- Caesium-137
-
For the band, see Cesium 137 (band).
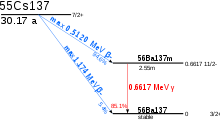
Caesium-137 General Name, symbol Caesium-137,137Cs Neutrons 82 Protons 55 Nuclide data Natural abundance 0 (artificial element) Half-life 30.17 y[1] ± 0.03 y Parent isotopes 137Xe (β−) Decay products 137mBa Isotope mass 136.907 u Spin 11⁄2− Decay mode Decay energy beta, gamma 1.176 [2] MeV Caesium-137 (137
55Cs, Cs-137) is a radioactive isotope of caesium which is formed as a fission product by nuclear fission.It has a half-life of about 30.17 years,[3] and decays by beta emission to a metastable nuclear isomer of barium-137: barium-137m (137mBa, Ba-137m). (About 95 percent of the nuclear decay leads to this isomer. The other 5.0 percent directly populates the ground state, which is stable.) Ba-137m has a half-life of about 153 seconds, and it is responsible for all of the emissions of gamma rays. One gram of caesium-137 has an activity of 3.215 terabecquerel (TBq).[4]
The photon energy of Ba-137m is 662 keV. These photons can be useful in food irradiation and in the radiotherapy of cancer. Caesium-137 is not widely-used for industrial radiography because it is quite chemically reactive, and hence, difficult to handle. Also the salts of caesium are very soluble in water, and this complicates the safe handling of caesium. Cobalt-60, 60
27Co, is preferred for radiography, since it is chemically a rather nonreactive metal offering higher energy gamma-ray photons. Caesium-137 can be found in some moisture and density gauges, flow meters, and related sensors.Contents
Uses
Caesium-137 has a small number of practical uses. In small amounts, it is used to calibrate radiation-detection equipment. It is used as a gamma emitter for oilfield wireline density measurements. It is also sometimes used in cancer treatment, and it is also used industrially in gauges for measuring liquid flows and the thickness of materials.[5]
Radioactive caesium in the environment
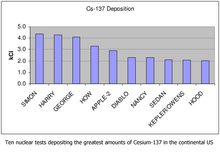 The ten highest deposits of caesium-137 from U.S. nuclear testing at the Nevada Test Site. Test explosions "Simon" and "Harry" were both from Operation Upshot-Knothole in 1953, while the test explosions "George" and "How" were from Operation Tumbler-Snapper in 1952
The ten highest deposits of caesium-137 from U.S. nuclear testing at the Nevada Test Site. Test explosions "Simon" and "Harry" were both from Operation Upshot-Knothole in 1953, while the test explosions "George" and "How" were from Operation Tumbler-Snapper in 1952
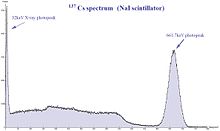 Cs-137 γ-spectrum: 661.7 keV γ- and 32 keV Ba K-lines.
Cs-137 γ-spectrum: 661.7 keV γ- and 32 keV Ba K-lines.
Small amounts of caesium-134 and caesium-137 were released into the environment during nearly all nuclear weapon tests and some nuclear accidents, most notably the Chernobyl disaster. As of 2005, caesium-137 is the principal source of radiation in the zone of alienation around the Chernobyl nuclear power plant. Together with caesium-134, iodine-131, and strontium-90, caesium-137 was among the isotopes, distributed by the reactor explosion, which constitute the greatest risk to health.
As of April 2011, it was also being found in the plumes emanating from the continuing leakage at the Fukushima reactors in Japan. In July 2011, meat from 11 cows shipped to Tokyo from Fukushima prefecture was found to have 3 to 6 times the legal limit of 500 becquerels per kilogram of radioactive caesium.[6]
The mean contamination of caesium-137 in Germany following the Chernobyl disaster was 2000 to 4000 Bq/m2. This corresponds to a contamination of 1 mg/km2 of caesium-137, totaling about 500 grams deposited over all of Germany.[citation needed]
All caesium-137 existing today is unique in that it is totally anthropogenic (man-made). Unlike most other radioisotopes, caesium-137 is not produced from its non-radioactive isotope but from uranium,[7] meaning that until now, it has not occurred on Earth for billions of years. By observing the characteristic gamma rays emitted by this isotope, it is possible to determine whether the contents of a given sealed container were made before or after the advent of atomic bomb explosions. This procedure has been used by researchers to check the authenticity of certain rare wines, most notably the purported "Jefferson bottles". [8]
Health risk of radioactive caesium
Actinides Half-life Fission products 244Cm 241Pu f 250Cf 243Cmf 10–30 y 137Cs 90Sr 85Kr 232U f 238Pu f is for
fissile69–90 y 151Sm nc➔ 4n 249Cf f 242Amf 141–351 No fission product
has half-life 102
to 2×105 years241Am 251Cf f 431–898 240Pu 229Th 246Cm 243Am 5–7 ky 4n 245Cmf 250Cm 239Pu f 8–24 ky 233U f 230Th 231Pa 32–160 4n+1 234U 4n+3 211–290 99Tc 126Sn 79Se 248Cm 242Pu 340–373 Long-lived fission products 237Np 4n+2 1–2 My 93Zr 135Cs nc➔ 236U 4n+1 247Cmf 6–23 My 107Pd 129I 244Pu 80 My >7% >5% >1% >.1% 232Th 238U 235U f 0.7–12 Ty fission product yield Caesium-137 reacts with water producing a water-soluble compound (caesium hydroxide), and the biological behavior of caesium is similar to that of potassium and rubidium. After entering the body, caesium gets more or less uniformly distributed throughout the body, with higher concentration in muscle tissues and lower in bones. The biological half-life of caesium is rather short at about 70 days.[9] Experiments with dogs showed that a single dose of 3800 μCi/kg (140 MBq/kg, or approximately 44 μg/kg) is lethal within three weeks.[10]
Accidental ingestion of caesium-137 can be treated with Prussian blue, which binds to it chemically and then speeds its expulsion from the body.[11]
Incidents
The improper handling of caesium-137 gamma ray sources can lead to release of this radio-isotope and radiation injuries. Perhaps the best-known case is the Goiânia accident of 1985, in which an improperly-disposed-of radiation therapy system from an abandoned clinic in the city of Goiânia, Brazil, was scavenged from a junkyard, and the glowing caesium salt sold to curious, uneducated buyers. This led to four deaths and serious injuries from radiation exposure.
