 was identical to its current alignment between Mount Morris and Pavilion; however, the route deviated significantly from its modern routing past those points as it extended southwest from Mount Morris to Hinsdale and north from Pavilion to Hamlin. It was rerouted north of Pavilion ca. 1939 and south of Mount Morris in the early 1940s. The latter realignment supplanted New York State Route 36A, a Dansville – Mount Morris highway assigned in 1930. For a brief period during the 1970s, NY 63 began in Dansville instead of Wayland.
Contents
Route description
Wayland to Geneseo
NY 63 begins at a four-way intersection with NY 15 and NY 21 in the northern Steuben County village of Wayland. From here it heads west, paralleling Interstate 390 (I-390) on the side of the valley the interstate travels through. It enters Livingston County and the village of Dansville, where it briefly shares a street with NY 36, which at this point parallels I-390 on its other side for most of its route. NY 256 splits off for Conesus Lake in Dansville as well.[3]
Continuing north into Groveland, the short remnant of NY 258 comes in from the west at the town line. At the north end the highway runs much closer to I-390, and indirectly connects to the expressway by way of NY 408. From this point north, the road becomes busier as NY 63 is the primary route to Geneseo for northbound traffic on I-390 itself, as there is no exit at the point where the expressway crosses under NY 63.[4]
Geneseo to Batavia
After joining with U.S. Route 20A (US 20A) and NY 39, NY 63 enters Geneseo from the south, passing the campus of SUNY Geneseo. At the edge of the village, the highway crosses the Genesee River, then begins to curve up and out of the valley until it runs east–west again through the town of York.
The major junction in York is the hamlet of Greigsville, where NY 63 intersects NY 36. This next section of highway has become a major shortcut for traffic heading to the Buffalo area, despite remaining a two-lane road through open rural country, since it is both physically shorter than going all the way to the New York State Thruway as well as toll-free, and especially for traffic headed to the communities east or south of Buffalo this route is actually preferable. Most of this Buffalo-bound traffic has followed NY 36 up from Mt. Morris, and turns on to NY 63 here. Signage along this route reflects this use.[4]
From Greigsville, the route heads east through open land, into a brief corner of Wyoming County, where it turns to head due northwest, its direction for the next 30 miles (48 km). The next intersection with a state highway, the northern end of NY 246, comes just after the Genesee County line. A mile beyond, NY 63 drops down slightly to intersect with NY 19 at Pavilion. After the traffic light at the center of the hamlet, NY 63 crosses Oatka Creek and climbs back up out of the Wyoming Valley. Atop the hill, it narrows again and continues due northwest to its next junction, the underdeveloped crossing of US 20. Here at least some Buffalo-bound traffic will turn west. Eventually acquiring the name Ellicott Street, NY 63 finally enters Batavia, where it intersects the two major east–west trunk routes in this corridor, NY 5 and NY 33, as well as the north–south NY 98, which connects to the Thruway just north of the city.[4]
Batavia to Yates Center
Past Batavia, NY 63 itself crosses the Thruway, but without an exit. It continues northwestward as Lewiston Road to the village of Oakfield, where NY 262 departs to the east. Finally, just north of Oakfield, NY 63 turns due west on Judge Road and follows it several miles to NY 77, which it joins north of Basom.[5]
At Alabama, NY 77 turns to the west and NY 63 continues northwards, across the Iroquois National Wildlife Refuge and into Orleans County, to reach Medina. This village begins at a junction with NY 31 and NY 31A. Route 31A continues eastward while NY 31 joins NY 63 through the village.[6] The portion of the overlap between Starr and Center Streets is maintained by the village of Medina and is the only segment of NY 63 not maintained by the New York State Department of Transportation.[7] At Center Street, NY 31E comes in from the west and NY 31 leaves NY 63 to continue east. Route 63 crosses the Erie Canal, and leaves town.[6] Several miles further on, at Ridgeway, NY 63 crosses NY 104. This penultimate east–west trunk road through the region is followed by a descent into the last village along the route, Lyndonville. A short distance past it, Route 63 reaches its northern terminus at NY 18.[8]
