- Criel Mound
-
South Charleston Mound
 The Criel Mound
The Criel MoundLocation: US 60, in city park, South Charleston, West Virginia Coordinates: 38°22′7″N 81°41′48″W / 38.36861°N 81.69667°WCoordinates: 38°22′7″N 81°41′48″W / 38.36861°N 81.69667°W Area: 1.5 acres (0.61 ha) Governing body: Local NRHP Reference#: 70000655[1] Added to NRHP: October 15, 1970 The Criel Mound is a Native American burial mound located in South Charleston, West Virginia, USA. The mound was built by the Adena culture, probably around 250-150 BC, and lay equidistant between two “sacred circles”, earthwork enclosures each 556 feet (169 m) in diameter. It was originally 33 feet (10 m) high and 173 feet (53 m) in diameter at the base, making it the second-largest such burial mound in the state of West Virginia. (The Grave Creek Mound in Moundsville is the largest.) The Criel Mound is located at 38°22′8.0″N 81°41′48.2″W / 38.36889°N 81.696722°W. This archaeological site is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
History
The mound was originally conical in shape. Residents of the area leveled the top in 1840 to erect a judges' stand, as they ran horse races around the base of the mound at the time.
The Criel Mound was excavated in 1883-84 under the auspices of the US Bureau of Ethnology and the supervision of Col. P.W. Norris. The actual excavation was performed by Professor Cyrus Thomas of the Smithsonian Institution. Inside the mound, Professor Thomas found thirteen skeletons: two near the top of the mound, and eleven at the base. The skeletons at the base consisted of a single very large skeleton at the center, surrounded by ten other skeletons arranged in a spoke-like pattern, with their feet pointing toward the central skeleton. The skeletons at the base had been wrapped in elm bark and were lying on a floor of white ash and bark. Several artifacts were found buried with the skeletons, including arrowheads, lanceheads, and shell and pottery fragments. The central skeleton was accompanied by a fish-dart, a lance-head, and a sheet of hammered native copper near the head. Holes found at the base of the mound suggest that the bodies at the base had been enclosed in a wooden vault. [2]
The Criel Mound is part of the second-largest known concentration of Adena mounds and circular enclosures. This area extends for eight miles (13 km) along the upper terraces of the Kanawha River floodplain, in the vicinity of present-day Charleston. In 1894, Cyrus Thomas reported 50 mounds in this area, ranging from 3’ to 35’ in height and from 35’ to 200’ in diameter. He also reported finding eight to ten circular earthworks, enclosing from 1 to 30 acres (120,000 m2). Stone mounds dotted the bluffs above the floodplain.
While many of the original Adena mounds were destroyed during later development of the area, a few remain. The Wilson Mound is in a private cemetery in South Charleston. The Shawnee Reservation Mound still exists in Institute, West Virginia.
Today, the Criel Mound is the centerpiece of Staunton Park, a small municipal park maintained by the city of South Charleston. It is a gathering place for community activities, such as arts and crafts fairs, revivals, memorial services, sunrise services, and town carnivals.
See also
- Adena culture
- Mound builders
- Prehistory of West Virginia
- South Charleston, West Virginia
Notes
- ^ "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. 2009-03-13. http://nrhp.focus.nps.gov/natreg/docs/All_Data.html.
- ^ South Charleston History Book Publications Committee. The History of South Charleston. 392 pages. Privately printed: 1995.
Further reading
- Dragoo, Don W. Mounds for the Dead. 315 pages. The Carnegie Museum of Natural History: 1963. ISBN 0-911239-09-X.
- Silverberg, Robert. The Mound Builders. 276 pages. Ohio University Press: 1970. ISBN 0-8214-0839-9.
- Webb, Willam S., and Snow, Charles E. The Adena People. 369 pages. The University of Tennessee Press: 1974. ISBN 0-87049-568-2.
- Woodward, Susan L., and McDonald, Jerry N. Indian Mounds of the Middle Ohio Valley. 130 pages. McDonald and Woodward Publishing Co.: 1986. ISBN 0-939923-00-9.
External links
- Criel Mound
- The Kanawha Valley and its Prehistoric People
- Mounds & Mound Builders
- The South Charleston Museum
List of Adena culture sites · Woodland period · Mound builder (people) · List of archaeological periods (North America)Ohio Sites Adena Mound · Austin Brown Mound · Arledge Mounds I and II · Beam Farm · Clemmons Mound · Conrad Mound Archeological Site · Coon Hunters Mound · George Deffenbaugh Mound · Enon Mound · Fortner Mounds · Great Mound · Highbanks Metropolitan Park Mounds I and II · Hillside Haven Mound · Hodgen's Cemetery Mound · Horn Mound · Hurley Mound · Jackson Mound · Karshner Mound · Kinzer Mound · Luthor List Mound · Miamisburg Mound · Odd Fellows' Cemetery Mound · Old Maid's Orchard Mound · Orators Mound · Carl Potter Mound · Reeves Mound · D.S. Rose Mound · Ross Trails Adena Circle · Short Woods Park Mound · Snead Mound · Spruce Run Earthworks · David Stitt Mound · Story Mound (Cincinnati) · Story Mound (Chillicothe) · Wolf Plains Group · Zaleski Mound Group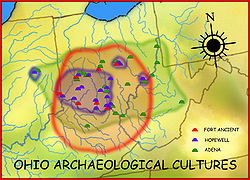
Kentucky Sites West Virginia Sites Indiana Sites Related topics · Ancient Monuments of the Mississippi Valley · burial mound · Eastern Agricultural Complex · Hopewell traditionU.S. National Register of Historic Places in West Virginia Lists by county Barbour • Berkeley • Boone • Braxton • Brooke • Cabell • Calhoun • Clay • Doddridge • Fayette • Gilmer • Grant • Greenbrier • Hampshire • Hancock • Hardy • Harrison • Jackson • Jefferson • Kanawha • Lewis • Lincoln • Logan • Marion • Marshall • Mason • McDowell • Mercer • Mineral • Mingo • Monongalia • Monroe • Morgan • Nicholas • Ohio • Pendleton • Pleasants • Pocahontas • Preston • Putnam • Raleigh • Randolph • Ritchie • Roane • Summers • Taylor • Tucker • Tyler • Upshur • Wayne • Webster • Wetzel • Wirt • Wood • Wyoming
Other lists Categories:- Adena culture
- Archaeological sites on the National Register of Historic Places in West Virginia
- Mounds of West Virginia
- Protected areas of Kanawha County, West Virginia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.