Caesium gamma-ray sources that have been encased in metallic housings can be mixed-in with scrap metal on its way to smelters, resulting in production of steel contaminated with radioactivity.[12]
One notable example was the Acerinox accident of 1998, when the Spanish recycling company Acerinox accidentally melted down a mass of radioactive caesium-137 that came from a gamma-ray generator.[13]
In 2009, a Chinese cement company (in Tongchuan, Shaanxi Province) was demolishing an old, unused cement plant and did not follow standards for handling radioactive materials. This caused some caesium-137 from a measuring instrument to be included with eight truckloads of scrap metal on its way to a steel mill, where the radioactive caesium was melted down into the steel.[14]
See also
Medium-lived
fission productsProp:
Unit:t½
aYield
%Q *
keVβγ
*155Eu 4.76 .0803 252 βγ 85Kr 10.76 .2180 687 βγ 113mCd 14.1 .0008 316 β 90Sr 28.9 4.505 2826 β 137Cs 30.23 6.337 1176 βγ 121mSn 43.9 .00005 390 βγ 151Sm 90 .5314 77 β References
- ^ National Institute of Standards and Technology. "Radionuclide Half-Life Measurements". http://www.nist.gov/pml/data/halflife-html.cfm. Retrieved 2011-11-07.
- ^ The Lund/LBNL Nuclear Data Search. "Nuclide Table". http://nucleardata.nuclear.lu.se/NuclearData/toi/nuclide.asp?iZA=550137. Retrieved 2009-03-14.
- ^ National Institute of Standards and Technology. "Radionuclide Half-Life Measurements". http://www.nist.gov/pml/data/halflife-html.cfm. Retrieved 2011-11-07.
- ^ "NIST Nuclide Half-Life Measurements". NIST. Retrieved 13 March 2011. http://www.nist.gov/pml/data/halflife.cfm.
- ^ http://www.bt.cdc.gov/radiation/isotopes/cesium.asp
- ^ "High levels of caesium in Fukushima beef". Independent Online. 9 July 2011. http://www.iol.co.za/news/world/high-levels-of-caesium-in-fukushima-beef-1.1096205.
- ^ Takeshi Okumura (October 21, 2003). "The material flow of radioactive cesium-137 in the U.S. 2000". http://www.epa.gov/. US Environmental Protection Agency. http://www.epa.gov/rpdweb00/docs/source-management/csfinallongtakeshi.pdf.
- ^ http://www.winespectator.com/webfeature/show/id/42436
- ^ R. Nave. "Biological Half-life". Hyperphysics. http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/nuclear/biohalf.html.
- ^ H.C. Redman et al. (1972). "Toxicity of 137-CsCl in the Beagle. Early Biological Effects". Radiation Research 50 (3): 629–648. doi:10.2307/3573559. JSTOR 3573559. PMID 5030090.
- ^ http://www.bt.cdc.gov/radiation/prussianblue.asp
- ^ "Radioactive Scrap Metal". NuclearPolicy.com. Nuclear Free Local Authorities. October 2000. http://www.nuclearpolicy.info/publications/scrapmetal.php.
- ^ J.M. LaForge (1999). "Radioactive Caesium Spill Cooks Europe". Earth Island Journal (Earth Island Institute) 14 (1). http://www.earthislandprojects.org/EIJOURNAL/winter99/wr_winter99cesium.html.
- ^ "Chinese 'find' radioactive ball". BBC News. 27 March 2009. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/7967285.stm.
External links
Categories:- Isotopes of caesium
- Fission products
- Nuclear safety
- Radioisotope fuels
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.