History
NY 63 was assigned as part of the 1930 renumbering of state highways in New York. The initial routing of NY 63 was significantly different than its modern alignment; in fact, the only portion of modern NY 63 that still follows its original alignment is the section between Mount Morris (at Hampton Corners) and Pavilion. South of Mount Morris, the route followed what is now NY 408 to Dalton[1] and continued south on Old State Road and west on Allegany County Route 16 (CR 16) to NY 19 west of the village of Angelica. NY 63 overlapped NY 19 south to Belvidere,[9] where NY 63 turned west onto modern CR 20. It continued west on CR 20 and NY 446 through Cuba to a junction with NY 16 in Hinsdale, where it ended. North of Pavilion, NY 63 followed modern NY 19 to the Lake Ontario shoreline in Hamlin.[1]
The portion of what is now NY 63 north of Pavilion was designated as part of NY 19 in the 1930 renumbering. However, unlike current NY 63, NY 19 continued north for another 2 miles (3.2 km) on Lyndonville Road past NY 18 to the Lake Ontario shoreline.[1] The routings of NY 19 and NY 63 north of Pavilion were swapped ca. 1939, placing both routes on their modern alignments.[10][11] The portion of Lyndonville Road north of NY 18 remained part of NY 63 until April 1, 1989, when ownership and maintenance of the highway was transferred from the state of New York to Orleans County as part of a highway maintenance swap between the two levels of government.[12] It was subsequently redesignated as CR 63-1.[13][14]
South of Mount Morris, modern NY 63 was designated as NY 36A from Mount Morris to Dansville and became part of NY 39 (later NY 245) from Dansville to Wayland in the 1930 renumbering.[1][9] NY 63 was rerouted south of Mount Morris in the early 1940s to follow the former routing of NY 36A south to Dansville, from where it overlapped NY 245 east to Wayland.[15][16] Ca. 1972, NY 245 was truncated northeastward to Naples[17][18] and NY 63 was cut back to NY 36 in Dansville,[19][20] leaving the Dansville–Wayland highway as an unsigned reference route.[21] This was partially reversed in the late 1970s or early 1980s when NY 63 was reextended to Wayland.[22][23]
Prior to the 1930 renumbering, modern NY 63 was a mix of numbered and unnumbered highways, with three different routes (all assigned in the mid-1920s) occupying the numbered sections of the highway. From Wayland to Dansville, what is now NY 63 was originally designated as the westernmost part of NY 52. It was unnumbered from Dansville northwest to Hampton Corners, where NY 36 entered from the west on current NY 408 and followed the path of modern NY 63 to Geneseo. The road was unnumbered again until Pavilion, at which point NY 62 joined from the south and utilized all of current NY 63 and CR 63-1 to reach the Lake Ontario shoreline in Yates.[24][25]
Proposed Mount Morris – Pavilion bypass
As part of a large scale study in the early 2000s, the New York State Department of Transportation (NYSDOT) determined that NY 63 from Mount Morris to Pavilion, along with US 20 and NY 77—termed the "Route 63 Corridor"—were major trouble routes, primarily because of increased truck traffic using the corridor as a bypass between I-390 in Mount Morris and the New York State Thruway in Pembroke.[26]
The most publicized and perhaps most fought-over possibility mentioned was that of a new expressway[27] from Mount Morris to Pembroke, bypassing these three routes. The Wyoming County Chamber of Commerce was a driving force behind this, hoping interchanges in Perry, Warsaw and Attica would promote business growth.[28]
While residents along the Route 63 corridor are against the increased truck traffic along the corridor (spurred by the North American Free Trade Agreement), most of those same residents, along with other groups, also fought the proposed expressway. The general consensus of all of these groups is that NYSDOT should impose restrictions on the Route 63 corridor and force trucks to remain on I-390 and the Thruway to travel between Buffalo and Pennsylvania.[28]
Future
