- Ethylamine
-
Ethylamine[1] 
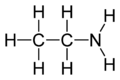
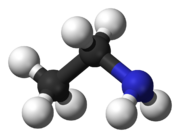 EthanamineOther namesMonoethylamine, Aminoethane, 1-Aminoethane, Ethamine
EthanamineOther namesMonoethylamine, Aminoethane, 1-Aminoethane, EthamineIdentifiers CAS number 75-04-7 
PubChem 6341 ChemSpider 6101 
UNII YG6MGA6AT5 
EC number 200-834-7 KEGG C00797 
ChEBI CHEBI:15862 
ChEMBL CHEMBL14449 
RTECS number KH2100000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - NCC
Properties Molecular formula C2H7N Molar mass 45.08 g/mol Appearance Light yellow liquid Density 0.689 g/cm3 Melting point -81 °C, 192 K, -114 °F
Boiling point 16.6 °C, 290 K, 62 °F
Solubility in water Miscible Vapor pressure 121 kPa (20 °C) Hazards R-phrases R12, R20, R22, R34, R36, R37, R38 S-phrases S16, S26, S29 Main hazards Harmful, corrosive, highly flammable NFPA 704 Flash point -17 °C Autoignition
temperature385 °C Explosive limits 3.5-14%V  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Ethylamine is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2NH2. This colourless gas has a strong ammonia-like odor. It is miscible with virtually all solvents and is considered to be a weak base, as is typical for amines. Ethylamine is widely used in chemical industry and organic synthesis.
Contents
Synthesis
Ethylamine is produced on a large scale by two processes. Most commonly ethanol and ammonia are combined in the presence of an oxide catalyst:
- CH3CH2OH + NH3 → CH3CH2NH2 + H2O
In this reaction, ethylamine is coproduced together with diethylamine and triethylamine. In aggregate, approximately 80M kilograms/year of these three amines are produced industrially.[2] It is also produced by reductive amination of acetaldehyde.
- CH3CHO + NH3 + H2 → CH3CH2NH2 + H2O
Ethylamine can be prepared by several other routes, but these are not economical. Ethylene and ammonia combine to give ethylamine in the presence of an sodium amide or related basic catalysts.[3]
- H2C=CH2 + NH3 → CH3CH2NH2
Hydrogenation of acetonitrile, acetamide, and nitroethane affords ethylamine. These reactions can be effected stoichiometrically using lithium aluminium hydride. In another route, ethylamine can be synthesized via nucleophilic substitution of a haloethane (such as chloroethane or bromoethane) with ammonia, utilizing a strong base such as potassium hydroxide. This method affords significant amounts of byproducts, including diethylamine and triethylamine.[4]
- CH3CH2Cl + NH3 + KOH → CH3CH2NH2 + KCl + H2O
Reactions and applications
Ethylamine undergoes the reactions anticipated for a primary alkyl amine, such as acylation and protonation. Reaction with sulfuryl chloride followed by oxidaton of the sulfonamide give diethyldiazene, EtN=NEt.[5] Ethylamine may be oxidized using a strong oxidizer such as potassium permanganate to form acetaldehyde.
Ethylamine like some other small primary amines is a good solvent for lithium metal, giving the ion [Li(amine)4]+ and the solvated electron. Evaporation of these solutions, gives back lithium metal. Such solutions are used for the reduction of unsaturated organic compounds, such as naphthalenes[6] and alkynes.
Ethylamine is a precursor to many herbicides including atrazine and simazine. It is found in rubber products as well.
References
- ^ Merck Index, 12th Edition, 3808.
- ^ Karsten Eller, Erhard Henkes, Roland Rossbacher, Hartmut Höke, “Amines, Aliphatic” Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005.doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_001
- ^ Ulrich Steinbrenner, Frank Funke, Ralf Böhling, Method and device for producing ethylamine and butylamine, United States Patent 7161039.
- ^ Nucleophilic substitution, Chloroethane & Ammonia, St Peter's School
- ^ Ohme, R.; Preuschhof, H.; Heyne, H.-U. Azoethane, Organic Syntheses, Collected Volume 6, p.78 (1988)
- ^ Kaiser, E. M.; Benkeser R. A. Δ9,10-Octalin, Organic Syntheses, Collected Volume 6, p.852 (1988)
External links
- Safety data at www.inchem.org
- Safety MSDS data
- Atrazine News - an Atrazine specific news site
Categories:- Ethylamines
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

