- Insulator (genetics)
-
For electrical insulator, see Insulator (Electrical).For other uses, see Insulation (disambiguation).
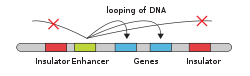
An insulator is a genetic boundary element that plays two distinct roles in gene expression, either as an enhancer-blocking element, or more rarely as a barrier against condensed chromatin proteins spreading onto active chromatin. The need for them arises where two adjacent genes on a chromosome have very different transcription patterns, and it is critical that the inducing or repressing mechanisms of one do not interfere with the neighbouring gene.[1]
References
- ^ Burgess-Beusse, B, et al. (December 2002). "The insulation of genes from external enhancers and silencing chromatin". Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 9 (Suppl 4): 16433–16437. doi:10.1073/pnas.162342499. PMC 139905. PMID 12154228. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139905.
Transcriptional regulation prokaryoticeukaryoticbothPromotion Promoter (Pribnow box, TATA box, BRE, CAAT box, Response element) · Enhancer (E-box, Response element) · Insulator · SilencerInitiation (prokaryotic,
eukaryotic)Transcription start siteElongation Termination
(prokaryotic,
eukaryotic)Categories:- Genetics stubs
- Gene expression
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.