The New York State Department of Transportation has plans to slightly realign NY 63 via new construction to eliminate Peoria Curve, a sharp curve in the town of Covington, which has been prone to accidents and can create problems for truckers in winter. The short sharp curve will be lengthened and softened via construction of a new intersection on Peoria Road north of the current intersection. The new intersection will be constructed first, with the new road being constructed to its junction points on NY 63. The route will be closed for approximately four weeks while the realignment is connected at those points. What capacity the former NY 63 will take on (reference route, county route, etc.) has not been specified yet. Construction is expected to take place during 2008, with a scheduled completion date of December 2008.[29]
NY 63A
NY 63A was an alternate route of NY 63 between Angelica, Allegany County, and Nunda, Livingston County. The route was assigned as part of the 1930 renumbering[1] and redesignated as NY 408A in the early 1940s.[15][16]
Major intersections
County Location Mile[2] Destinations Notes Steuben Village of Wayland 0.00 
 NY 15 / NY 21
NY 15 / NY 21Livingston Dansville 6.29  NY 36 south
NY 36 southSouthern terminus of NY 36 / NY 63 overlap 6.42  NY 36 north
NY 36 northNorthern terminus of NY 36 / NY 63 overlap 6.51  NY 256
NY 256Southern terminus of NY 256 Groveland 14.43  NY 258
NY 258Eastern terminus of NY 258 Village of Mount Morris 21.05 
 NY 408 to I-390
NY 408 to I-390Northern terminus of NY 408; hamlet of Hampton Corners Town of Geneseo 24.05 
 US 20A west / NY 39 west
US 20A west / NY 39 westSouthern terminus of US 20A / NY 63 and NY 39 / NY 63 overlaps Village of Geneseo 24.36 
 US 20A east / NY 39 east
US 20A east / NY 39 eastNorthern terminus of US 20A / NY 63 and NY 39 / NY 63 overlaps York 30.26  NY 36
NY 36Hamlet of Greigsville Genesee Pavilion 36.92  NY 246
NY 246Northern terminus of NY 246 37.89  NY 19
NY 1940.90  US 20
US 20Hamlet of Texaco Town City of Batavia 49.83 
 NY 5 east / NY 33 east
NY 5 east / NY 33 eastEastern terminus of NY 5 / NY 63 and NY 33 / NY 63 overlaps 50.10 


 NY 33 west / NY 98 to I-90 / Thruway
NY 33 west / NY 98 to I-90 / ThruwayWestern terminus of NY 33 / NY 63 overlap 50.85  NY 5 west
NY 5 westWestern terminus of NY 5 / NY 63 overlap Village of Oakfield 56.23  NY 262
NY 262Western terminus of NY 262 Alabama 62.57  NY 77 south
NY 77 southSouthern terminus of NY 63 / NY 77 overlap 64.06  NY 77 north
NY 77 northNorthern terminus of NY 63 / NY 77 overlap Orleans Medina 71.80 
 NY 31 west / NY 31A
NY 31 west / NY 31ASouthern terminus of NY 31 / NY 63 overlap; western terminus of NY 31A 72.76 
 NY 31 east / NY 31E
NY 31 east / NY 31ENorthern terminus of NY 31/ NY 63 overlap; eastern terminus of NY 31E / NY 63 overlap; eastern terminus of NY 31E 73.00  NY 31E west
NY 31E westWestern terminus of NY 31E / NY 63 overlap Ridgeway 76.43  NY 104 west
NY 104 westWestern terminus of NY 63 / NY 104 overlap 76.59  NY 104 east
NY 104 eastEastern terminus of NY 63 / NY 104 overlap Yates 82.20  NY 18
NY 18Hamlet of Yates Center 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi References
- ^ a b c d e f Dickinson, Leon A. (January 12, 1930). "New Signs for State Highways". The New York Times: p. 136.
- ^ a b "2008 Traffic Data Report for New York State" (PDF). New York State Department of Transportation. June 16, 2009. pp. 204–205. https://www.nysdot.gov/divisions/engineering/technical-services/hds-respository/NYSDOT_Traffic_Data_Report_2008.pdf. Retrieved November 15, 2009.
- ^ Google, Inc. Google Maps – overview map of NY 63 from Wayland to Mt. Morris (Map). Cartography by Google, Inc. http://maps.google.com/maps?f=d&source=s_d&saddr=E+Naples+St%2FRT-63+%4042.567620,+-77.591560&daddr=NY-63%2FState+Route+63+N+to:42.737935,-77.831268&geocode=FcSHiQId-Atg-w%3BFVTAigIdophd-w%3B&hl=en&mra=dme&mrcr=0&mrsp=2&sz=11&via=1&sll=42.722804,-77.757797&sspn=0.228007,0.4422&ie=UTF8&ll=42.642546,-77.711792&spn=0.228302,0.4422&t=h&z=11. Retrieved March 6, 2008.
- ^ a b c Google, Inc. Google Maps – overview map of NY 63 from Mt. Morris to Batavia (Map). Cartography by Google, Inc. http://maps.google.com/maps?f=d&source=s_d&saddr=42.740709,-77.836075&daddr=Genesee+St%2FNY-63+to:W+Main+St%2FNY-33%2FNY-5%2FNY-63&geocode=%3BFT56jQIdiTNc-w%3BFfIgkAIdTuJW-w&hl=en&mra=dme&mrcr=0&mrsp=0&sz=13&via=1&sll=42.746382,-77.83247&sspn=0.05698,0.11055&ie=UTF8&ll=42.870932,-78.004303&spn=0.454924,0.884399&z=10. Retrieved March 6, 2008.
- ^ Google, Inc. Google Maps – overview map of NY 63 from Batavia to South Alabama (Map). Cartography by Google, Inc. http://maps.google.com/maps?hl=en&q=from:+RT-33/RT-5%20@42.998520,%20-78.188610+to:+RT-63%20@43.073779,%20-78.331509. Retrieved March 6, 2008.
