- Radium chloride
-
Radium chloride 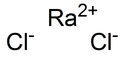
Identifiers CAS number 10025-66-8 
ChemSpider 20138060 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [Ra+2].[Cl-].[Cl-]
Properties Molecular formula RaCl2 Molar mass 296.094 g/mol Solubility in water 19.6 g/100 mL (20 °C)  chloride (verify) (what is:
chloride (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Radium chloride, RaCl2, was the first radium compound to be prepared in a pure state and was the basis of Marie Curie's original separation of radium from barium.[1] The first preparation of radium metal was by the electrolysis of a solution of radium chloride using a mercury cathode.
Contents
Preparation
Radium chloride crystallises from solution as the dihydrate. It may be dehydrated by heating to 100 °C in air for one hour followed by 5½ hours at 520 °C under argon.[2] If the presence of other anions is suspected, the dehydration may be effectuated by fusion under hydrogen chloride.[3]
Properties
Radium chloride is a white solid with a blue-green luminescence, especially when heated. It is less soluble in water than other alkaline earth metal chlorides, a fact which is used in the first stages of the separation of radium from barium by fractional crystallization. It is only sparingly soluble in azeotropic hydrochloric acid and virtually insoluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid.[4]
Gaseous radium chloride exists as RaCl2 molecules, as with other alkaline earth metal halides. The gas shows strong absorptions in the visible spectrum at 676.3 nm and 649.8 nm (red): the dissociation energy of the radium–chlorine bond is estimated as 2.9 eV,[5] and its length as 292 pm.[6]
Uses
Radium chloride is still used for the initial stages of the separation of radium from barium during the extraction of radium from pitchblende. The large quantities of material involved (tonnes of ore for milligrams of radium) favour this less costly (but less efficient) method over those based on radium bromide or radium chromate (used for the later stages of the separation).
It is also used in medicine to produce radon gas which in turn is used as a cancer treatment.[citation needed]
See also
- Alpharadin, a radiopharmaceutical based on radium chloride
Sources
- Gmelins Handbuch der anorganischen Chemie (8. Aufl.), Berlin:Verlag Chemie, 1928, pp. 60–61.
- Gmelin Handbuch der anorganischen Chemie (8. Aufl. 2. Erg.-Bd.), Berlin:Springer, 1977, pp. 362–64.
References
- ^ Curie, M.; Debierne, A. (1910). C. R. Hebd. Acad. Sci. Paris 151:523–25.
- ^ Weigel, F.; Trinkl, A. (1968). Radiochim. Acta 9:36–41.
- ^ Hönigschmid, O.; Sachtleben, R. (1934). Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 221:65–82.
- ^ Erbacher, O. (1930). Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 63:141–56.
- ^ Lagerqvist, A. (1953). Arkiv Fisik 6:141–42.
- ^ Karapet'yants, M. Kh.; Ch'ing, Ling-T'ing (1960). Zh. Strukt. Khim. 1:277–85; J. Struct. Chem. (USSR) 1:255–63.
Categories:- Radium compounds
- Chlorides
- Metal halides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
