- Luminol
-
Luminol[1] 
 5-Amino-2,3-dihydro-
5-Amino-2,3-dihydro-
1,4-phthalazinedioneOther nameso-Aminophthaloyl hydrazide
o-Aminophthalyl hydrazide
3-Aminophthalhydrazide
3-Aminophthalic hydrazideIdentifiers CAS number 521-31-3 
PubChem 10638 ChemSpider 10192 
EC number 208-309-4 ChEMBL CHEMBL442329 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - c1cc2c(c(c1)N)c(=O)[nH][nH]c2=O
Properties Molecular formula C8H7N3O2 Molar mass 177.16 g/mol Melting point 319 °C, 592 K, 606 °F
Hazards MSDS MSDS for luminol NFPA 704  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Luminol (C8H7N3O2) is a versatile chemical that exhibits chemiluminescence, with a striking blue glow, when mixed with an appropriate oxidizing agent. It is a white to slightly yellow crystalline solid that is soluble in most polar organic solvents, but insoluble in water.
Luminol is used by forensic investigators to detect trace amounts of blood left at crime scenes as it reacts with iron found in hemoglobin. It is used by biologists in cellular assays for the detection of copper, iron, and cyanides, in addition to the detection of specific proteins by Western Blot.
For analysis of an area, luminol can be sprayed evenly across the area, and trace amounts of an activating oxidant will cause the luminol to emit a blue glow that can be seen in a darkened room. The glow lasts for about 30 seconds, but the effect can be documented by a long-exposure photograph. It is important that the spraying be evenly applied to avoid creating a slanted, or biased impression, such as blood traces appearing to be more concentrated in areas which received more spray. The intensity of the glow does not indicate the original amount present, but only the distribution of trace amounts of substances left in the area.
Contents
Synthesis
Luminol may be synthesized by a reverse phosphorescence 2-step process. It begins from 3-nitrophthalic acid.[2][3] First, hydrazine (N2H4) is heated with the 3-nitrophthalic acid in a high-boiling solvent such as triethylene glycol. A condensation reaction occurs, with loss of water, forming 3-nitrophthalhydrazide. Reduction of the nitro group to an amino group with sodium dithionite (Na2S2O4) produces luminol.
The product luminol is obtained the after addition of electrons from the dithionite, protonation, and a loss of water from the intermediate hydroxylamine. Luminol was first synthesized in Germany in 1902, but the compound was not named luminol until the late 1920s.
Chemiluminescence
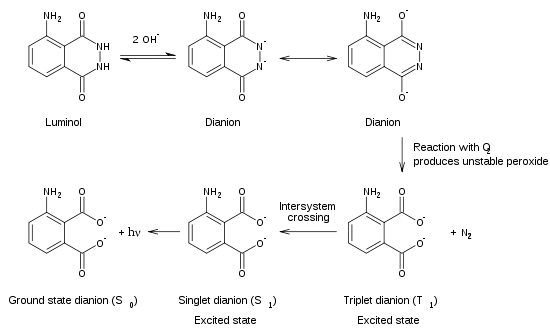
To exhibit its luminescence, the luminol must first be activated with an oxidant. Usually, a solution of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and a hydroxide salt in water is used as the activator. In the presence of a catalyst such as an iron compound, the hydrogen peroxide is decomposed to form oxygen and water:
- 2 H2O2 → O2 + 2 H2O
In a laboratory setting, the catalyst used is often potassium ferricyanide. In the forensic detection of blood, the catalyst is the iron present in hemoglobin. Enzymes in a variety of biological systems may also catalyze the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
When luminol reacts with the hydroxide salt, a dianion is formed. The oxygen produced from the hydrogen peroxide then reacts with the luminol dianion. The product of this reaction, an organic peroxide, is very unstable and is made by losing a nitrogen, electrons going from excited state to ground state, and energy emitting as a photon. This emitting of the photon is what ultimately gives off the blue light.
Use by crime scene investigators
Theory
Luminol is used by crime scene investigators to locate traces of blood, even if it has been cleaned or removed. The investigator prepares a solution of luminol and the activator and sprays it throughout the area under investigation. The iron present in any blood in the area catalyzes the chemical reaction that leads to the luminescence revealing the location of the blood. The amount of catalyst necessary for the reaction to occur is very small relative to the amount of luminol, allowing the detection of even trace amounts of blood. The glow lasts for about 30 seconds and is blue. Detecting the glow requires a fairly dark room. Any glow detected may be documented by a long exposure photograph.
Drawbacks
Luminol has some drawbacks that may limit its use in a crime scene investigation:
- Luminol chemiluminescence can also be triggered by a number of substances such as copper or copper-containing alloys, and certain bleaches; and, as a result, if a crime scene is thoroughly cleaned with a bleach solution or horseradish, residual cleaner will cause the entire crime scene to produce the typical blue glow, effectively camouflaging any organic evidence, such as blood.
- Luminol will also detect the small amounts of blood present in urine, and it can be distorted if animal blood is present in the room that is being tested.
- Luminol reacts with fecal matter, causing the same glow as if it were blood.
- Luminol's presence may prevent other tests from being performed on a piece of evidence. However, it has been shown that DNA can be successfully extracted from samples treated with luminol reagent.[4]
Related molecules
Luminol: 5-Amino-2,3-dihydro-1,4-phthalazinedione ; 3-Amino-phthalhydrazide ; 1,4-phthalazinedione, 5-amino-2,3-dihydro ; CAS: [521-31-3] C8H7N3O2 - MW: 177.16 λabs.(in 0.1 N NaOH) λmax 1 : 347 nm & λmax 2 : 300 nm; EC(at λmax 1): 7650 L/mol x cm λabs./λem.(MetOH): 355/413 nm
Luminol, hemihydrate 3-Amino-phthalhydrazide Na salt; CAS: [206658-90-4] C8H6N3O2Na.1/2H2O - MW: 217.16
Luminol, Na salt: 3-Amino-phthalhydrazide Na salt; CAS: [20666-12-0] C8H6N3O2Na - MW: 199.12
Luminol, HCl: 3-Amino-phthalhydrazide HydroChloride; CAS: [74165-64-3] C8H7N3O2.HCl - MW: 213.62
isoluminol: 4-Aminophthalhydrazide; CAS: [3682-14-1] C8H7N3O2 – MW: 117.16 (Xi)
isoluminol, monohydrate: 4-Aminophthalhydrazide monohydrate C8H7N3O2.H2O - MW: 195.15
isoluminol ABEI: 4-Aminophthalhydrazide monohydrate; CAS: [66612-29-1]
See also
- fluorescin converted to fluorescein
- Diphenyl oxalate
References
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 5470.
- ^ Ernest Huntress, Lester Stanley, Almon Parker (1934). "The Preparation of 3-Aminophthalhydrazide for Use in the Demonstration of Chemiluminescence". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 56 (1): 241–242. doi:10.1021/ja01316a077.
- ^ Synthesis of luminol
- ^ Technical note about Hemaglow
External links
Categories:- Aromatic amines
- Chemical tests
- Forensic chemicals
- Hydrazides
- Phthalazines
- Lactams
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.