- ^ a b Google, Inc. Google Maps – overview map of NY 63 from South Alabama to Alabama (Map). Cartography by Google, Inc. http://maps.google.com/maps?hl=en&q=from:+RT-63%20@43.073779,%20-78.331509+to:+Lewiston%20Rd%20@43.096400,%20-78.390970. Retrieved March 6, 2008.
- ^ New York State Department of Transportation (1996). Medina Digital Raster Quadrangle (Map). 1:24,000. http://www.nysgis.state.ny.us/gisdata/quads/drg24/dotpreview/index.cfm?code=o11. Retrieved November 15, 2009.
- ^ Google, Inc. Google Maps – overview of NY 63 from Alabama to Yates Center (Map). Cartography by Google, Inc. http://maps.google.com/maps?hl=en&q=from:+Lewiston%20Rd%20@43.096400,%20-78.390970+to:+N%20Lyndonville%20Rd%20@43.373430,%20-78.388730. Retrieved February 6, 2008.
- ^ a b Standard Oil Company of New York (1930). Road Map of New York (Map). Cartography by General Drafting.
- ^ Thibodeau, William A. (1938). The ALA Green Book (1938–39 ed.). Automobile Legal Association.
- ^ Standard Oil Company (1939). New York (Map). Cartography by General Drafting.
- ^ New York State Legislature. "New York State Highway Law § 341". http://public.leginfo.state.ny.us/menugetf.cgi?COMMONQUERY=LAWS. Retrieved November 15, 2009.
- ^ New York State Department of Transportation (1996). Lyndonville Digital Raster Quadrangle (Map). 1:24,000. http://www.nysgis.state.ny.us/gisdata/quads/drg24/dotpreview/index.cfm?code=n11. Retrieved November 15, 2009.
- ^ "Orleans County Inventory Listing" (CSV). New York State Department of Transportation. March 2, 2010. https://www.nysdot.gov/divisions/engineering/technical-services/hds-repository2/INV_2010-03-02_orleans.csv. Retrieved April 30, 2010.
- ^ a b Gulf Oil Company (1940). New York Info-Map (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally and Company.
- ^ a b Esso (1942). New York with Pictorial Guide (Map). Cartography by General Drafting.
- ^ Humble Oil & Refining Company (1971). New York (Map). Cartography by General Drafting.
- ^ Exxon (1972). Eastern United States (Map). Cartography by General Drafting (1972–73 ed.).
- ^ New York State Thruway Authority (1971). New York Thruway (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally and Company.
- ^ Gulf Oil Company (1972). New York and New Jersey Tourgide Map (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally and Company (1972 ed.).
- ^ New York State Department of Transportation (1977). Wayland Digital Raster Quadrangle (Map). 1:24,000. http://www.nysgis.state.ny.us/gisdata/quads/drg24/dotpreview/index.cfm?code=t18. Retrieved November 23, 2010.
- ^ Exxon (1979). New York (Map). Cartography by General Drafting.
- ^ State of New York (1981). I Love New York Tourism Map (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally and Company.
- ^ "New York's Main Highways Designated by Numbers". The New York Times: p. XX9. December 21, 1924.
- ^ State of New York Department of Public Works (1926). Official Map Showing State Highways and other important roads (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally and Company.
- ^ "Route 63 Corridor Study" (PDF). New York State Department of Transportation. https://www.nysdot.gov/regional-offices/region4/projects/route63-corridor-study/rte63-repository/corridorneeds.pdf. Retrieved December 14, 2007.
- ^ "Route 63 Corridor Study: FAQs". New York State Department of Transportation. https://www.nysdot.gov/regional-offices/region4/projects/route63-corridor-study/rte63-faqs. Retrieved December 14, 2007.
- ^ a b "Rural Preservation League – Public Meeting Minutes". Archived from the original on October 22, 2009. http://web.archive.org/web/20091022062047/http://geocities.com/ruralwyoming/publicmeetingminutes.htm. Retrieved December 14, 2007.
- ^ "Road Work - Region 4". New York State Department of Transportation. September 12, 2007. https://www.nysdot.gov/regional-offices/region4/road-work#w0b. Retrieved November 25, 2007.
External links
Categories:- State highways in New York
- Transportation in Livingston County, New York
- Transportation in Genesee County, New York
- Transportation in Orleans County, New York
- Transportation in Steuben County, New York
- Transportation in Wyoming County, New York
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.




